We have made all the MEDICINE Instruments full set or list with the Names, Description, Uses with Pictures. in you medical ward you will see all this instruments/equipments/devices. So full knowledge regarding all this devices is necessary for your medical and surgical practice and also during exams.
AUTOCLAVE

Description :
Made up of metal mainly. Has 8 parts for functioning :
- Pressure gauze
- Safety valve
- Autoclave Lid
- Handles
- autoclave Body
- Steam release valve
- Vacuum release valve
- Outer stand
Uses :
1. Sterilization : To Sterilize all the medical and Surgical Instruments which makes the instruments and equipments reusable.
BED PAN

Description :
Hollow structure, can be made up of steel, plastic.
Two ends : One faces towards front of patient & another end stays under buttocks.
Uses :
1. Urine and Feces : Patients who are unable to move from bed due to weakness or unconsciousness can release urine and faecal matter into Bedpan.
SURGICAL CAP

Description :
These are disposable caps made up of PP Spun bond fabric.
—Covers the head portion.
Uses :
1. Operative Procedures : In various operative procedures it is used to prevent spreading of infection from hair/scalp between the doctor and the patient.
2. Pandemic/Epidemic : In any kind of Pandemic or Epidemic we use Bonnets for prevention of infection from the environment.
CARDIOVERTER-DEFIBRILLATOR/PACE-MAKER

Description :
This is a battery powered device placed under the skin that keeps track the heart rate.
It detects a rapid heartbeat coming from the bottom of the hart.
It has mainly two functional parts :
- ICD(Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator)
- Lead
Uses :
1. Electrical Pulse : these are device which makes the heartbeat normal by sending an electric pulse or signal to the heart.
2. Used in Cardiac dysrhythmias like Ventricular Fibrillation and Non-Perfusing Ventricular Tachycardia.
IV CANNULA

Description :
The body is made up of plastic and the body hold a metal needle.
—There are total 10 parts :
- Luer Lock plug
- Flashback chamber
- Needle Grip
- Luer Connector
- Injection port cap
- Wings
- Valve
- Bushing
- Catheter
- Needle
Uses :
1. To Create a long term path for accessing the venous blog channel.
2. Used in repetitive invasive procedures like :
- Administration of fluids
- Blood Products
- Normal Saline and Medications
- Parenteral Nutrition
- And also can be used in chemotherapy
FOLEY’S SLEF RETAINING CATHETER
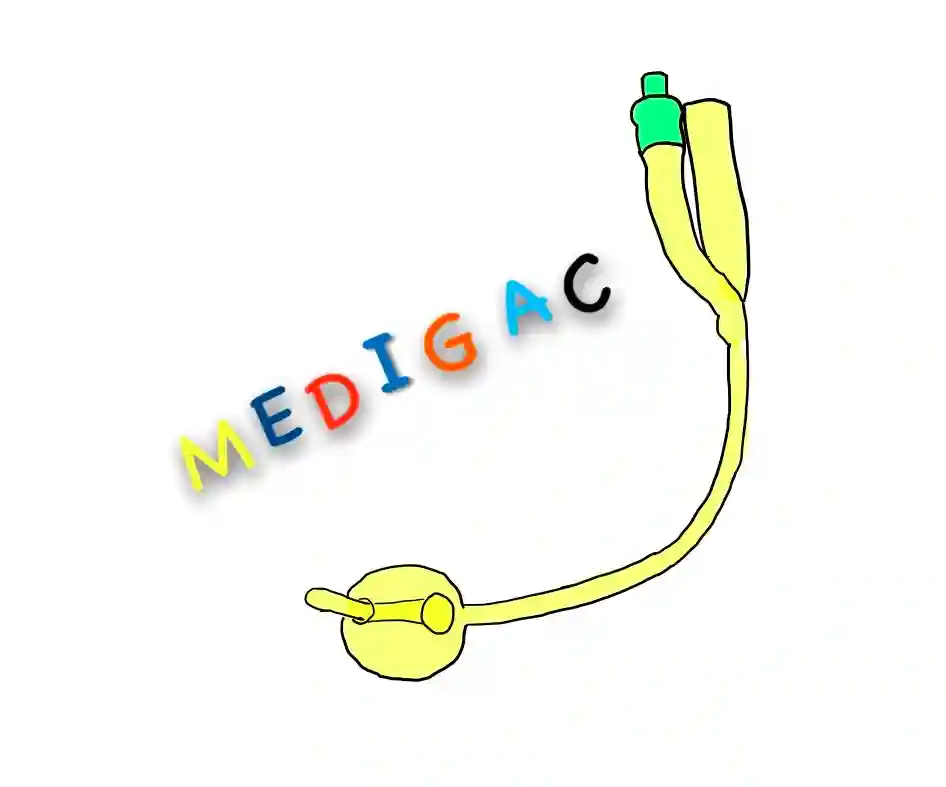

