
A dog bite might result in tetanus or rabies. Infection signs include leaking, redness, swelling, and increasing pain. Dog bite injuries can range in severity from minor to life-threatening, and they must be treated right away to avoid infection or trauma-related consequences.
1. Category – I :

I. Type of Wound :
- Touching or feeding animals
- Licking on intact skin
II. Management :
- Washing of exposed skin surfaces, no PEP(Post exposure prophylaxis)
2. Category – II :
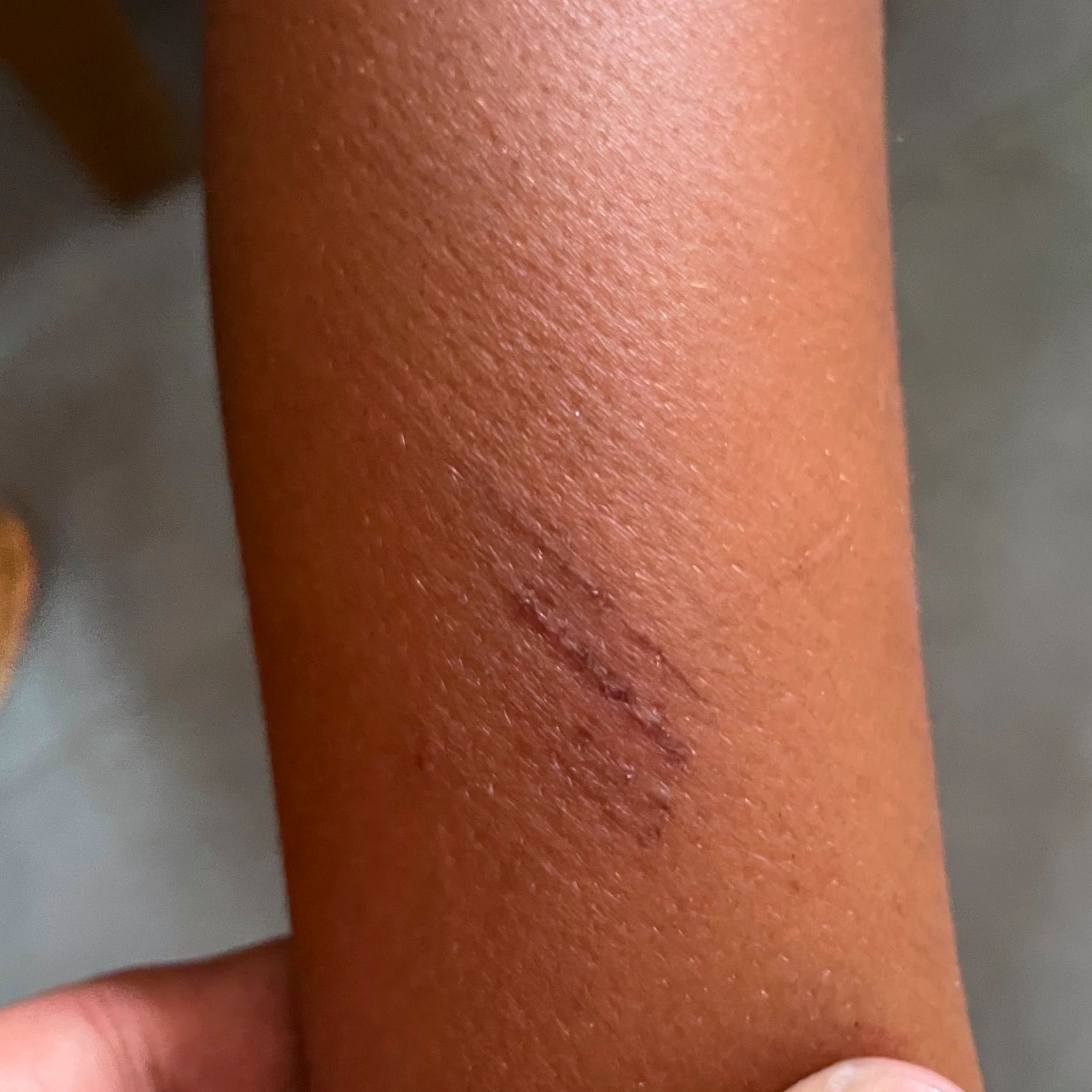
