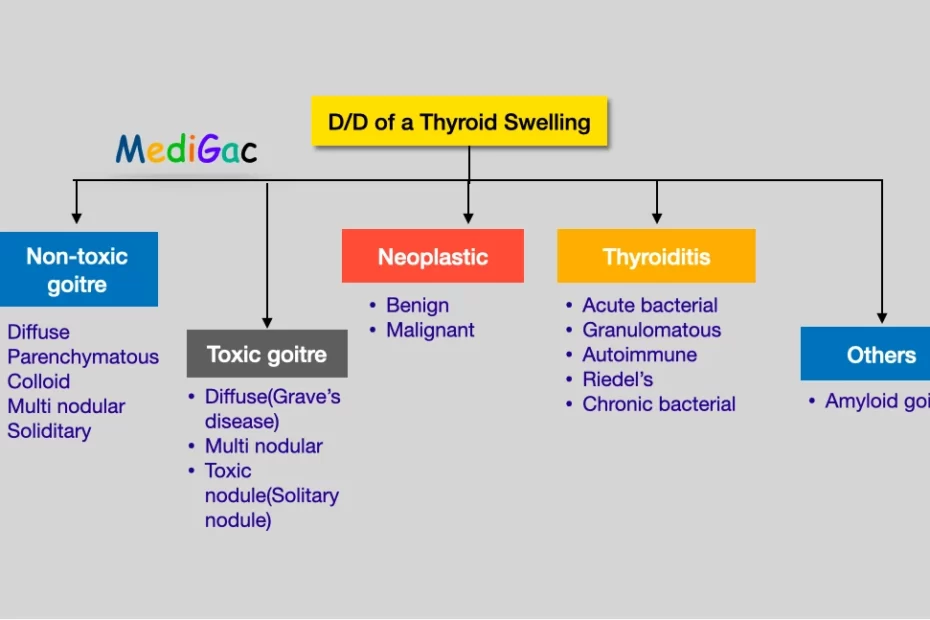
All the possible differential diagnosis of a thyroid swelling patient. Important diseases related with a thyroid swelling. The causes can be toxic, non-toxic, neoplastic like benign and malignant, and Inflammatory causes.

There are mainly four causes of classification of a thyroid swelling. and they are –
- Simple goitre – This occurs in euthyroid condition that is due to the normal range of T3 and T4 level. This can be of two types and they are Diffuse hyperplastic and Multinodular goitre.
- Toxic goitre – This is mainly of three types and they are Diffuse(Grave’s disease), Multinodular and toxic adenoma.
- Neoplastic swelling – This is of two types benign and malignant, this are further classified as various neoplastic disorders.
- Inflammatory swelling – Occurs due to inflammation, and this are Autoimmune, Granulomatous, Fibrosing, Infective, and others like Amyloid.
I. What is the classification of simple goitre :
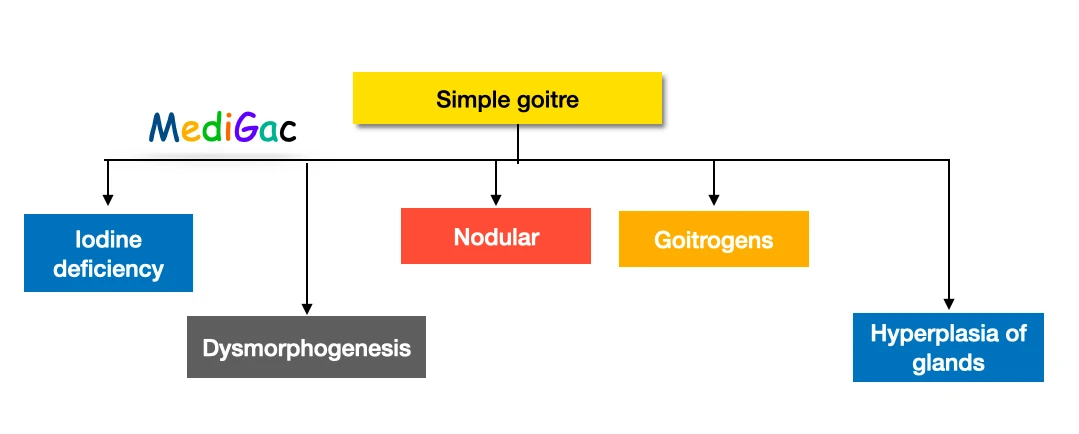
There are mainly two types of simple goitre and they are – Diffuse hyper plastic and Multinodular goitre.
