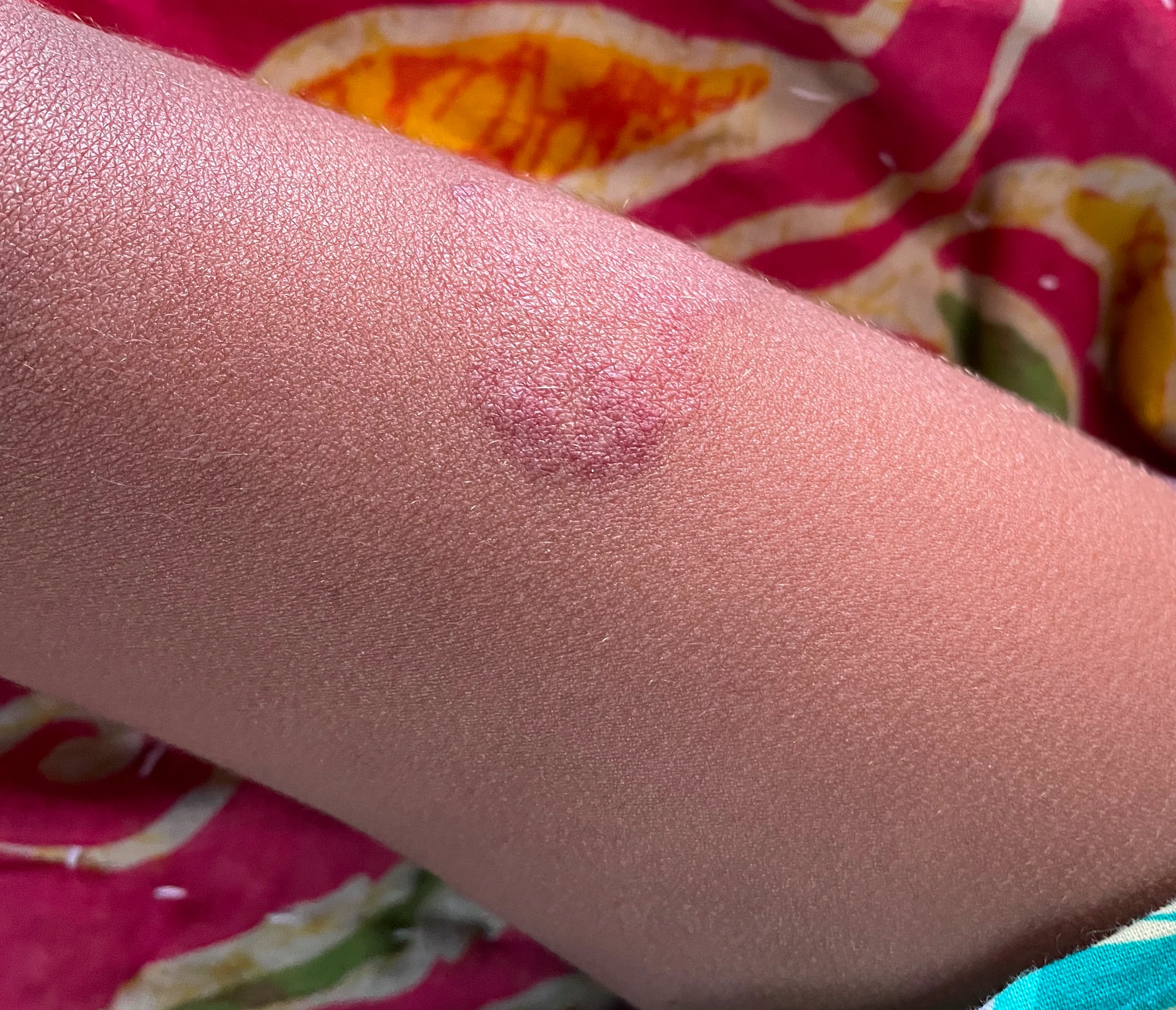
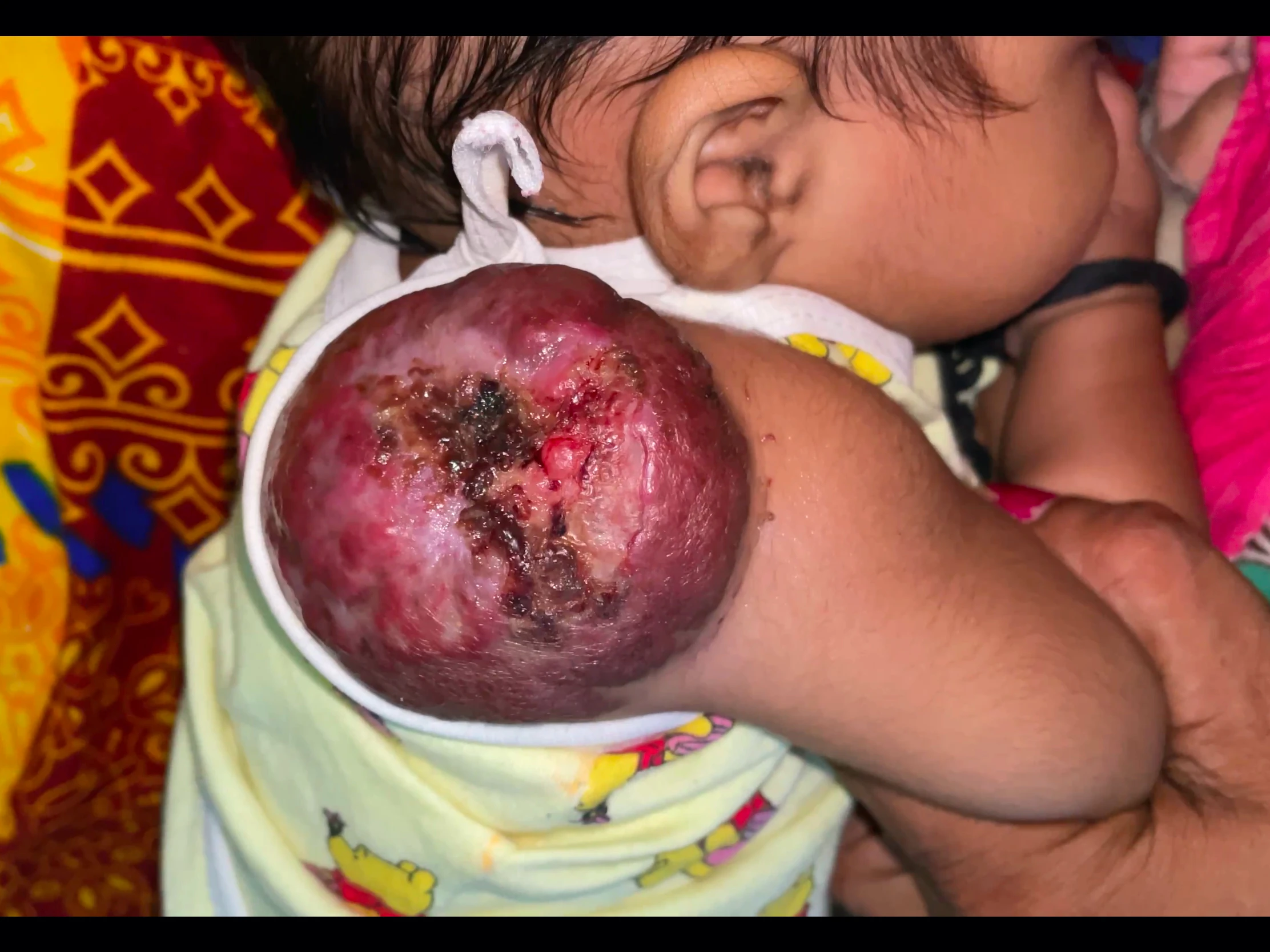
These are the most common tumors composed of blood-filled vessels. Hemangiomas present since birth and holds the record of 7% all benign tumors of infancy and childhood.