Description :
Two ports are present at the distal end of the tube :
1. Urine drainage port
2. Balloon port
Other parts are Balloon, Bladder opening are present at the proximal end.
Uses :
When abnormal micturition process occurs, the catheter is inserted into the bladder to drain and collect the urine properly.
Various Conditions :
- Kidney Stone.
- Blood Clots in Urine.
- Severe enlargement of the Prostate gland.
- Spinal cord Injury.
- Bladder nerves Injury.
- Secondary Use – Can be also used as a makeshift oxygen tube.
HARTMAN ALIGATOR FORCEPS
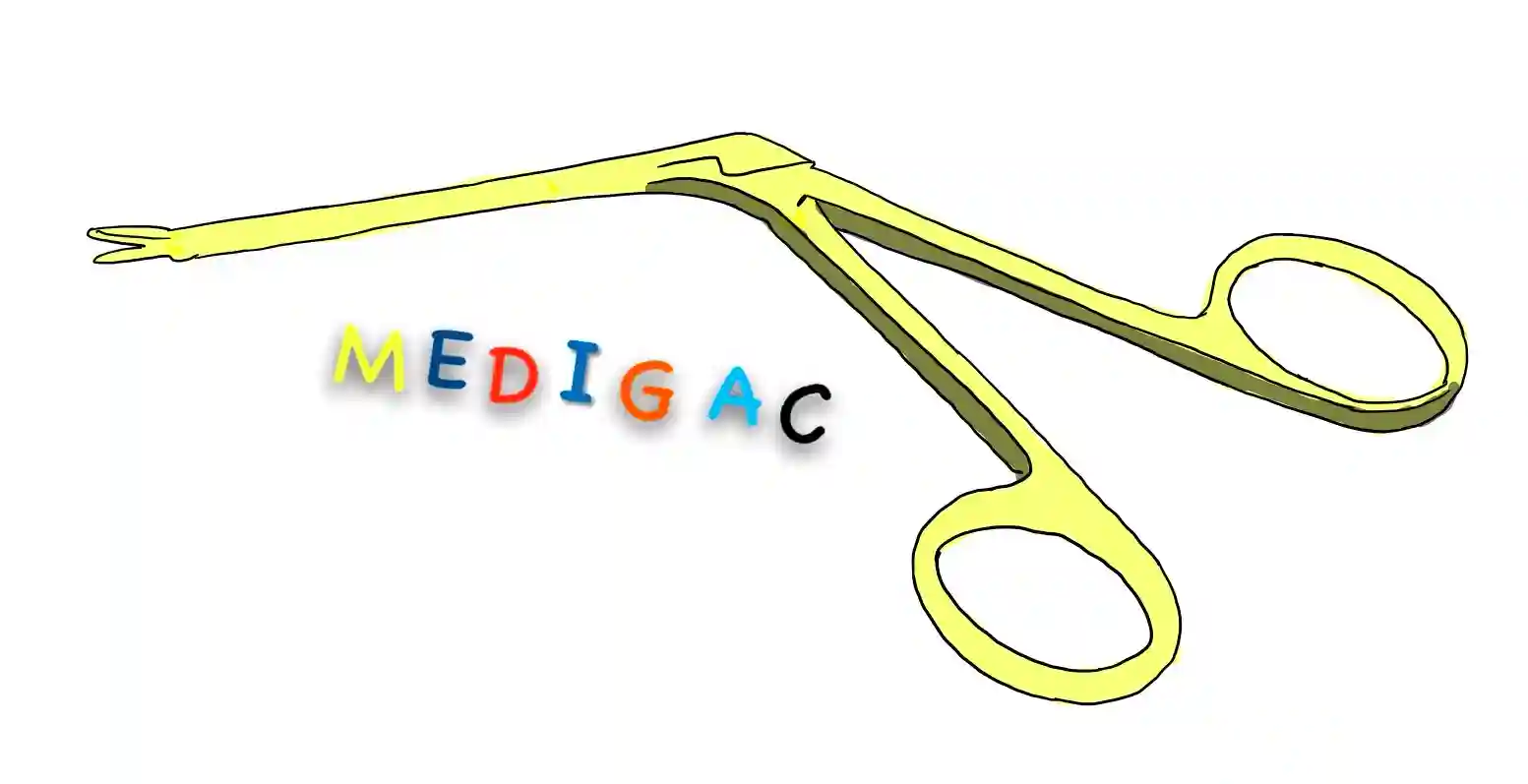
Description :
Made up of stainless steel and has two parts the limbs and the tips.
There is presence of Box joint at the middle of the Forceps.