Several causes can cause simple goitre, the causes are – Iodine deficiency, Dysmorphogenesis, Nodular goitre, Goitrogens and due to hyper plastic thyroid gland.
1. When it occurs due to Iodine deficiency :
This mainly occurs due to iodine deficiency in the body due to low iodine intake. This scenario mainly seen in endemic areas where the iodine intake or supply via food is less. Daily requirement of iodine is about 0.1 – 0.15 mg.
2. When it occurs due to dysmorphogenesis :
This is the deficiency of an enzyme. Dysmorphogenesis is the formation of abnormal tissue. enzyme deficiencies of varying severity may be responsible for many sporadic goitrs that is in non-endemic areas.
3. When it occurs as a nodular goitre :
- This can be due to cystic degeneration, haemorrhage, subsequent calcification.
- Multiple nodules commonly create a multinodular goitre.
- Because of the presence of oestrogen receptors in thyroid tissue, all kinds of simple goitre are more common in women than in men.
4. When it occurs due to goitrogens :
This refers to brassica plants such as cabbage, kale, and rape, which are high in thiocyanate, as well as medications like para-aminosalicylic acid and anti-thyroid drugs.
5. When it occurs due to hyperplastic thyroid gland :
- Because of a hyperplastic thyroid gland that produces too much thyroid hormone.
- The goitre is soft and diffuse, and it can become large enough to be uncomfortable.
- The goitre may resolve if TSH stimulation is stopped, but it is more likely to reoccur later during periods of stress, such as pregnancy.
II. What is the classification of toxic goitre/Hyperthyroidism :
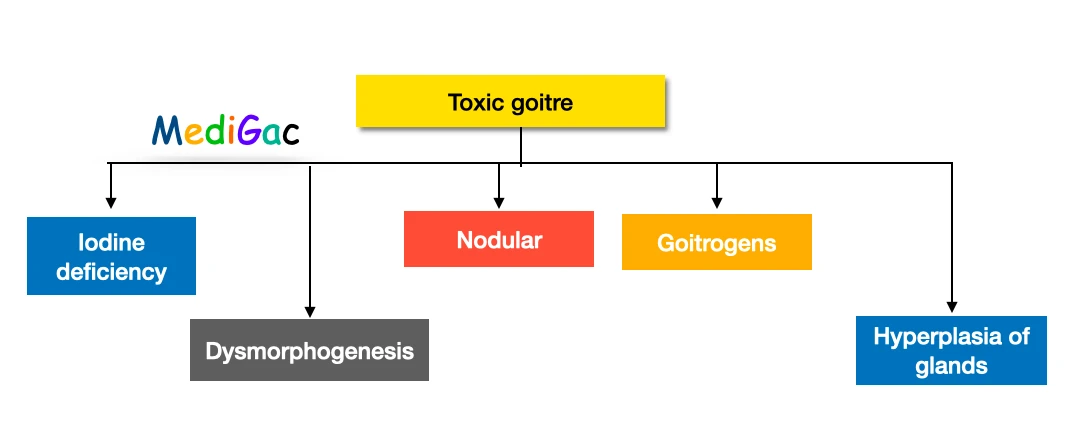
Toxic goitre can be three types – Diffuse(Grave’s disease), Multinodular and Toxic adenoma.
1. When it is diffuse toxic goitre/Grave’s disease :
- This is a vascular goitre that appears at the same time as hyperthyroidism.
- The hypertrophy and hyperplasia are caused by aberrant TSH-RAb that bind to TSH receptor sites and generate a disproportionate and protracted impact.
- Primary thyrotoxicosis is a syndrome in which 50% of patients have a family history of autoimmune endocrine disorders.
2. When it is toxic multinodular goitre :
- A multinodular goitre is characterised by the presence of several lumps (nodules) within the gland.
- This is most likely the most frequent thyroid problem.
- Nodules can be easily seen or only discovered after a thorough examination or scan.
