
I. What are the Physical Examinations to be done
[Inspection – Palpation – Percussion – Auscultation]
I. How to do the Inspection part :
In the Inspection part we mostly see few things, and they are :
- Respiratory Rate
- Face Characteristics
- Neck features
- Hands and Arms
- Thorax
A. Checking the Respiratory Rate :
Normal rate is 12-15 per minute, Anxious patients have 15-20 breaths per minute and it seems abnormal when the rate is above 20 per minutes.
B. Checking the Face :
- SVC obstruction – Dark coloured, swelling of the head, neck and face and also having subconjunctival oedema.
- Tumour at the root of the neck – Unilateral ptosis and pupillary constriction
- Conjunctiva of eye for checking anaemia
- Colour of the tongue for checking the central cyanosis which confirms hypoxia.
C. Observing the Neck :
- Examine JVP – If it is raised then the chances of occurrence are Pulmonary hypertension, Tension pneumothorax, and also in large pulmonary embolism.
- Checking tracheal division and Cricosternal distance
- Cervical lymph nodes checking
D. Checking the Hands and Arms :
- Clubbing of Hand – Occurs in chronic suppurative lung disease such as bronchiectasis, lung carcinoma and pulmonary fibrosis.
- Cyanosis
- Small muscle wasting
- Yellow brown discolouration of nails
- Tar staining of fingers
E. Checking the Thorax :
- Thin chest wall
- Increased respiratory drive
Both of these signifies Asthma/COPD.
II. How to do the Palpation Part :
In the palpation part we palpate various things, they are :
- Apex Beat is checked
- Radial pulse – Assessing the pulse rate.
- Jugular venous pressure – The jugular venous pressure is assessed with patient at 45 degree. The area is located between the two heads of sternocleidomastoid raised in cor pulmonale.
- Hyperinflation – When the lingula of the left upper lobe comes between the heart and the chest wall due to hyperinflation in obstructive lung disease, the apex beat becomes impalpable and the heart sounds become inaudible. The epigastrium is the ideal place to hear heart sounds in this circumstances.
