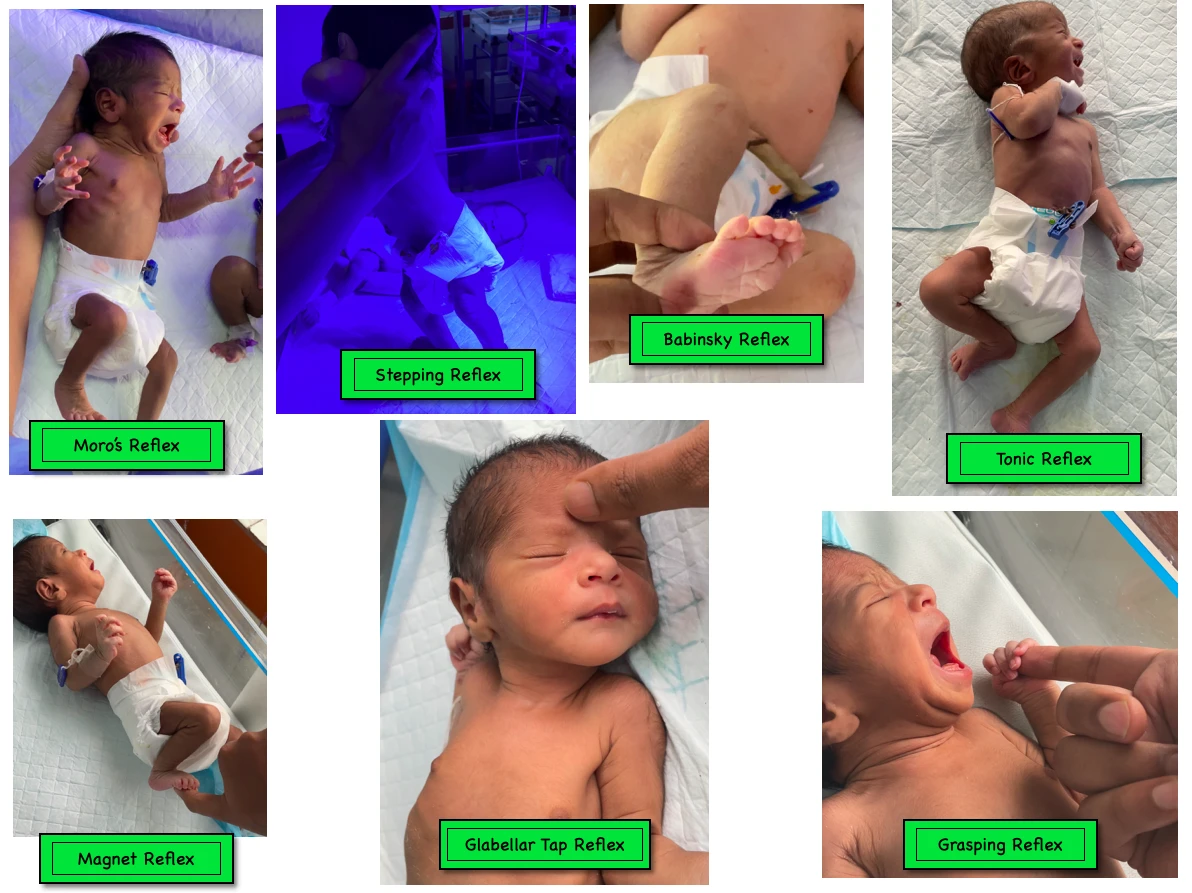
All the types of new born reflexes are discussed here. There are mainly 13 reflexes shown by a new born baby, and they are described below.
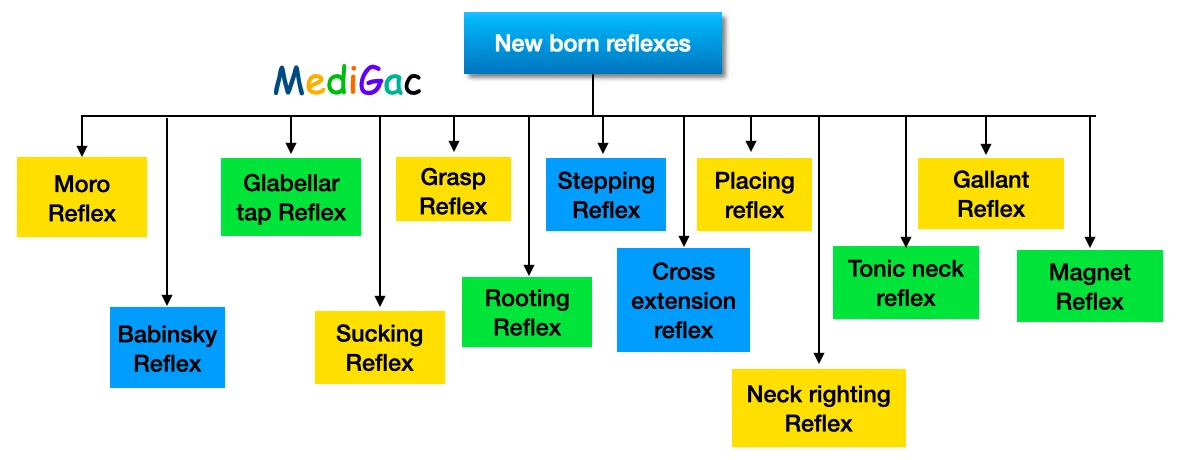
1. Moro reflex, 2. Babinsky reflex, 3. Glabellar tap reflex, 4. Sucking reflex, 5. Grasp reflex, 6. Rooting reflex, 7. Stepping reflex, 8. Cross extension reflex, 9. Placing reflex, 10. Neck righting reflex, 11. Tonic neck reflex, 12. Gallant reflex, 13. Magnet reflex.
