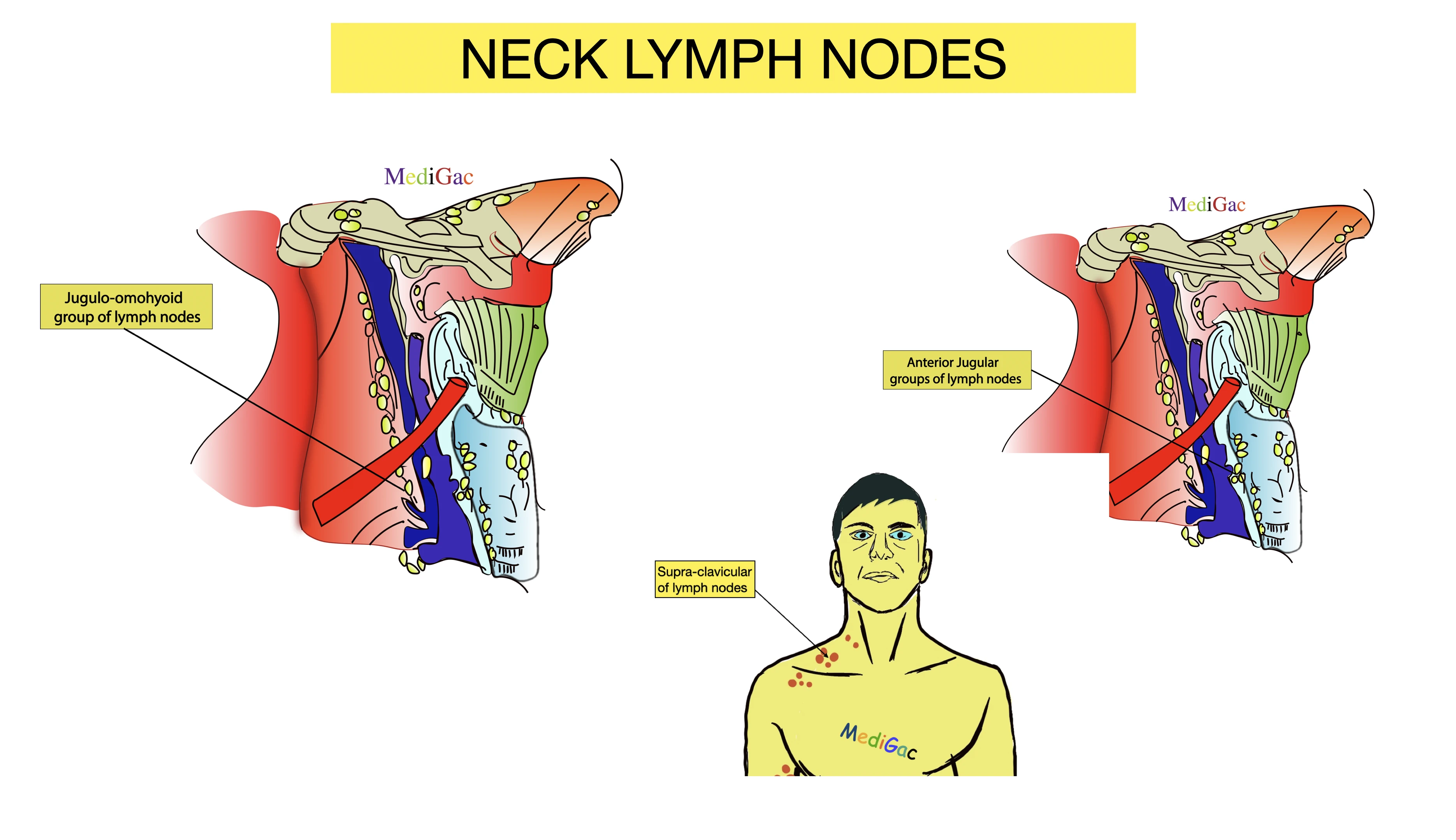
Groups of lymph nodes – Deep(Submental, Submandibular/Submaxillary), Anterior cervical(Prelaryngeal, Thyroid, Pretracheal, Para-tracheal), Deep cervical(Lateral and Anterior jugular), Inferior deep cervical(Jugulo-omohyoid, Jugulo-digastric), Supraclavicular/Virchow’s.
II. What are the lymph nodes of the Neck
A. Deep groups of lymph nodes :
1. Submental nodes :
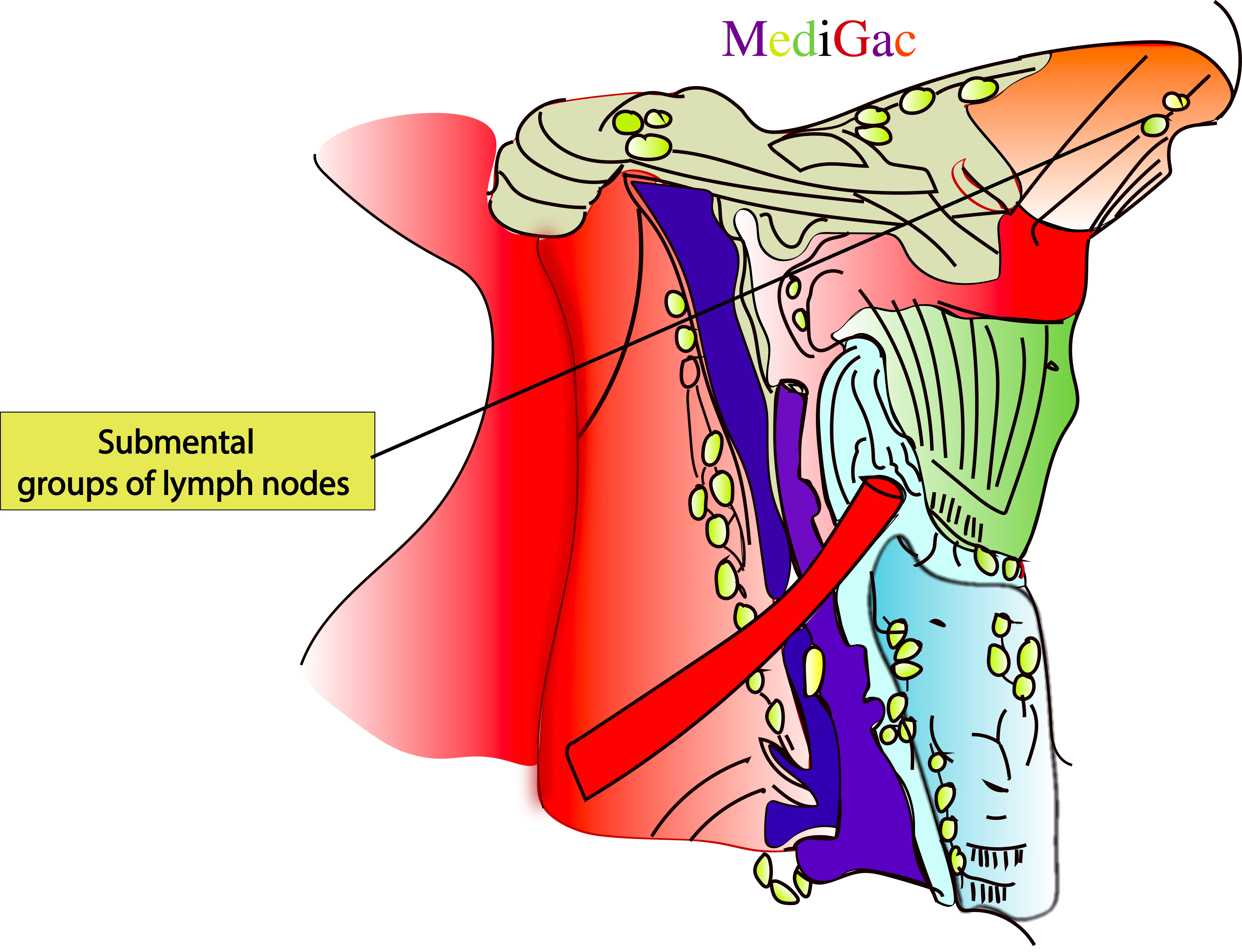
I. Location/Position/Relations of Submental lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Present above the lower lateral surface of Mandible bone.