And at the tip has cups, teeth or scissors.
Uses :
1. To hold graft materials and transfer temporalis fascia.
2. Transferring temporalis fascia graft material from one place to another place.
3. Foreign body removal, oral & nasal packing.
DIALYSER
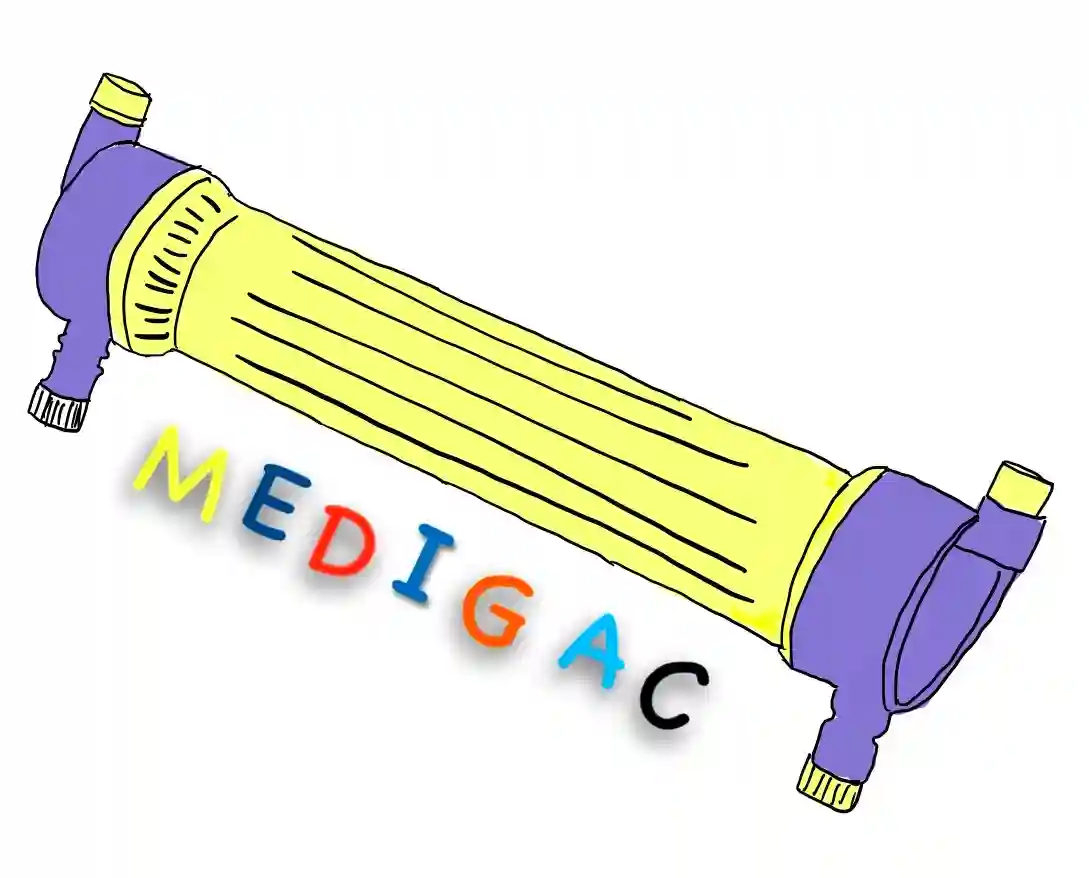
Description :
There are mainly three components to a :
- The Haemodialyser(Artificial Kidney)
- Dialyser Membrane
- The Dialysate
Uses :
1. kidney Failure : When the blood fills with toxic materials and kidney does not works properly, we use Dialyser to purify the blood by removing all the toxic materials.
2. Removal of extra Fluid : Extra fluid which areharmful and not necessary for the body are removed by the Dialyser.
DROPPER

