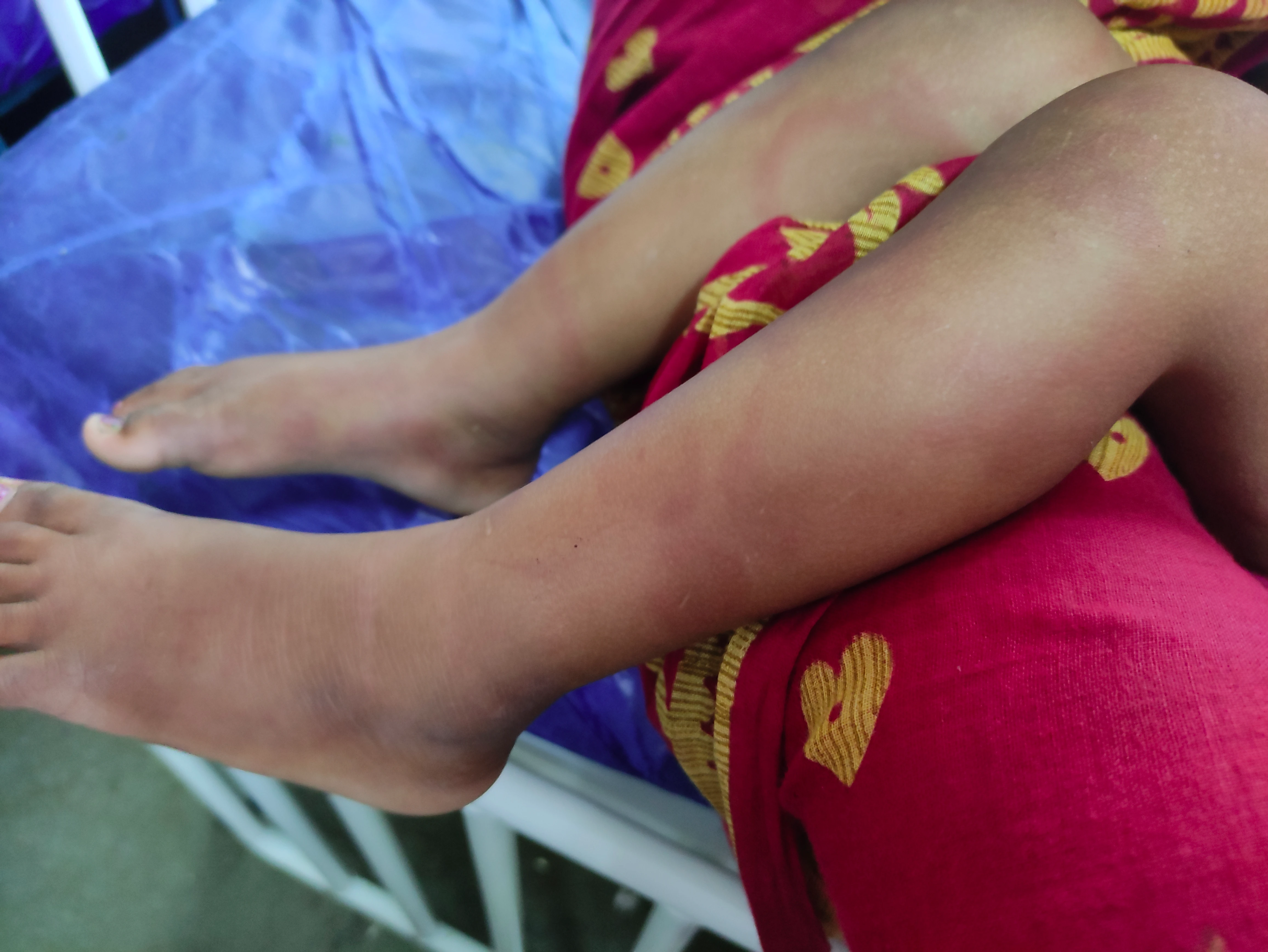
This are type of Skin rashes which is mainly formed due to IgE mediated allergic reaction. This is formed when allergens activates the mast cells in the skin. When this episodes lasts for less than 6 weeks then it is called Acute urticaria and when lasts more than 6 weeks called Chronic urticaria.