- Muscle relations – Above the insertion of Platysma muscle, and above the origin of depressor anguli iris.
- Vascular relations – Along the submental branch of facial vein.
II. Drainage of Submental lymph nodes :
- The neck is where the lymph from the right side of the face and scalp enters the submental nodes.
- The lymph then empties into the deep cervical lymph nodes, which are found along the internal jugular vein’s path.
III. Pathologies of Submental lymph nodes :
- Any kind of dental infections(e.g., periodontitis)
- Viral infections (mononucleosis, Epstein-Barr virus infection, and cytomegalo virus infections)
- Toxoplasmosis
2. Submandibular/Submaxillary nodes :
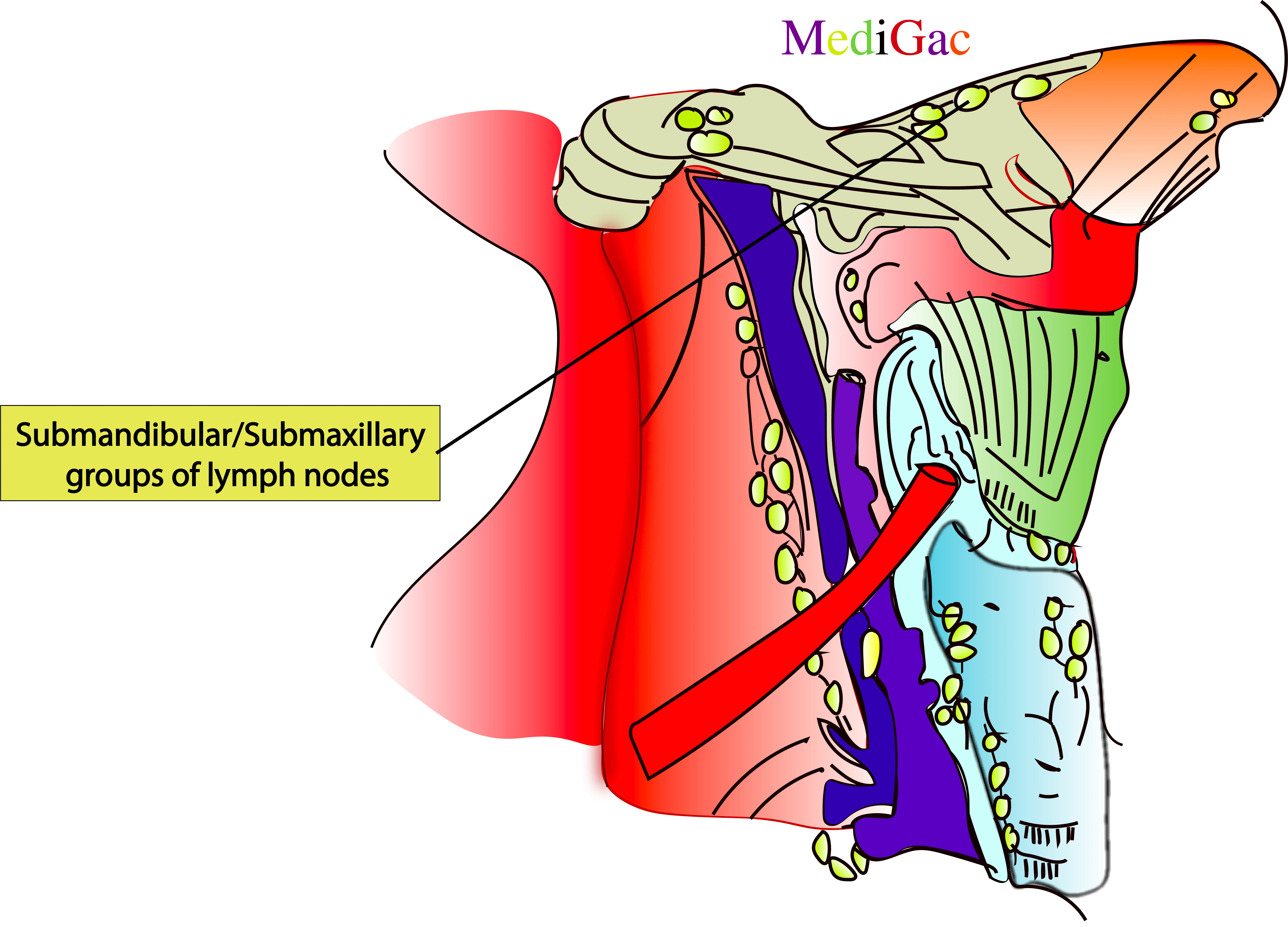
I. Location/Position/Relations of Supmandibular/Submaxillary lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Chain of lymph nodes starting from Mental protuberance of Mandible and ending to mandible condyle
- Muscle relations – Insertion of platysma muscle
- Vascular relations – Marginal mandibular branch of Facial nerve
II. Drainage of Supmandibular/Submaxillary lymph nodes :
- The neck is where the lymph from the right side of the face and scalp enters the submandibular nodes.