Description :
It has a rubber handle and glass tube.
Uses :
1. Measurement of Doses : to measure drug doses which are in liquid forms.
2. To provide drugs inside oral cavity : Sometimes liquid drugs needed to be assisted by the caretaker incase of children.
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY MACHINE
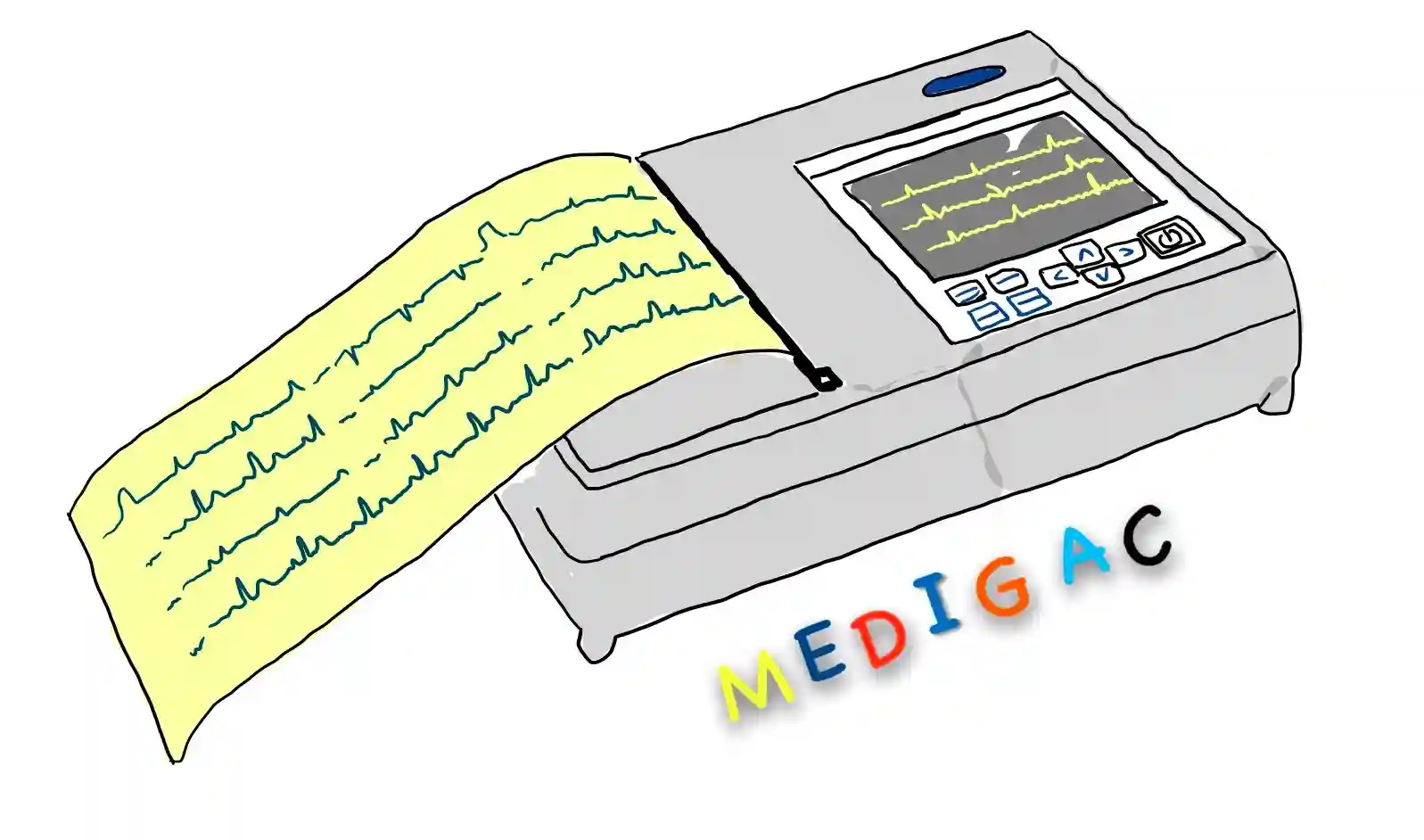
Description :
This is machine which function the process of Echocardiography to produce an echocardiogram.
Uses :
1. Heart Rhythm and Electrical Activity : To check heart rate and electrical activity by checking PQRST wave pattern.
2. Screening of heart diseases : Coronary artery diseases can be detected early by checking the waves.
ENDOSCOPE

