In this post we have discussed all the Important topics of brain or neuro anatomy which can help you to perform well in the theory and viva exam.
Meaning/ Definition :
The science of neuroanatomy is the study of the whole nervous system(Brain, Brain Stem and Spinal cord)
Genetics, neuropsychology, psychology, neurology (the study), and behaviour therapy are examples of sub-disciplines.
What are the important topics :
1. Development of the Nervous System :
Except for blood vessels and certain neural components, the nervous system is entirely made up of ectoderm.
Later on, the neural ectoderm divides into three structures: the neural tube, neural crest, and ectodermal placodes.
Nearly all of the peripheral nervous system is made up of neural crest cells. Nearly all of the peripheral nervous system is made up of neural cells, and ectodermal placodes lead to the cranial sensory ganglia, hypophysis, and inner ear.
2. Ganglia – Sensory ganglia and Autonomic ganglia
A ganglion is a series of nerve cell bodies located outside of the CNS.
Sensory ganglia and autonomic ganglia are two types of ganglia.
Sensory Ganglia :
The sensory ganglia are found on the dorsal roots of spinal nerves as well as the trunks of certain cranial nerves, such as the Trigeminal, Facial, Glossopharyngeal, and Vagus nerves.
Autonomic Ganglia :
Sympathetic and parasympathetic autonomic ganglia are the two forms of autonomic ganglia.
3. Structure of the Nervous System :
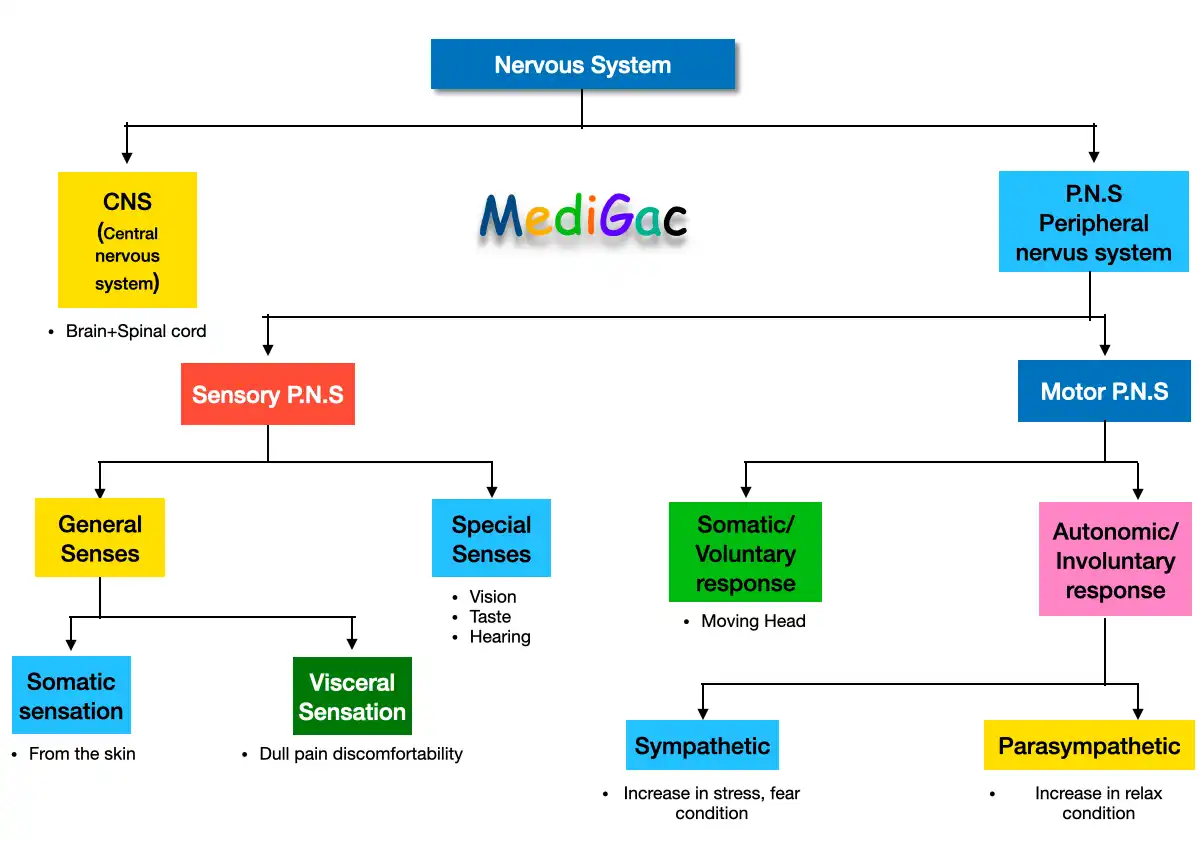
- Central Nervous system : Brain + Spinal cord
- Peripheral nervous system : Sensory P.N.S(Special senses and general senses) and Motor P.N.S(Somatic and Autonomic)
4. Interpeduncular Fossa :
This is a Rhomboidal space.