- COPD with Hyperinflation – On inspiration, the typical outward movement of the lower ribs is replaced with paradoxical inward movement induced by contraction of the abnormally low flat diaphragm in COPD with hyperinflation.
- Right ventricular heave
III. How to do the Percussion Part :
In percussion of the chest we mainly check Anterior and posterior part of the chest wall.
In anterior chest wall percussion, we check total six sites, and they are :
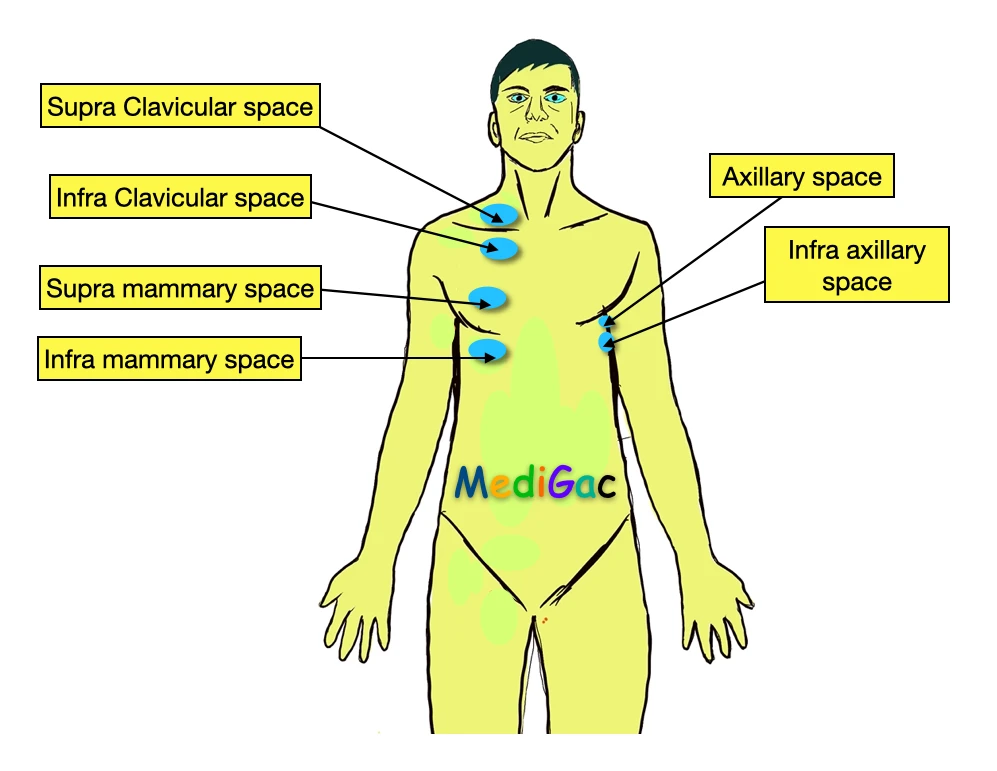
- Supra clavicular space
- Infra clavicular space
- Supra mammary space
- Infra mammary space
- Axillary space
- Infra axillary space
And in posterior chest wall percussion, we check total three sites, and they are :
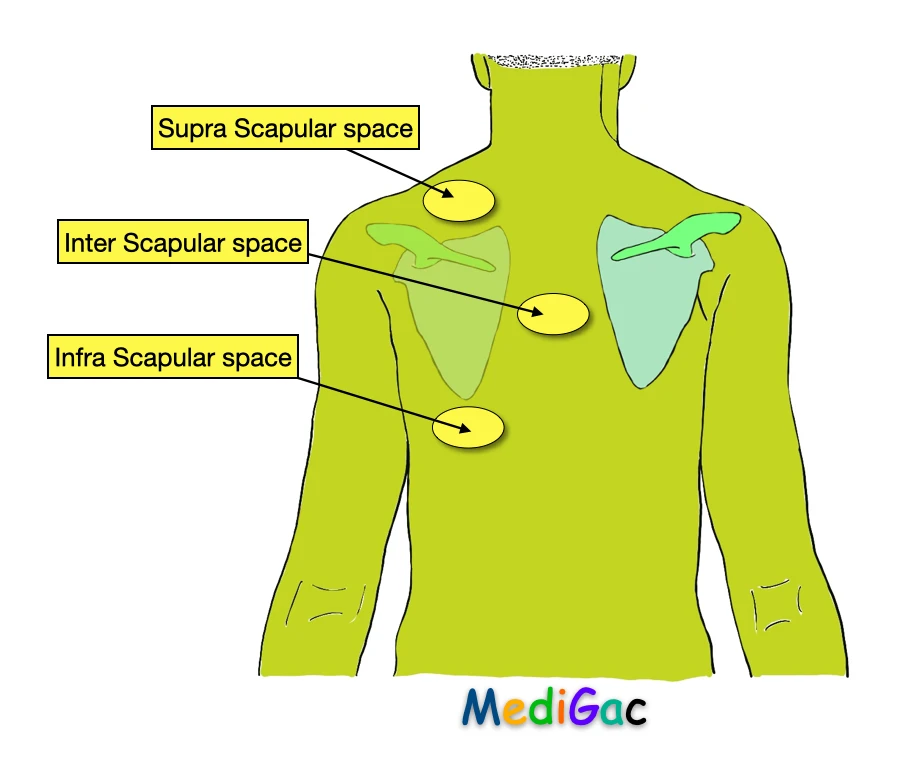
- Supra scapular space
- Inter scapular space
- Infra scapular space
IV. How to do the Auscultation part :
- Pneumonia and Lung Fibrosis – In this disease, the healthy lung becomes consolidated, so the bronchial breath sounds heard clearly and loudly on the overlying chest wall
- Pneumothorax – Here the breath sounds are usually absent.
- Vocal Resonance – This occurs in presence of consolidation, fibrosis, and pleural air. This is also checked by stethoscope at the anterior chest wall and posterior chest wall same as Percussion.
- Wheezes – When the airways gets small and narrow, then the whistle like sound starts to appear. Occurs in Asthma, COPD and Bronchitis.
- Crackles – This occurs due to sudden opening of the small airways. Also this can occur when the lung starts secretion in lung fibrosis.
- Rub – Occurs during pleurisy.
What are the Investigation procedures we use for respiratory system
- Chest X-Ray can show Tuberculosis, Pneumonia, carcinoma etc.
- CT Scan can show severe respiratory problems.
- HRCT can show ILD that is Interstitial lung disease
- USG
- Arterial blood gas
- Respiratory function test