Description :
This device is used to see inside of the body/organs.
It has mainly 5 parts :
- Eyepiece
- Opening for wires and instruments
- Flexible Shaft
- Flexible shaft transmitting light, air and water
- Flexible tip
Uses :
1. Viewing and Operating the Inner Structures : Normally it is used to view/operate the inner structures like organs, blood vessels of the body.
Various Endoscopies are :
—-Bronchoscopy
—-Laryngoscope
—-Oesophagoscopy
2. Taking Biopsy samples : It is also used to take Biopsy samples for examination purpose.
ENEMA EQUIPMENT
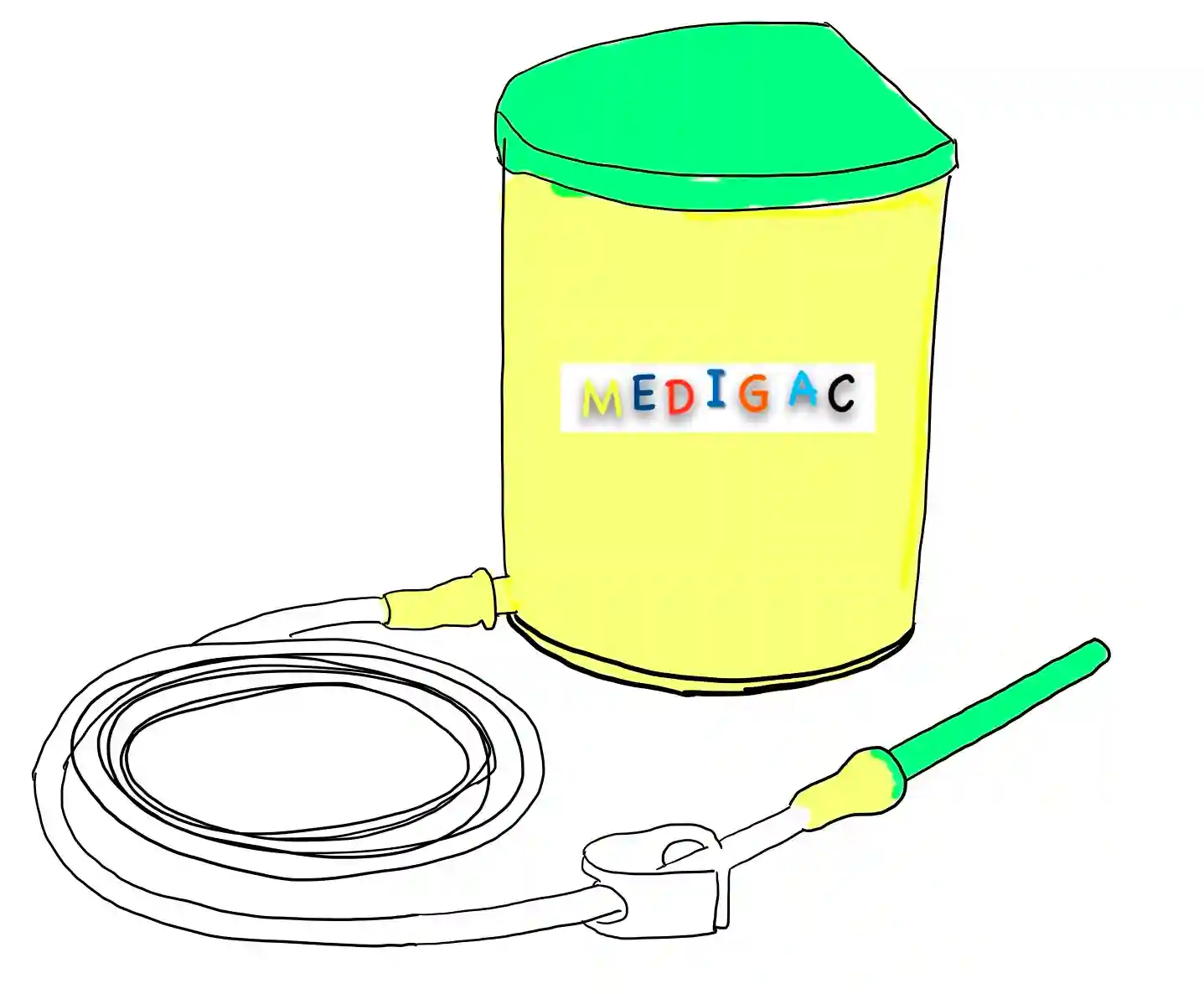