- Along the path of the right internal jugular vein, the lymph then empties into the right deep cervical lymph nodes.
III. Pathologies of Supmandibular/Submaxillary lymph nodes :
- Neoplasia
- Liver disease due to non-alcoholic cirrhosis
- Infections due to Mumps virus, Staphylococcal bacteria
- Inflammation of the salivary gland excretory duct
B. Anterior cervical groups of lymph nodes :
1. Prelaryngeal nodes :
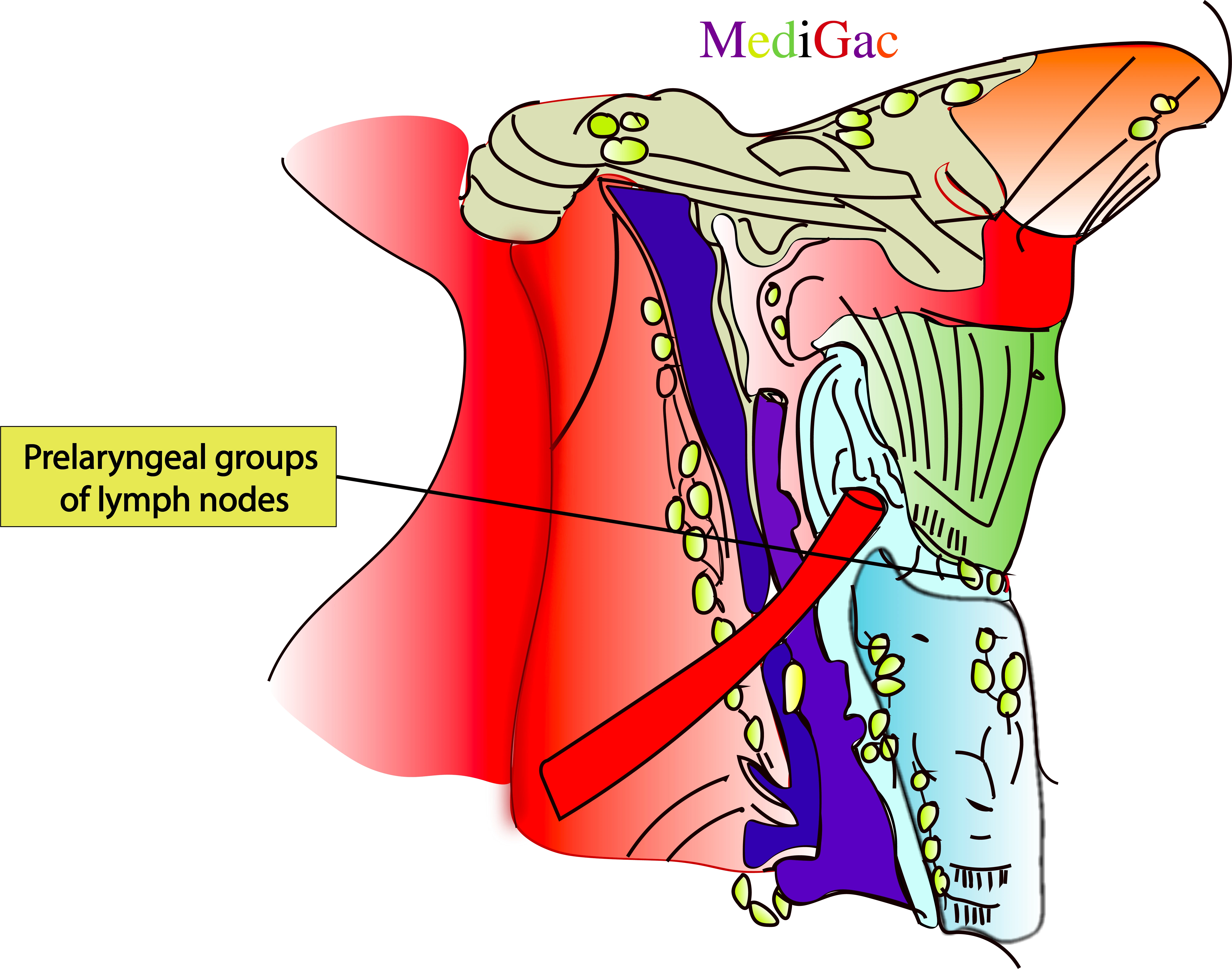
I. Location/Position/Relations of Prelaryngeal lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – The lymph nodes anterior to the larynx are called prelaryngeal lymph nodes.
- Muscle relations – Sternohyoid muscle
- Vascular relations – Anterior jugular vein
II. Drainage of Prelaryngeal lymph nodes :
- The neck is where the lymph from the right side of the face and scalp enters the Prelaryngeal nodes.
- Along the path of the right internal jugular vein, the lymph then empties into the right deep cervical lymph nodes.