1. Pathophysiology :
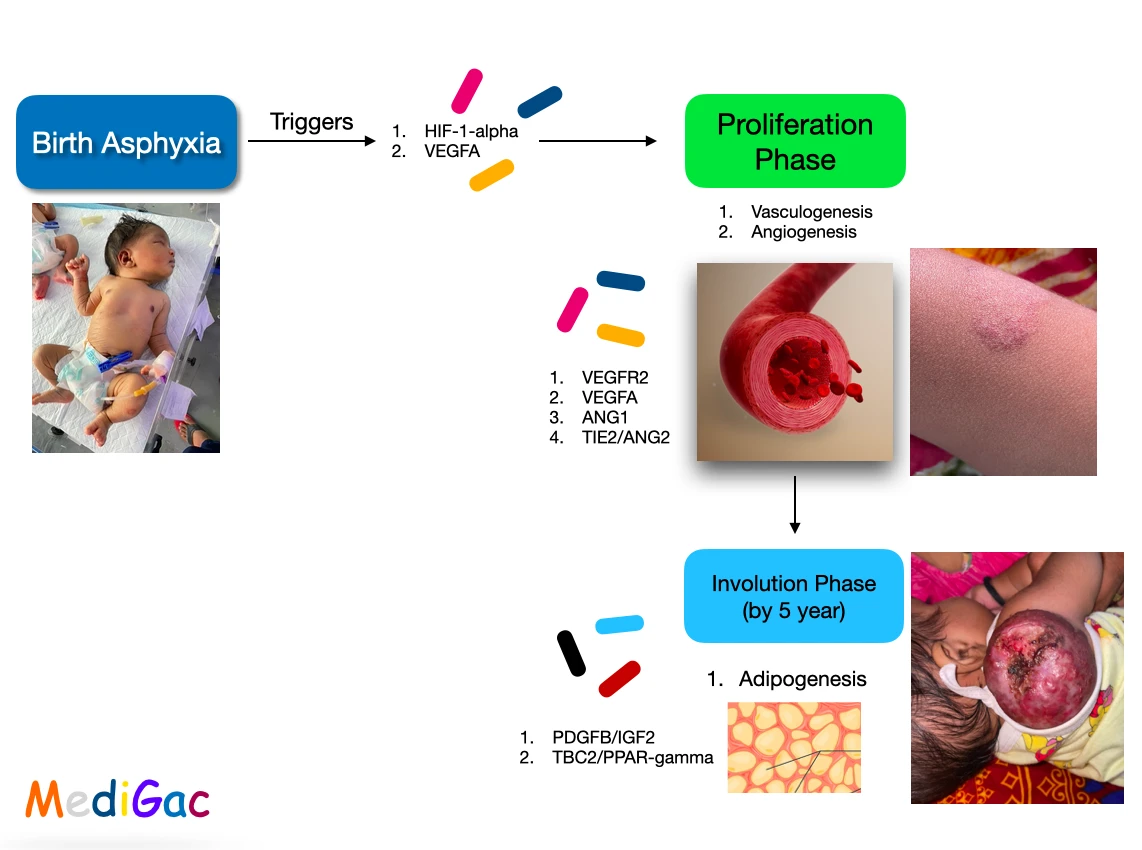
- Main cause of hemangioma is Asphyxia. After birth asphyxia triggers the HIF1-alpha and VEGFA.
- Next comes the Proliferation phase in which vasculogenesis and angiogenesis starts to occur. This occurs due to VEGFR2, VEGFA, TIE2/ANG2.
- Finally phase of Involution – After the vasculogenesis and angiogenesis, PDGFB/IGF2,TBC2/PPAR-gamma starts to act and Adipogenesis occurs. Ultimately the size of hemangioma starts to increase.This phase reach maximum by 5 years of age and 90-95% by 9 years of age. In this phase complications can be seen and they can be ulceration, haemorrhage, and infection.
2. Diagnosis :
- Inspection – Bight red, protuberant, and compressible which is sharply demarcated also.
- Immunohistochemical marker – GLUT-1 separates hemangiomas from other vascular tumors.
3. Treatment :
- PDL(Pulsed Dye Laser) therapy.
- Elastic bandage may reduce the growth.
- Prednisolone 2-3 mg/kg/24 hr.
- Propranolol 1 mg/kg PO q 8 hourly.
- Surgical excision is done if the size is massive.