Description :
The enema can is made up of Stainless steel.
Other parts are :
- Enema nozzle
- Colon tube
- Catheter
Uses :
Used to stimulate stool evacuation.
FACE SHIELD

Description :
The face shield is made up 5 parts :
- Headband Frame
- Headband Strap
- Transparent shield
- Headband strap hook
- Transparent shield mounting pegs
Uses :
1. Protection : To protect the eyes , nose, and mouth from spreading of any infection.
GAS CYLINDER

Description :
Hollow cylindrical structure which has a top and bottom.
—–The bottom is flat and closing the end of the cylinder.
—The top part has a Flow adjustment regulator with a nozzle, on-off valve, Pin Index Valve
—The nasal tube comes from the Nozzle.
Uses :
Oxygen, Nitrous Oxide, helium, and Carbon Dioxide are stored into these cylinders.
1. In emergency situations : In Hypoxemic situation low oxygen saturation occurs which requires external suppling of oxygen.
2. Anaesthesia Purpose : Anaesthetic gases like Nitrous Oxide was used for anaesthetic purpose.
But nowadays we avoid this anaesthetic process.
GAUGE SPONGE

Description :
These are disposable medical equipments made up of gauze( Thin medical fabric with a loose open weave used in wound care).
Uses :
1.Absorbing Purpose : mainly used to absorb blood and other fluids during any kind of wound occurs.
GLOVES

Description :
These are medical equipments made up of latex.
Uses :
1. Examining the patients : Medical Gloves are sued for examining the patient to prevent any transmission of infection between Patient and the Examiner.
2. Surgical Procedures : In almost all surgical procedures the Doctors wears gloves to prevent the spread of infection between the Patient and the Doctor.
GOGGLES
Description :
Made up plastic frame and polycarbonate polymer which helps to get good optical clarity.
Uses :
1. Protection of the eyes : To protect the eyes from spreading of any infection.
GOWNS
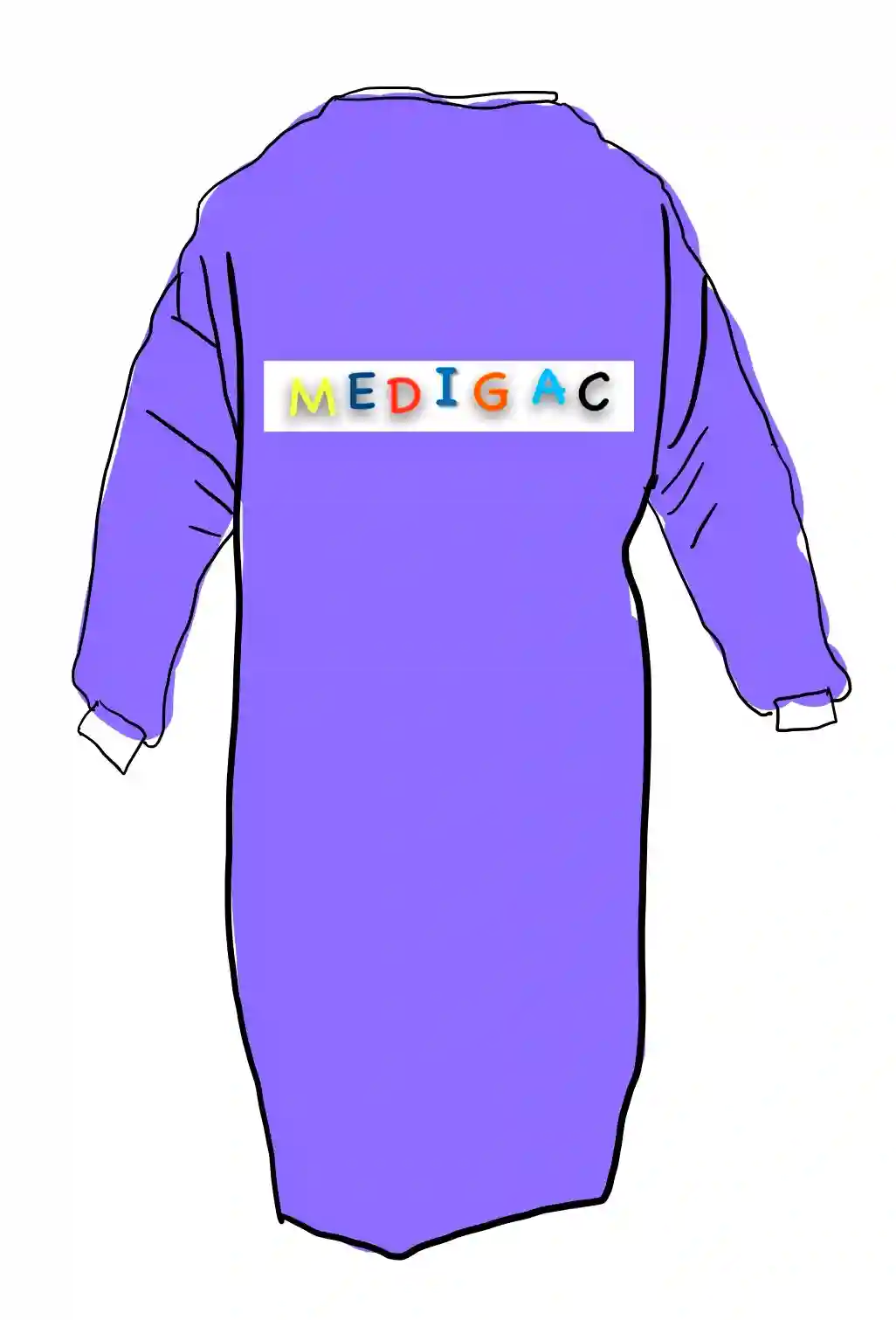