III. Pathologies of Prelaryngeal lymph nodes :
- Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Laryngeal cancer
- Thyroid carcinoma
- Infection of Larynx
2. Thyroid nodes :
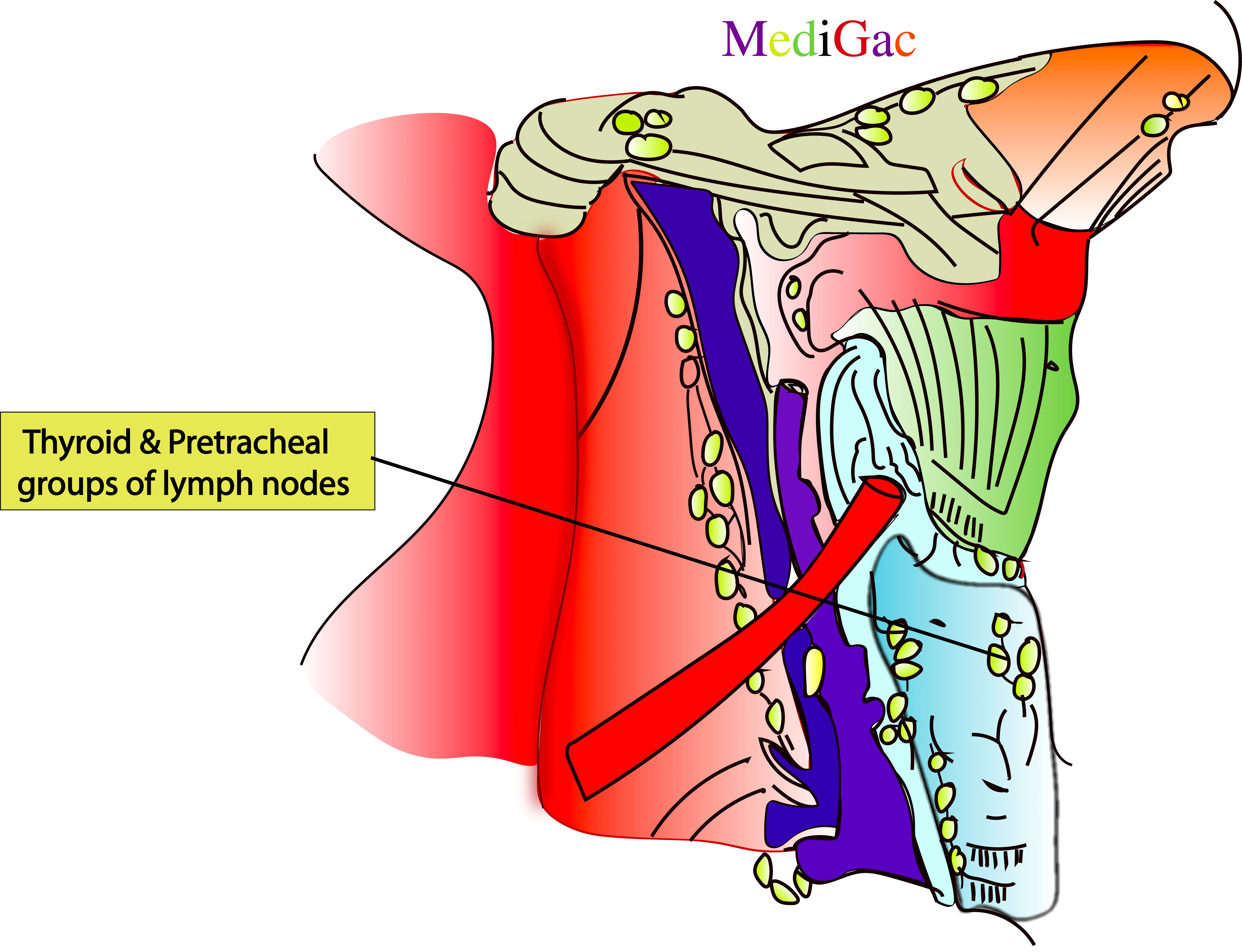
I. Location/Position/Relations of Thyroid lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Above the thyroid cartilage
- Muscle relations – Sternohyoid muscle
- Vascular relations – Anterior jugular lymph vessel and anterior jugular vein
II. Drainage of Thyroid lymph nodes :
- The neck is where the lymph from the right side of the face and scalp enters the Thyroid nodes.
- Along the path of the right internal jugular vein, the lymph then empties into the right deep cervical lymph nodes.
- Lymph veins found in the superficial tissues of the neck empty into the right external jugular vein and superficial cervical lymph nodes.
- The lymphatic trunk of the right jugular empties into the right lymphatic duct or the right venous angle, which is the point where the internal jugular and subclavian veins meet.
III. Pathologies of Thyroid lymph nodes :
- Thyroid carcinoma
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- Inflammation of thyroid gland
3. Pretracheal nodes :

I. Location/Position/Relations of Pretracheal lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Above thyroid cartilage
- Muscle relations – Sternohyoid muscle
- Vascular relations – Anterior jugular lymph vessels and anterior jugular vein
II. Drainage of Pretracheal lymph nodes :
- The neck is where the lymph from the right side of the face and scalp enters the Pretracheal nodes.
- Along the path of the right internal jugular vein, the lymph then empties into the right deep cervical lymph nodes.
- Lymph veins found in the superficial tissues of the neck empty into the right external jugular vein and superficial cervical lymph nodes.
- The lymphatic trunk of the right jugular empties into the right lymphatic duct or the right venous angle, which is the point where the internal jugular and subclavian veins meet.
III. Pathologies of Pretracheal lymph nodes :
- Tuberculosis
- Chronic lung diseases like emphysema
4. Para-tracheal nodes :
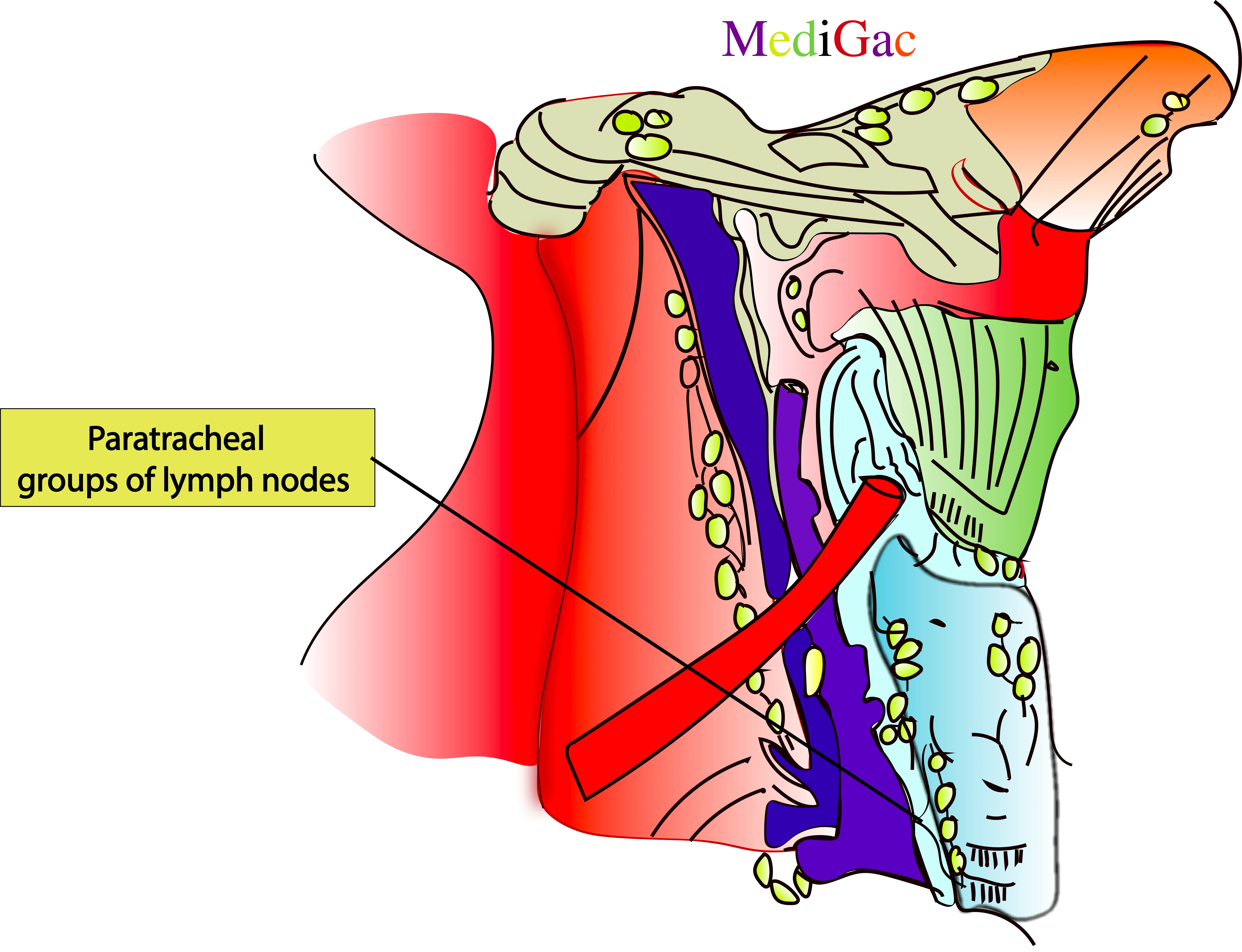
I. Location/Position/Relations of Para tracheal lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Parallel to thyroid cartilage
- Muscle relations – Sternohyoid muscle
- Vascular relations – Anterior jugular lymph vessels and anterior jugular vein
II. Drainage of Para tracheal lymph nodes :
- The neck is where the lymph from the right side of the face and scalp enters the Paratracheal nodes.
