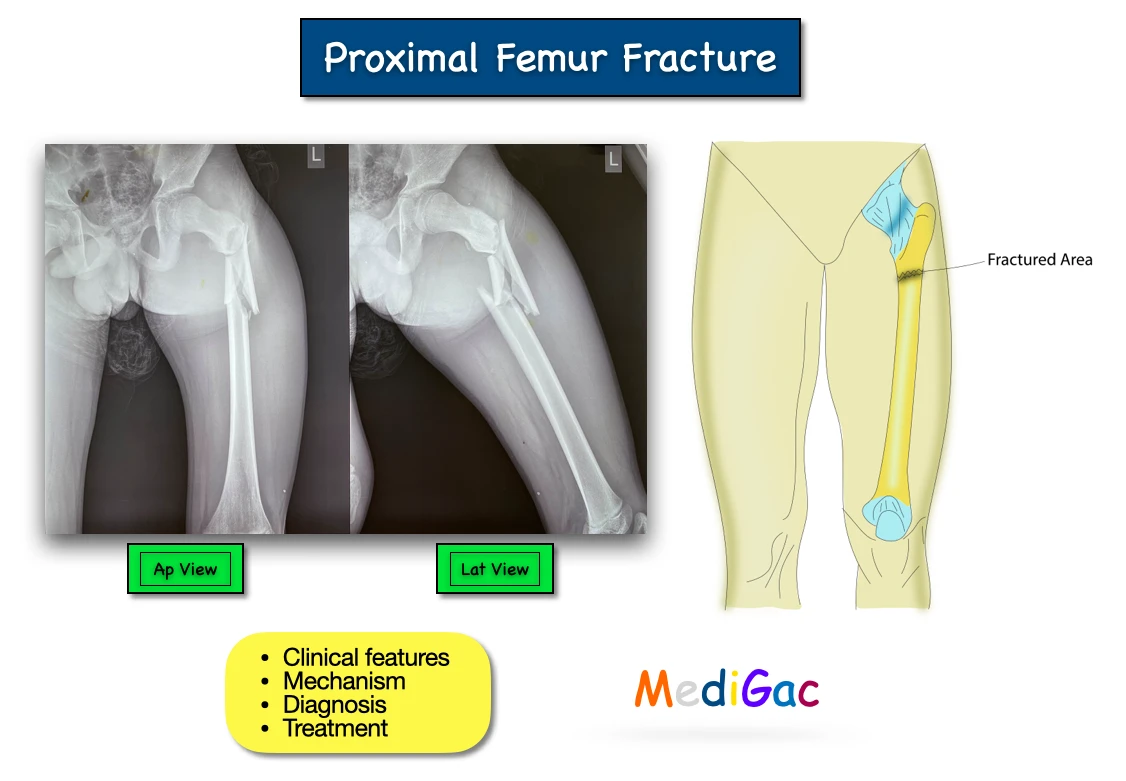
A fracture in the upper quarter of the femur, near the hip joint. This types of fracture can occur due to older age which leads to osteoporosis, in younger age also can be seen due to injury.
1. Clinical features :
The patient presents with :
- Swelling
- Pain
- External rotation deformity
2. Mechanism & Classification :
- In Adults – RTA is commonest one, fall from height, machine injury, gun shot injury.
- In Children – Fall from height, Birth injury.
Seinsheimer’s classification :

- Type – I : When the fracture is localised or undisplaced.
- Type -II(A) : When the fracture is below the lesser trochanter.
- Type – II(B) : When the fracture is above the lesser trochanter.
- Type – III(A) : Lesser trochanter becomes 3rd fragment.
- Type – III(B) : Fragment from original fracture line becomes 3rd fragment.
- Type IV : Along with Type III, another fragment joins and becomes “Four part fracture”.
- Type V : Along with Type IV, Subtrochanteric comminuted fracture with intertrochanteric extension.
3. Diagnosis :
- X-Ray : Helps to diagnose the fracture and severity of it. According to place and depth of fracture it can be classified by looking the Xray.
- Pulse checking – Presence of popliteal pulse means no vascular damage.
- CRT : IF it is <2 seconds that means no vascular injury occurred.
- Toe movements – Suggest no nerve injury.
4. Treatment :
- Conservative – If the patient is young, we mainly try to use modified cast brace with pelvic band.
- Surgery – This is done, in case of Adults and ORIF(Open reduction and internal fixation). Various surgeries are used in internal fixation : Proximal femoral nail, Dynamic condylar plate, condylar blade plate and dynamic condylar screw, Spiral blade plate are used.
| Type of fracture | Implant used |
| 1. Low transverse fracture and short oblique fracture with 1 degree intact cortex. 2. In fracture above this level without trochanteric extension. 3. In fracture above this level with trochanteric extension. | 1. Itra medullary nail or a interlocking nail. 2. Locking nail or Zickel nail. 3. Sliding compression, Hip screw, Bone graft is used. |
5. Complications :
- Malunion – When conservative treatment is done, there remains high chance of malunion.
- Secondary osteoarthritis of the hip.
- Shortening of bone.
- Due to altered weight bearing mechanism and limping, the patient may feel contralateral hip and knee pain.