Description :
These are disposable gowns made up of pure cotton(100%).
Uses :
1. Surgical Procedures : In various surgical procedures the Doctor and Patient both wears Gowns to prevent the transmission of infection between them.
2. Medical Ward : Sometimes a infection sensitive patient also wears gowns when admitted tom the ward.
HYPODERMIC SYRINGE & NEEDLE

Description :
Hypo – Under || Dermic – The Skin
It has mainly parts :
- Plunger Flange
- Plunger Barrel Flange
- Barrel
- Seal
- Luer Lock
This made up of plastic and the metal needle. Markings are present on the Plastic Barrel
Uses :
1. Venipuncture : In venipuncture process for taking blood form a vein.
2. Injecting substance : To Inject substances like medications.
KIDNEY TRAY

Description :
Made up of stainless steel and it is kidney shaped.
Uses :
1. Keeping the Sterilized Instruments : All the Sterilized sharp instruments are carried out by this tray.
2. Collecting Specimens : The shape of the tray is like kidney and has curves which makes it fit in various places of the body during collection of specimens.
MEASURING TAPE

Description :
It consists of a ribbon of cloth, plastic, fibre glass.
Uses :
1. To Measure :
- –Height
- –Length
- –Head Circumference
- –Girth Measurement
PENLIGHT
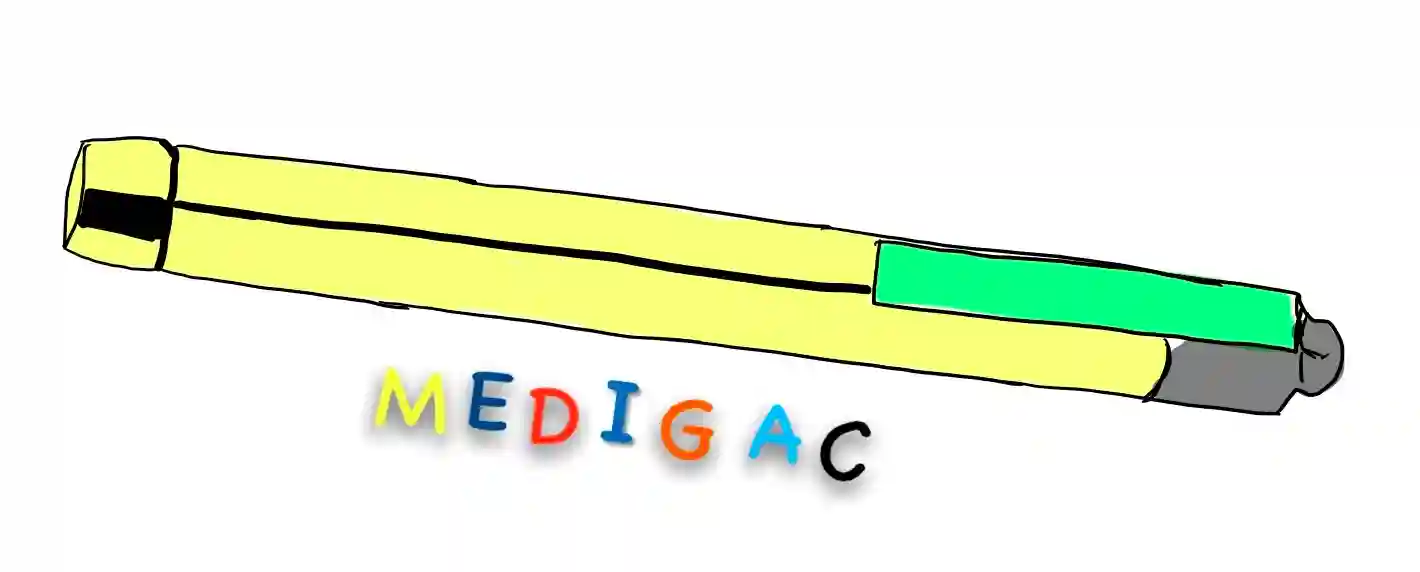
Description :
Metal or plastic body with a clip at one end.
And a LED at the tip.
Uses :