- Along the path of the right internal jugular vein, the lymph then empties into the right deep cervical lymph nodes.
- Lymph veins found in the superficial tissues of the neck empty into the right external jugular vein and superficial cervical lymph nodes.
- The lymphatic trunk of the right jugular empties into the right lymphatic duct or the right venous angle, which is the point where the internal jugular and subclavian veins meet.
III. Pathologies of Para tracheal lymph nodes :
- Smoking
- Cancer of head and neck
C. Deep cervical groups of lymph nodes :
1. Lateral Jugular nodes :
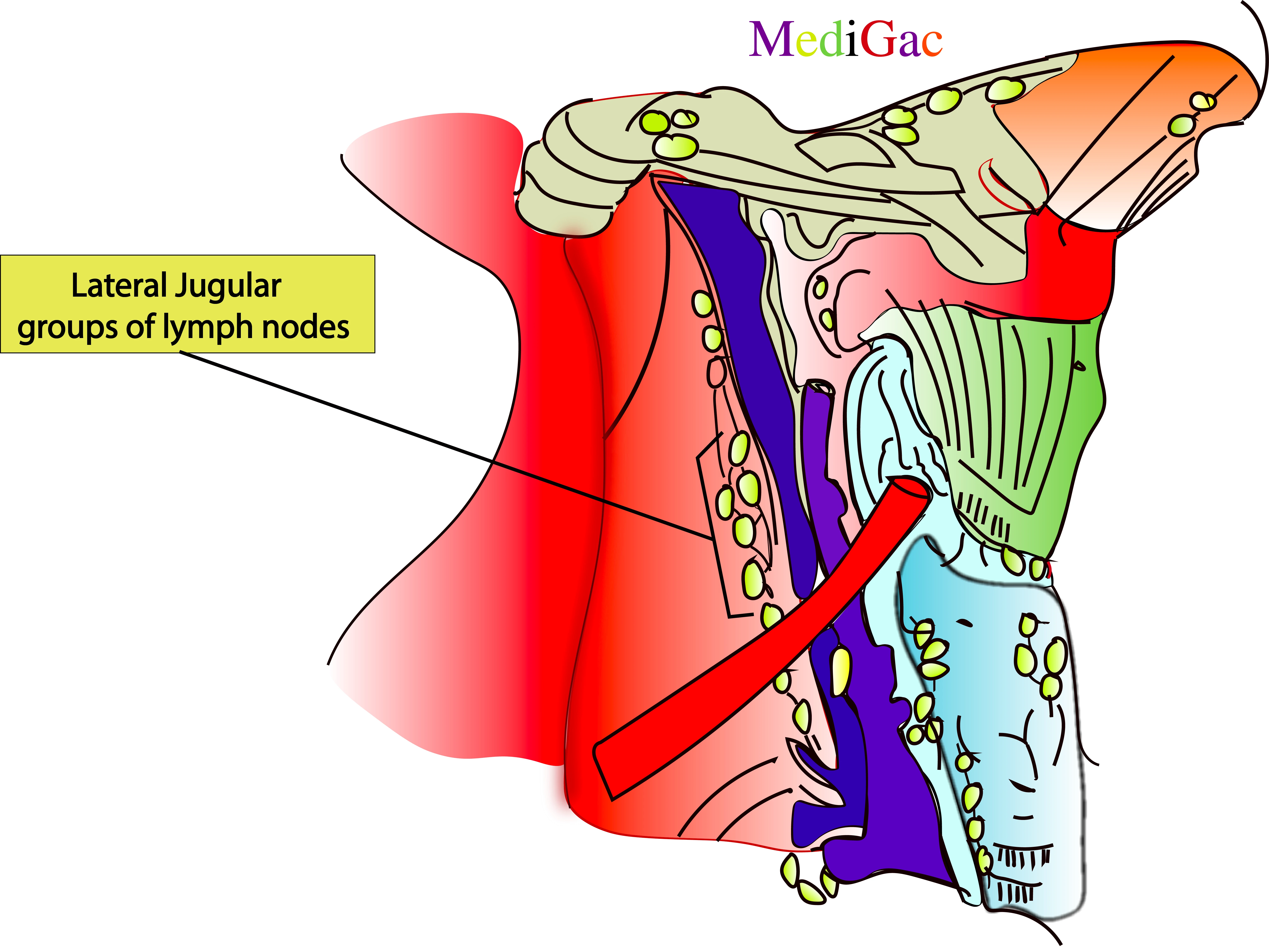
I. Location/Position/Relations of Lateral jugular lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Lateral to C1-C7 vertebra
- Muscle relations – Below Platysma and sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Vascular relations – Internal jugular vein
II. Drainage of Lateral jugular lymph nodes :
- The neck is where the lymph from the right side of the face and scalp enters the parotid, occipital, mastoid, submandibular, and submental, tracheal, laryngealnodes.
- Along the path of the right internal jugular vein, the lymph then empties into the right deep cervical lymph nodes.
- Lymph veins found in the superficial tissues of the neck empty into the right external jugular vein and superficial cervical lymph nodes.
