
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is the immediate treatment of a bite victim after rabies exposure. This prevents virus entry into the central nervous system, which results in prevention of imminent death.
PEP consists of :
- Extensive washing and local treatment of the bite wound or scratch as soon as possible after a suspected exposure.
- A course of potent and effective rabies vaccine that meets WHO standards.
- And the administration of rabies immunoglobulin (RIG), if indicated.
Starting the treatment soon after an exposure to rabies virus can effectively prevent the onset of symptoms and death.
Extensive wound washing
This first-aid measure includes immediate and thorough flushing and washing of the wound for a minimum of 15 minutes with soap and water, detergent, povidone iodine or other substances that remove and kill the rabies virus.
Intramuscular administration of vaccine for post-exposure prophylaxis :
PEP is done by injection 1ml or 0.5ml into the deltoid muscle. In children <2 years injection is given into the anterolateral aspect of thigh.
A. Essen Regimen :
Here we give 5 doses.
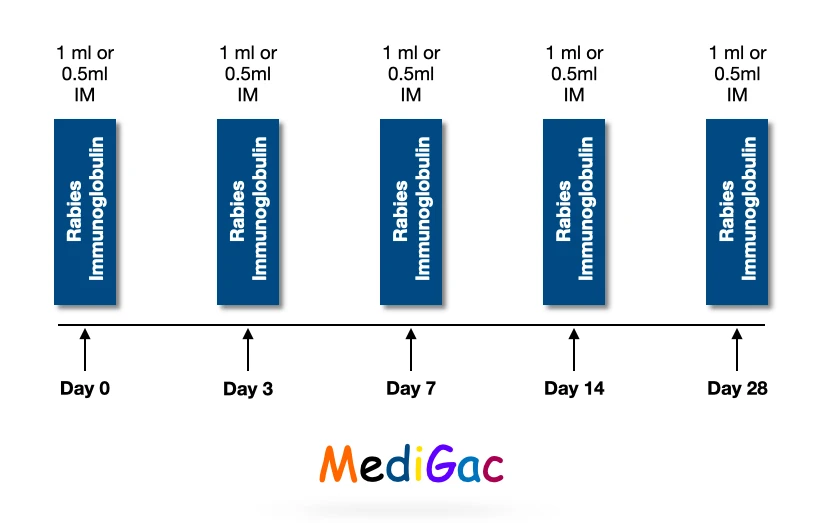
- 1 dose on each days of 0,3,7,14 and 28 days.
B. Zagreb Regimen :
Here we give 4 doses.

- Day 0 (2 doses) : 1 in each of the two deltoid or thigh sites
- 7 days : 1 dose
- 21 days : 1 dose
Intradermal administration of vaccine for post-exposure prophylaxis :
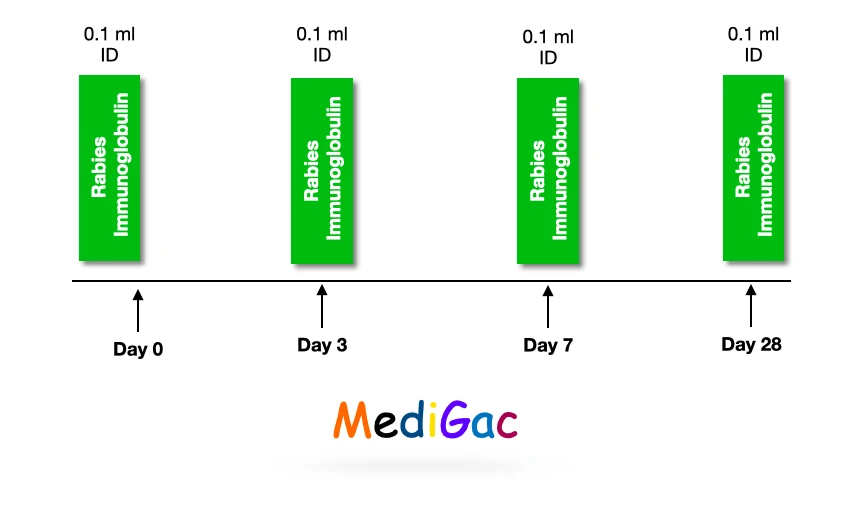
- Day 0 : 0.1 ml at two sites (deltoid or thigh)
- Day 3 : 0.1 ml at two sites (deltoid or thigh)
- Day 7 : 0.1 ml at two sites (deltoid or thigh)
- Day 28 : 0.1 ml at two sites (deltoid or thigh)