1. Examination purpose : For examining ;
- –The Eyes
- –External Ear Canal
- –Nose
- –Others natural orifices
- –To test pupillary light reflex
NASOGASTRIC TUBE
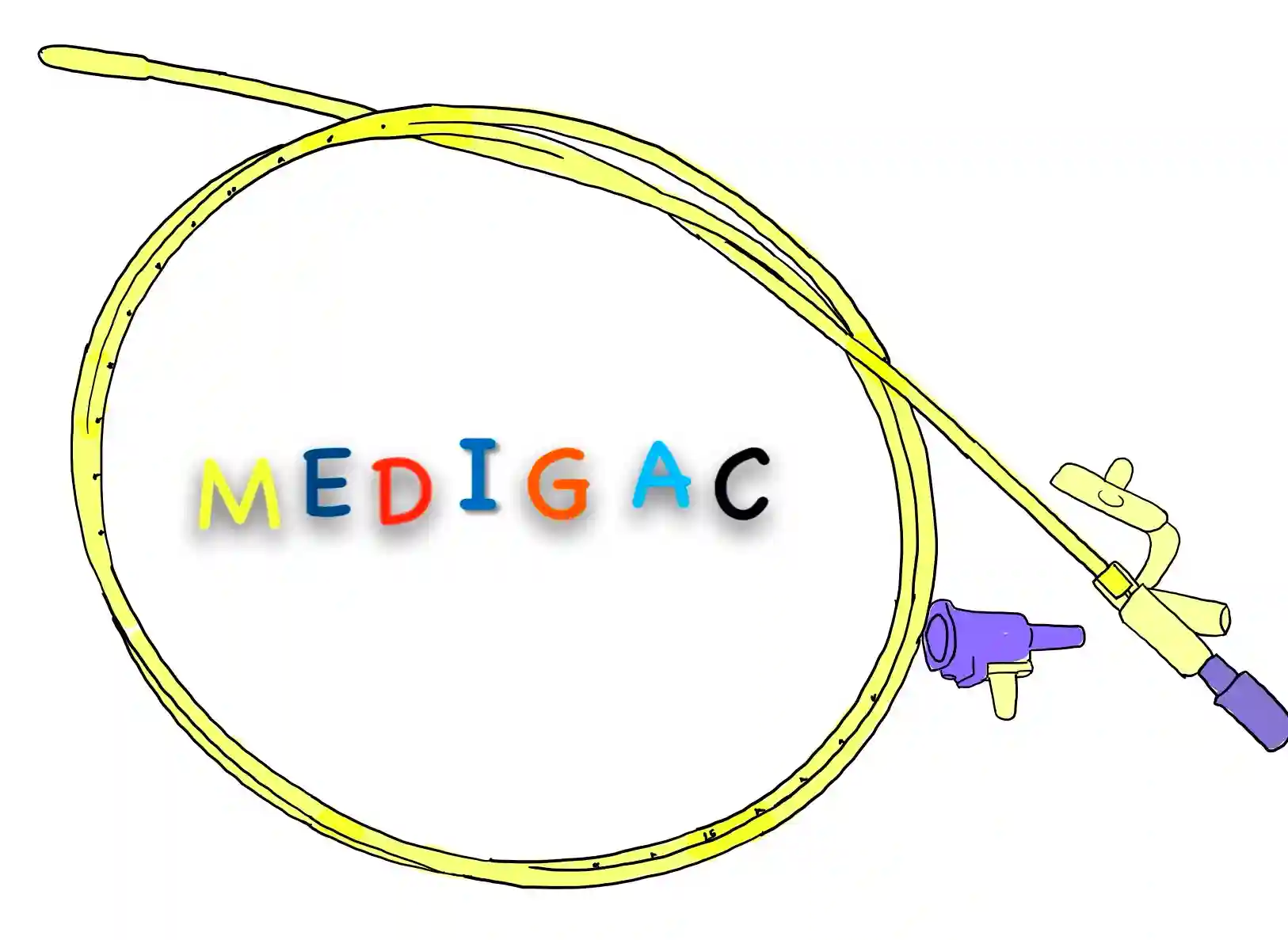
Description :
This is a flexible tube of rubber or plastic which can be passed through the nose.
Uses :
1. Substance Addition : To add substances directly into the stomach.
2. Removal of Substances : To remove substances from stomach.
3. Acute pancreatitis treatment : Incase of Acute Pancreatitis, the food substances are directly added into the stomach.
NEBULIZER
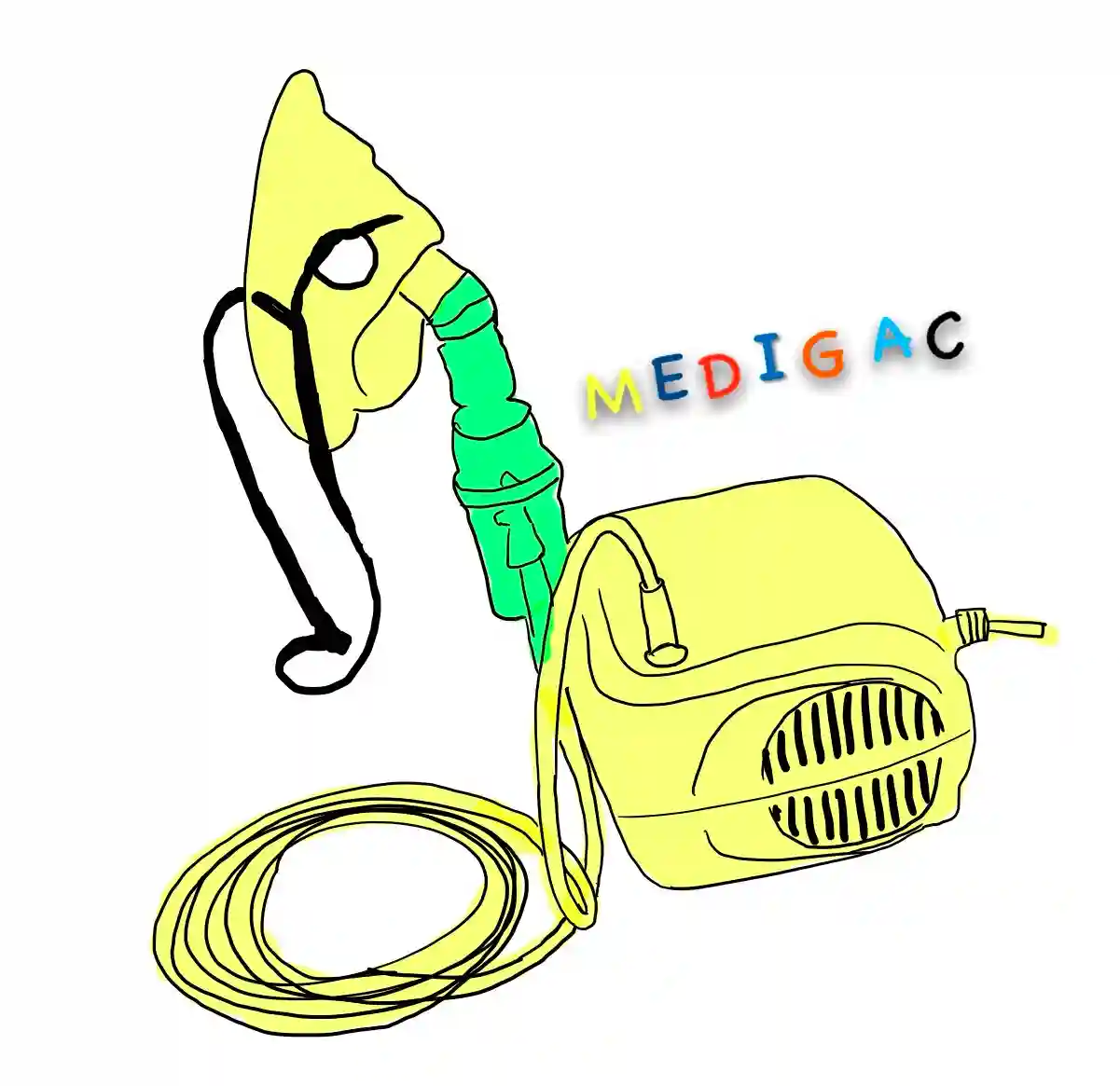
Description :
This is device made up of Plastic and has mainly $ parts :
- Mouthpiece
- Mask
- Compressor tubing
- Air compressor
Uses :
1. Liquid to Aerosol transfer : The compressor helps to transfer liquid drugs into aerosol form.
2. Breathing : From mouthpiece, the patient used to take breath.
3. COPD/Asthma : Used in COPD and Asthma for proper taking of drugs in gaseous forms.
OPHTHALMOSCOPE

Description :
This device has mainly two parts :
One handle and the plastic optic head.
—The plastic head has aperture dial.
Uses :
1. Eye Examination : To examine the eyes for any disease diagnosis.
2. Differentiation : To differentiate between retinal and choroidal lesions.
3. Examination of the Fundus : It is done by seeing through the dilated pupil by the Ophthalmoscope.