- The lymphatic trunk of the right jugular empties into the right lymphatic duct or the right venous angle, which is the point where the internal jugular and subclavian veins meet.
III. Pathologies of Lateral jugular lymph nodes :
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Cancer of head and neck
- Severe throat infection
2. Anterior Jugular nodes :
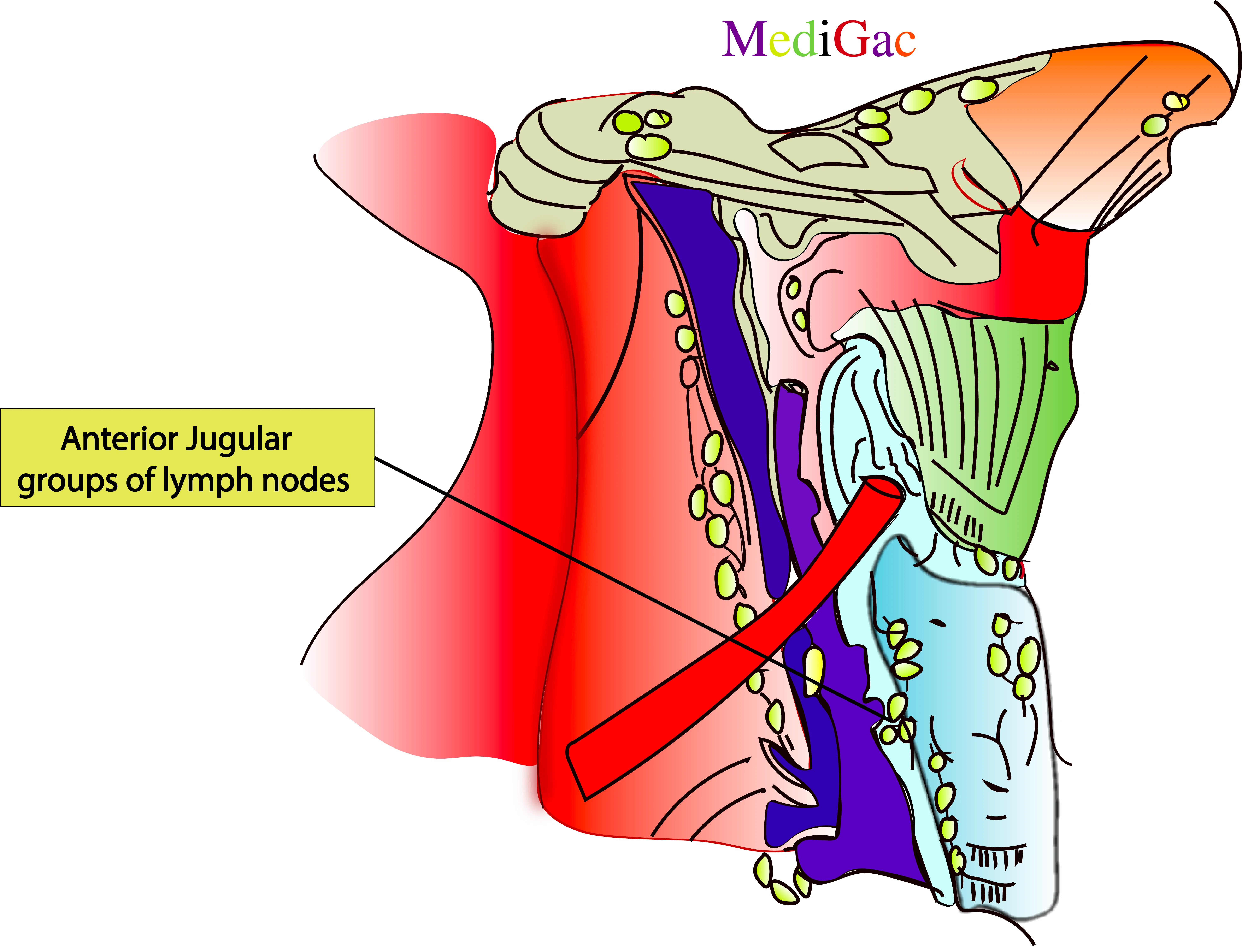
I. Location/Position/Relations of Anterior jugular lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – 5-6cm above and lateral to the Manubrium
- Muscle relations – Above Sternohyoid muscle
- Vascular relations – Anterior jugular vein
II. Drainage of Anterior jugular lymph nodes :
- The neck is where the lymph from the right side of the face and scalp enters the parotid, occipital, mastoid, submandibular, and submittal, tracheal, laryngeal nodes.
- Along the path of the right internal jugular vein, the lymph then empties into the right deep cervical lymph nodes.
- Lymph veins found in the superficial tissues of the neck empty into the right external jugular vein and superficial cervical lymph nodes.
- The lymphatic trunk of the right jugular empties into the right lymphatic duct or the right venous angle, which is the point where the internal jugular and subclavian veins meet.
