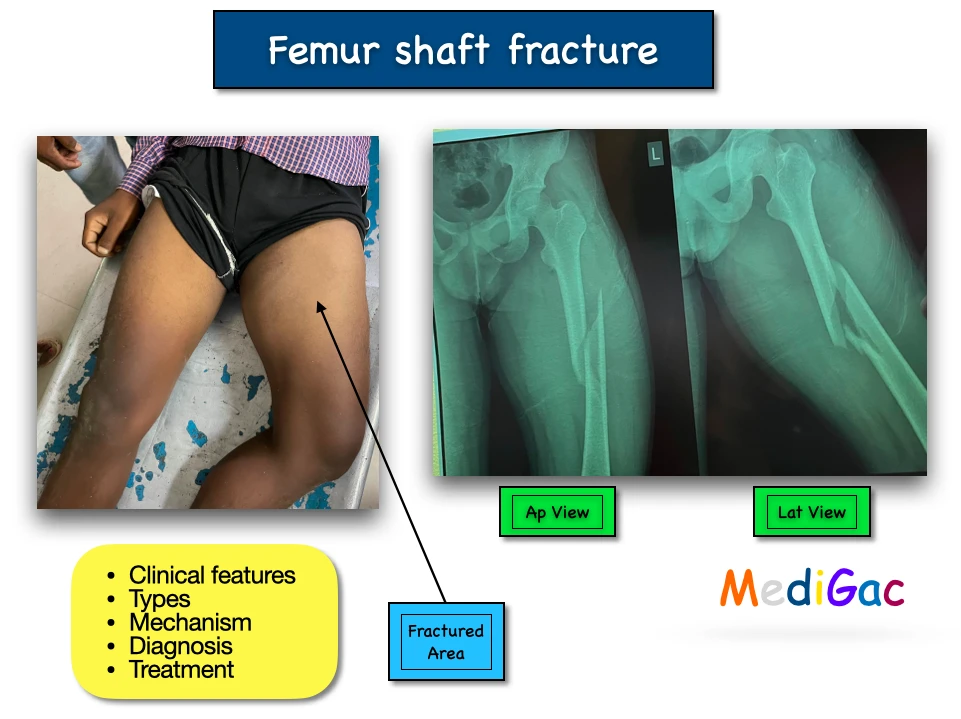
The femoral shaft is the name given to the long, straight portion of the femur. A femoral shaft fracture occurs when any point along this length of bone breaks.
1. Clinical features :
- Swelling.
- Deformity of thigh.
- Pain during making flexion, extension.
- Pain in the fractured area.
2. Types :
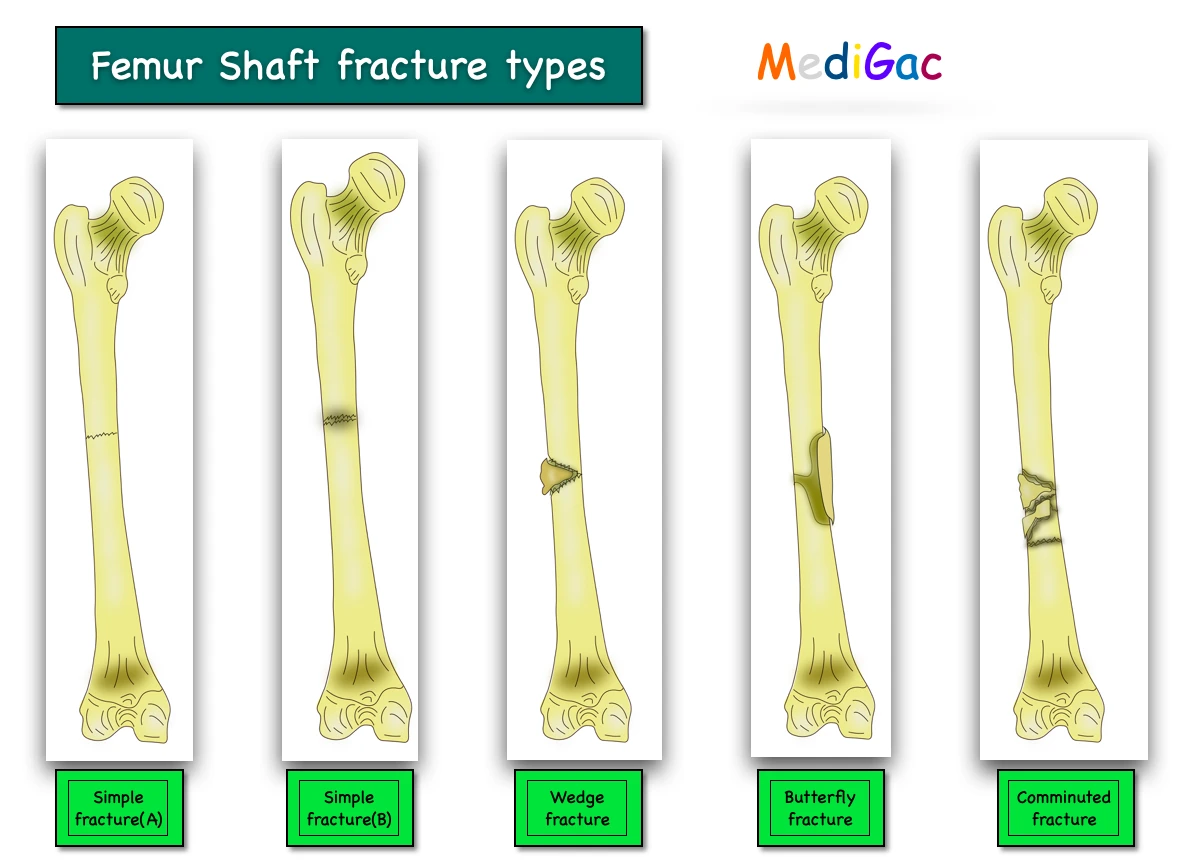
There are mainly four types of fracture are seen based on the severity and shape of the fracture.
- Simple fracture
- Wedge fracture
- Butterfly fracture
- Comminution fracture
3. Mechanism :
- Fall form height.
- RTA.
- Industrial accidents.
- Gun shot injuries.
- Birth injuries to children.
4. Diagnosis :
- Plain X-Ray – To help in diagnosing the severity and type of the fracture.
- Physical appearance can also help to diagnose the fractured area.
- CT scan if plain X-ray is not clear.
- MRI to see any vascular damage.
5. Treatment :
Firstly we give the patient a painkiller like Diclofenac IM, then we send the patient for X-Ray. Then we try to find out the fracture type by looking at the X-Ray plate. Based on the severity and types there are several types of treatments are available.
I. Conservative treatment :
IN CHILDREN :
- 0-2 years : Plaster spica.
- 2 – 10 years : Split Russel traction.
- 10 – 15 years : 90 to 90 degree femoral skeletal traction hip spica or both.
- >15 years : Same as Adults.
IN ADULTS :
- Traction.
- Cast bracing.
II. Surgical treatment :
- ORIF(Open reduction and internal fixation).
- Intramedullary nail(IM NAIL) : K Nail.
- Interlocking nail : Gross-Kempf nail is used in conditions like Segmental fractures, Comminuted fractures, Proximal and distal fractures, and incase of non-union.
- Flexible medullary nail like Ender’s nail.