Urticaria sometimes also can develop by non IgE mediated reactions, like incase of Viral agents like hepatitis B , Epstein-Barr virus, NSAIDS drugs, Opiates drugs.
1. Clinical features :
- Skin rashes which are red and itchy.
- Fever
- Irritability
2. Causes/Etiology :
The causes of Urticaria can be divided into two types – Acute Urticaria and Chronic Urticaria
A. Acute Urticaria :
- Contact allergy : Latex, pollen grains, caterpillars.
- Food allergy like egg, milk, sea foods etc
- Insect stings
- Infections like bacterial, parasites, fungal
- Blood transfusion
- Medications
B. Chronic Urticaria :
In 70-90% cases this is Idiopathic.
- Physical urticaria by effects of cold, solar, vibratory, cholinergic etc.
- Rheumatological urticaria by SLE, Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
- Endocrine effects like Hyperthroidism, Hypothyroidism.
- Neoplastic causes like Lymphoma, Leukemias, Mastocytosis.
- Angioedema
3. Pathophysiology :
- IgE Mediated – When an allergen comes in contact with the body, the IgE mediated reactions occurs. The allergen activates the mast cells of the skin and inflammation starts to occur in the skin.
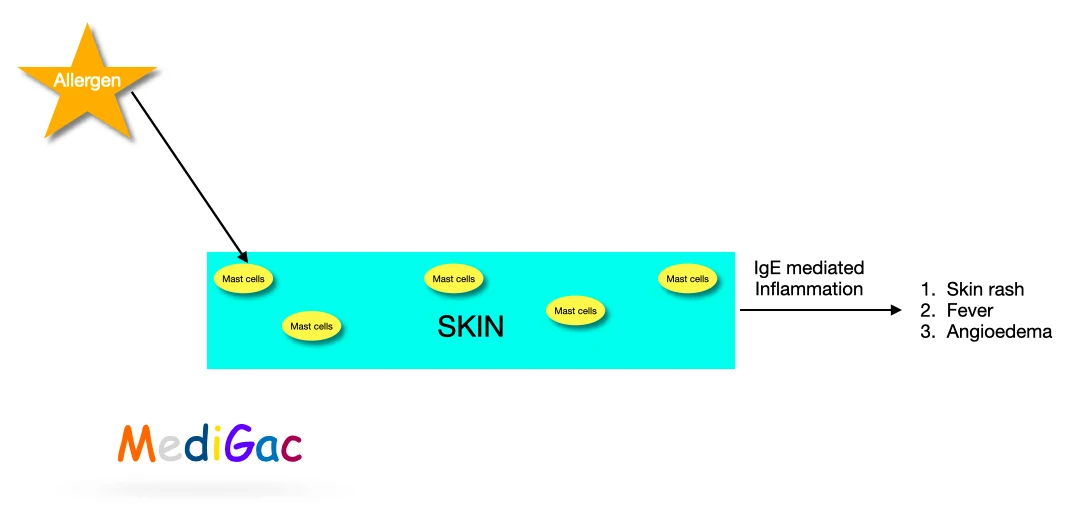
2. Non IgE Mediated – Sometimes the inflammation occurs are not IgE mediated, which can be caused by Epstein barr virus, hepatitis B, and drugs like opiates, and NSAIDS.
4. Management :
A. Investigations :
- Complete blood count – This can show increase in WBC count.
- Skin tests
- Cultures of serology
- Skin biopsy
- Ice cube test in case of cold urticaria
- Immunofluorescence tests
B. Treatment :
- Antihistamines – 2nd generation : Drugs like Fexofenadine, Cetirizine, Loratadine, and Desloratadine.
- Antihistamines types H2 : Cimetidine, Ranitidine and Famotidine.
- Leukotriene pathway modifiers : Montelukast and Zafirlukast.
- Immunomodulatory drugs : Cyclosporine, Sulfasalazine and IV Immunoglobulin(IVIG)