III. Pathologies of Anterior jugular lymph nodes :
- Head and neck cancer
- Pharyngitis
- Tuberculosis
- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Infectious mononucleosis
D. Inferior deep cervical groups of lymph nodes :
1. Jugulo-omohyoid nodes :
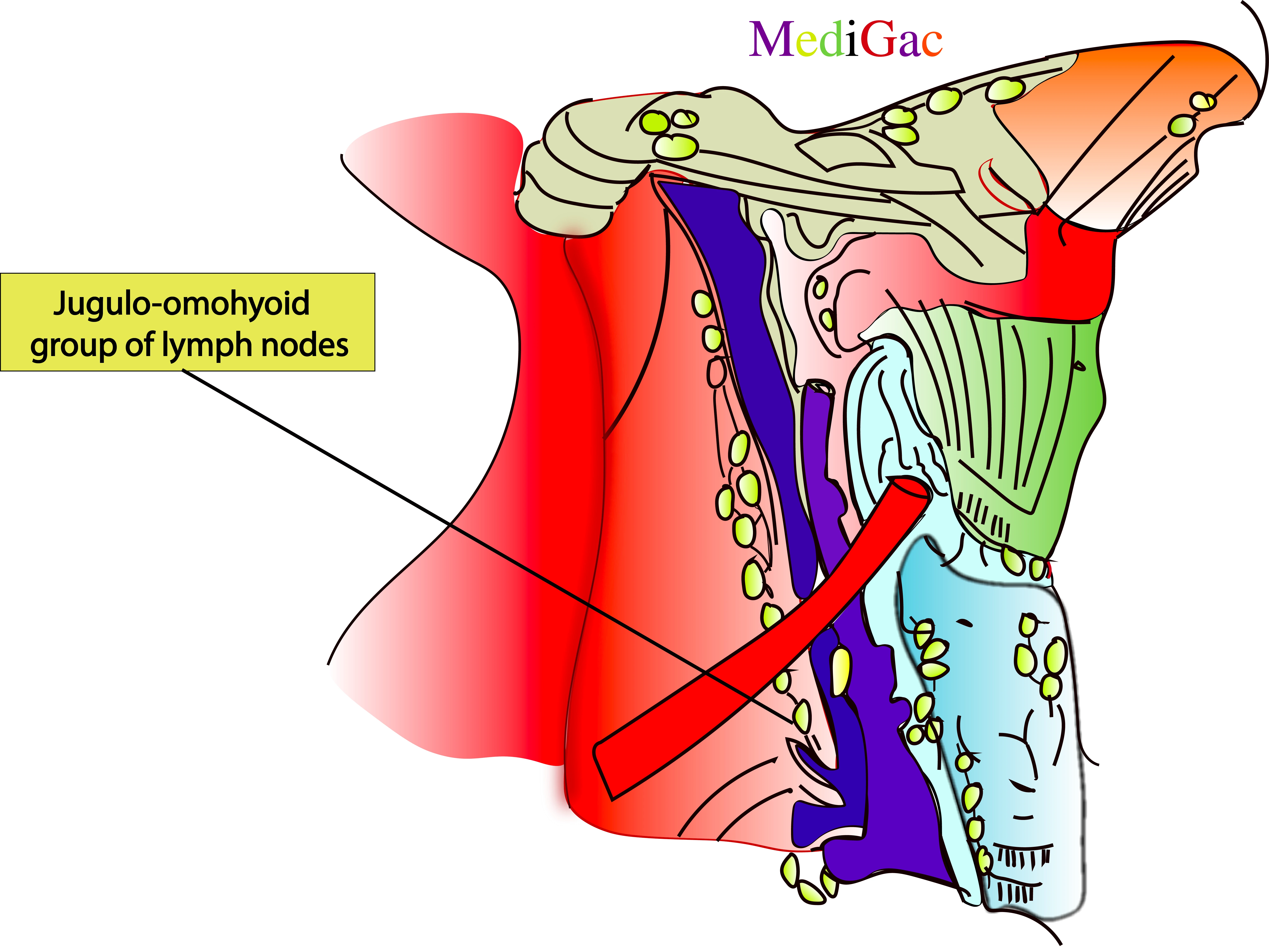
I. Location/Position/Relations of Jugulo-omohyoid lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – 3-4 cm above to the medial end of the clavicle
- Muscle relations – Back of sternohyoid
- Vascular relations – Start of the Internal jugular vein from Brachiocephalic vein
II. Drainage of Jugulo-omohyoid lymph nodes :
- The neck is where the lymph from the right side of the face and scalp enters the parotid, occipital, mastoid, submandibular, and submental nodes.
- Along the path of the right internal jugular vein, the lymph then empties into the right deep cervical lymph nodes.
- Lymph veins found in the superficial tissues of the neck empty into the right external jugular vein and superficial cervical lymph nodes.
- The lymphatic trunk of the right jugular empties into the right lymphatic duct or the right venous angle, which is the point where the internal jugular and subclavian veins meet.
III. Pathologies of Jugulo-omohyoid lymph nodes :
- Tongue carcinoma
- Any Viral or bacterial infection
- Autoimmune disease
2. Jugulo-digastric nodes :
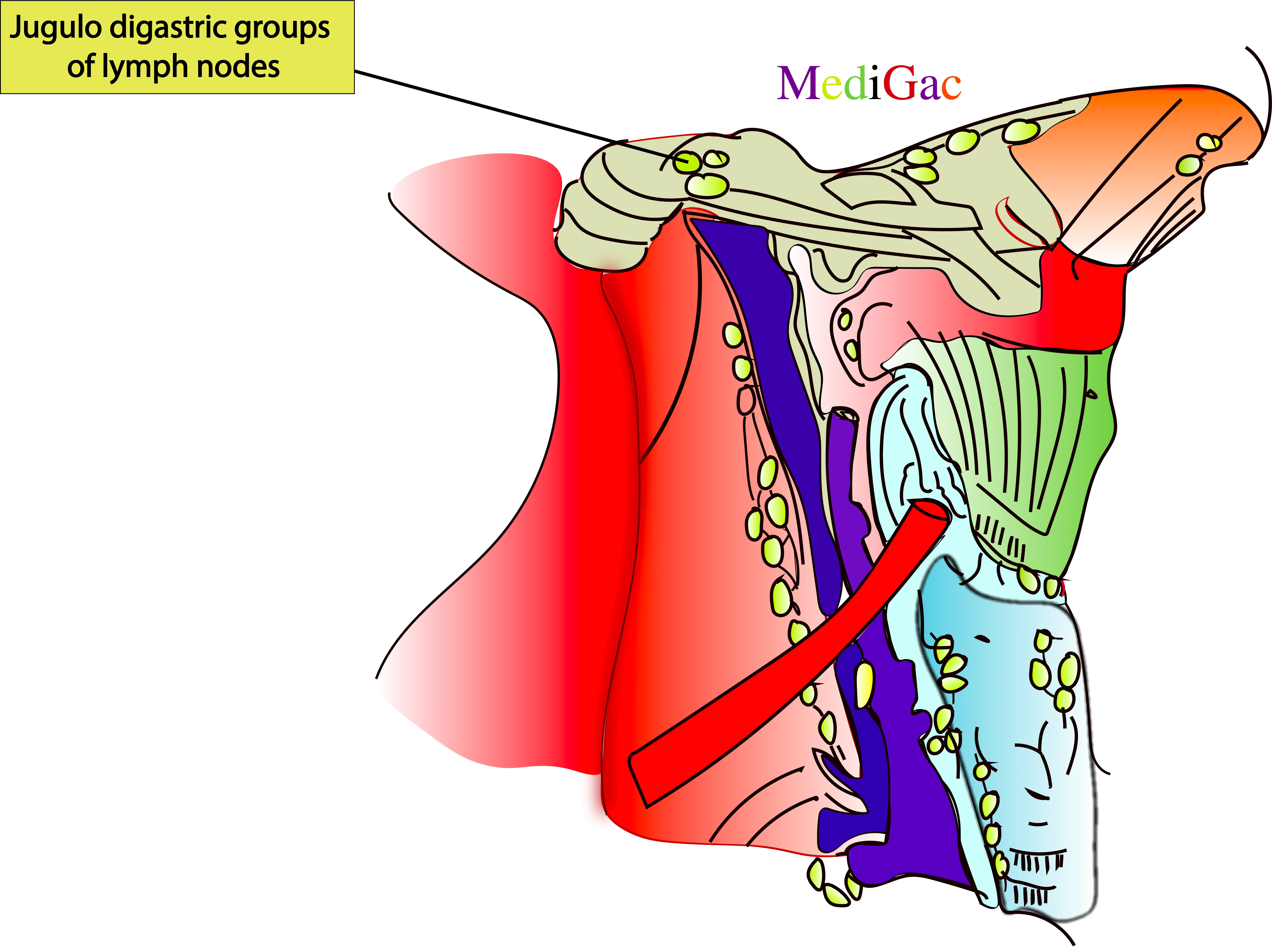
I. Location/Position/Relations of Jugulo digastric lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – lateral to C6 vertebra
- Muscle relations – at upper 1/3rd of Sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Vascular relations – Between upper end of External jugular and internal jugular vein
II. Drainage of Jugulo digastric lymph nodes :
- The neck is where the lymph from the right side of the face and scalp enters the parotid, occipital, mastoid, submandibular, and submittal nodes.