- The condition is referred to as secondary thyrotoxicosis.
- Some toxic nodular goitres, however, have one or more hyperactive nodules, and the hyperthyroidism is caused by autonomous thyroid tissue, similar to a toxic adenoma.
3. When it occurs due to toxic single nodule :
- A toxic nodule is a single hyperactive lesion that can be part of a larger nodule or a true toxic adenoma.
- It is self-contained, and the hypertrophy and hyperplasia it exhibits are not caused by TSH-RAb.
- The high level of circulating thyroid hormones suppresses TSH secretion, and the normal thyroid tissue surrounding the nodule is also repressed and inactive.
III. What is the classification of neoplastic swelling :

Neoplastic goitre can be two types Benign and Malignant.
Neoplasia is discussed in details in a different page, please follow the link given below.
IV. What is the classification of Inflammatory swelling :
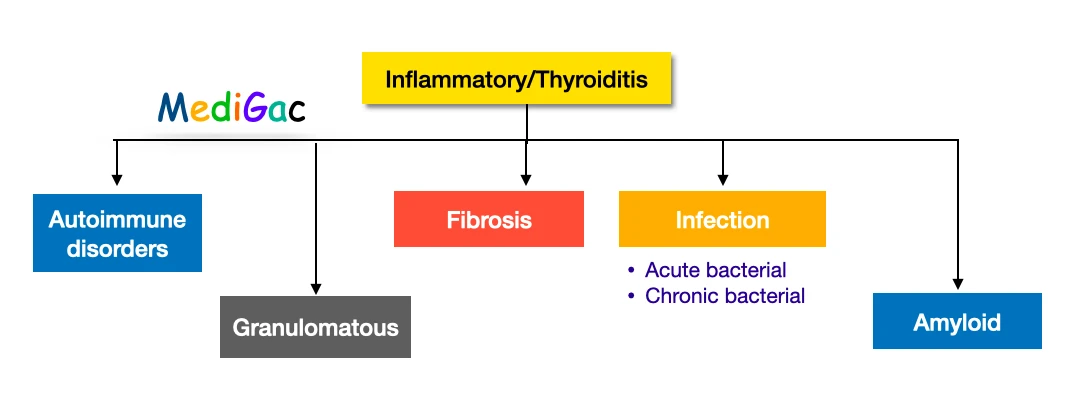
There are five types of inflammatory goitre and they are – Autoimmune, Granulomatous, Fibrosing, Infective and Amyloid.
1. When it occurs due to autoimmune disorders :
Raised thyroid antibody titres are frequently related with this prevalent disease. This often manifests as a widespread or nodular goitre with a characteristic ‘bosselated’ feel myxoedema without apparent thyroid enlargement, which is the end stage of the pathological process.
2. When it occurs due to granulomatous tissues :
Virus infection is the most common cause of infection. Thyroid antibodies are missing, inflammatory indicators are elevated, serum T4 is normal or slightly elevated, and the gland’s 123I uptake is poor. This thyroiditis is also known as Subacute thyroiditis, and de Quevain’s thyroiditis.
- Diagnosis – FNAC, radioactive iodine uptake, and a quick clinical response to prednisone can all confirm this.
- Treatment – Prednisone 10-20 mg daily for 7 days is the specific treatment for acute cases of severe pain, with the amount gradually decreasing over the next month.
3. When it occurs due to fibrosis of tissues :
Thyroid tissue is replaced by cellular fibrous tissue, which infiltrates the muscles and surrounding tissues, such as the parathyroid glands, recurrent nerves, and carotid sheath, through the capsule.
- Treatment includes high dose of steroid, tamoxifen and replacement of thyroxine.
- Most common fibrous tissue disease of thyroid gland is Riedel’s thyroid.
4. When it occurs due to any infection :
Thyroiditis is the swelling or inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can result in excessive or insufficient thyroid hormone production. Infective thyroiditis can be caused many virus and bacteria.
5. When it occurs due to amyloid :
Amyloid refers to fibrous, extracellular, proteinaceous deposits observed in organs and tissues that are abnormally fibrous, extracellular, and proteinaceous. Amyloid is insoluble and has a -sheet structure that dominates its structure.
This may occur due to any genetic abnormality or malfunction.