- Either side : Crus cerebra of cerebral peduncles
- Anteriorly : optic chiasma and optic tracts
- Posteriorly : Pons
5. Divisions and Functions of the Brain :
- Cerebreum : Basal ganglia and limbic system
- Diencephalon : Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Subthalamus, Epithalamus
- Brainstem : Midbrain, Pons and Medulla
- Cerebellum –
6. Blood supply of the Spinal cord :
By the :
- Anterior Spinal artery
- Two posterior spinal artery
- Segmental Arteries : The anterior spinal artery, Two posterior spinal artery
7. Midbrain – Internal structures, Transverse section of the Midbrain
The upper and shortest portion of the brain-stem is the midbrain. It measures 2.5cm in length and 2.5cm in width.
Mainly contains 5 structures : Cerebral aqueduct, Tectum, Tegmentum, Substantia nigra and Crus cerebri
—> Tegmentum, Substantia nigra and Crus cerebri there together are called ‘Cerebral Peduncle’
8. Grey matter, Pretectal nucleus, Red nucleus :
- Grey Matter : Grey matter is made up of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil (dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and capillaries, and is a major component of the central nervous system.
- Pretectal nucleus :
This is a small group of neurons located deep in the superolateral part of the superior colliculus.
The Edinger-Westphal nucleus receives afferents from the lateral root of the optic nerve and sends efferents to it.
- Red nucleus : This is a grey matter mass in the form of a cigar with an ovoid cross-section.It has a diameter of around 0.5cm and is located dorsomedial to the substantia nigra.
9. Weber’s Syndrome :
A vascular lesion in the basal region of the cerebral peduncle, caused by the occlusion of a branch of the posterior cerebral artery.
Signs and Symptoms :
- Ipsilateral lateral squint
- Contralateral hemiplegia
- Contralateral paralysis
- Drooping of the upper lid – Proptosis
- Dilated pupil
10. Argyll Robertson pupil :
This is a clinical disorder in which the pupil’s light reflex is lost but the accommodation reflex is still intact.
11. General Visceral Efferent Nuclei :
- Edinger-Westphal Nucleus(Visceral Oculomotor Nucleus)
- Superior Salivatory and Lacrimatory Nucleus
- Inferior Salivatory Nucleus
- Dorsal Nucleus of Vagus(Motor Nucleus of vagus)
12. Oculomotor Nerve :
–> 3rd cranial nerve
- General somatic efferent fibres and General visceral efferent fibres
- Course and Distribution
13. Trochlear Nerve :
–> 4th cranial nerve
- Functional component : Only General Somatic Efferent fibres that arises from trochlear nucleus
- Course and Distribution
14. Facial Nerve
Functional Component :
- Special viscera efferent fibres
- General visceral efferent fibres
- Special visceral afferent fibres
- General somatic afferent fibres
15. Hypoglossal Nerve :
Functional component : Generaal somatic efferent fibres.
Course and Distribution
16. Reflexes mediated by Cranial nerves :
- Corneal Refles
- Conjunctival Reflex
- Lacrimation Reflex
- Oculocardiac Reflex
- Gag Reflex
- Carotid sinus Reflex
- Sneezing reflex
- Jaw jerk
17. Cerebellum – Functions :
- Maintenance of posture
- Maintenance of muscle tone
- Coordination of voluntary motor activity
18. Ventricle – Fourth ventricle :
- Definition
- Recesses of the fourth ventricle
- Boundaries
19. Thalamic Nuclei :
Consists of 4 nuclei :
- Medial Nuclei : Medial dorsal and Medial ventral nuclei
- Lateral Nuclei : Dosal Nuclei(Lateral dorsal, lateral posterior, Large caudal mass & Vental Nuclei(Ventral Anterior, Ventral Lateral, Ventral Posterior and Ventral tier of nucleus)
- Anterior Nuclei
- Other Nuclei : Intralaminar, Paraventricular, Reticular, MGB & LGB
20. Third Ventricle : Communications and Boundaries
Communications :
Anteriorly : It communicates with the third ventricle through inter ventricular foramen(Foramen of Monro).
Posteriorly : With the fourth ventricle through cerebral aqueduct(Duct of Sylvius)
Boundaries :
- Anterior Wall
- Posterior wall
- Lateral wall
- Roof
- Floor
21. Motor Speech area of Broca
In most people, Broca’s motor speech region is found in the pars triangular (area 45) and pars opercularis (area 44) of the inferior frontal gyrus of the frontal lobe of the left hemisphere, and the people are right-handed.
22. Basal Ganglia :
Basal Ganglia include :
- Corpus striatum(caudate nucleus + putamen)
- Claustrum and
- Amygdaloid body