- Along the path of the right internal jugular vein, the lymph then empties into the right deep cervical lymph nodes.
- Lymph veins found in the superficial tissues of the neck empty into the right external jugular vein and superficial cervical lymph nodes.
- The lymphatic trunk of the right jugular empties into the right lymphatic duct or the right venous angle, which is the point where the internal jugular and subclavian veins meet.
III. Pathologies of Jugulo digastric lymph nodes :
- Dental caries
- Tuberculosis
- Pharyngitis
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
E. Supraclavicualr groups of lymph nodes(Virchow’s node) :
1. Supraclavicular nodes :
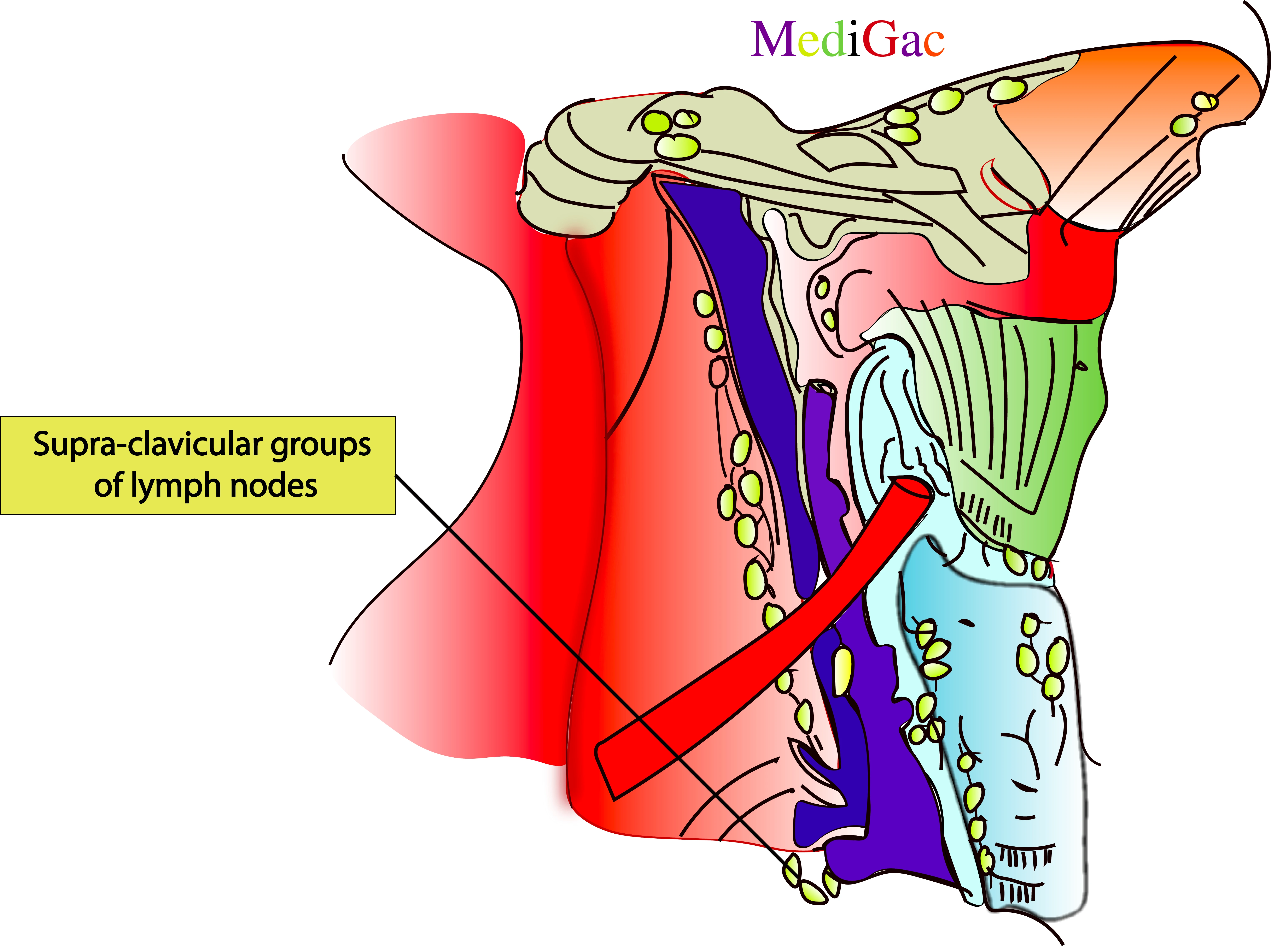
I. Location/Position/Relations of Supraclavicular lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Above the medial 1/3rd of clavicle
- Muscle relations – Under the lower end of Platysma and Sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Vascular relations – Between Subclavian artery and vein
II. Drainage of Supraclavicular lymph nodes :
- The neck is where the lymph from the right side of the face and scalp enters the parotid, occipital, mastoid, submandibular, and submental nodes.
- Along the path of the right internal jugular vein, the lymph then empties into the right deep cervical lymph nodes.
- Lymph veins found in the superficial tissues of the neck empty into the right external jugular vein and superficial cervical lymph nodes.
- The lymphatic trunk of the right jugular empties into the right lymphatic duct or the right venous angle, which is the point where the internal jugular and subclavian veins meet.
III. Pathologies of Supraclavicular lymph nodes :
- Lung infections
- Lung carcinoma
- Gastric carcinoma
- Tuberculosis
- Breast cancer