I. Type of Wound :
- Nibbling of uncovered skin
- Minor scratches or abrasions without bleeding
II. Management :
- Local treatment of the wound
- Immediate vaccination
3. Category – III :
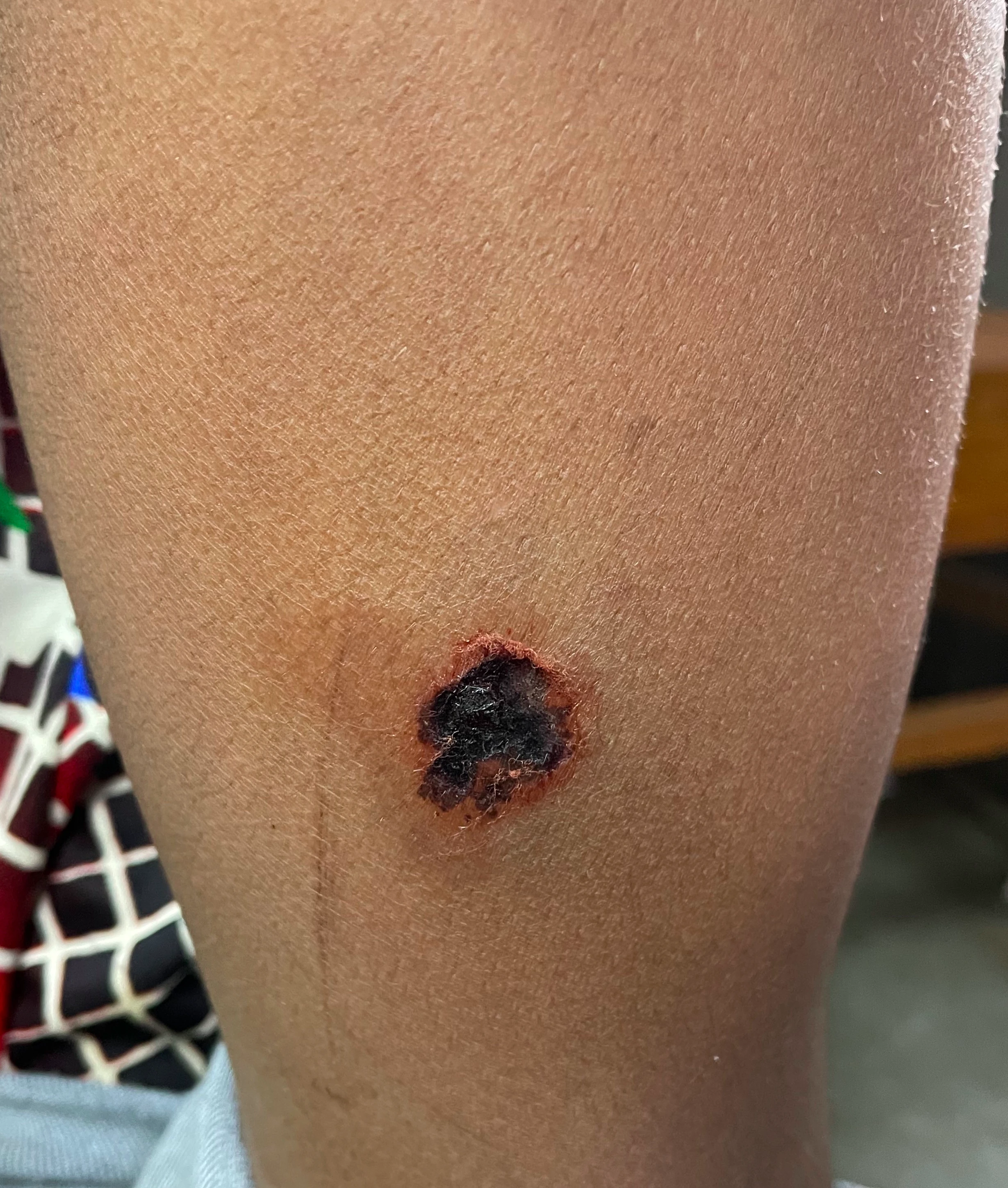
I. Type of Wound :
- Single or multiple transdermal bites or scratches
- Licks on broken skin
- Contamination of mucous membrane with saliva from lick
- Contact with bats
II. Management :
- Immediate vaccination and administration rabies immunoglobulin
- Local treatment of the wound