1. Moro Reflex :
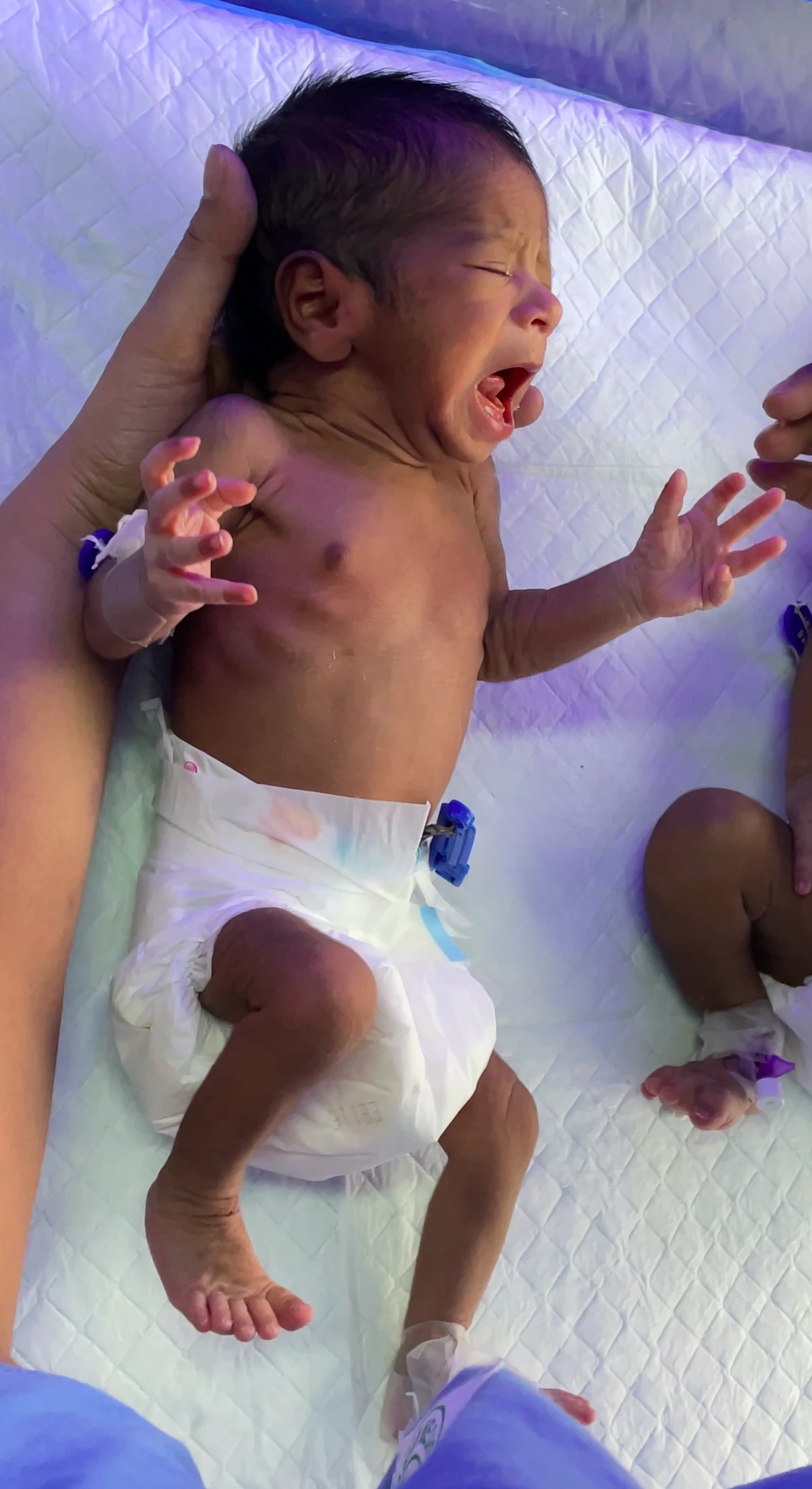
- This reflex is normally present in all newborns. The Moro reflex, also known as the startle reflex, is an involuntary motor reaction that develops in newborns shortly after birth.
- The infant may splay their arms and move their legs before putting their arms in front of their body in a Moro reflex.
2. Babinksy Reflex :
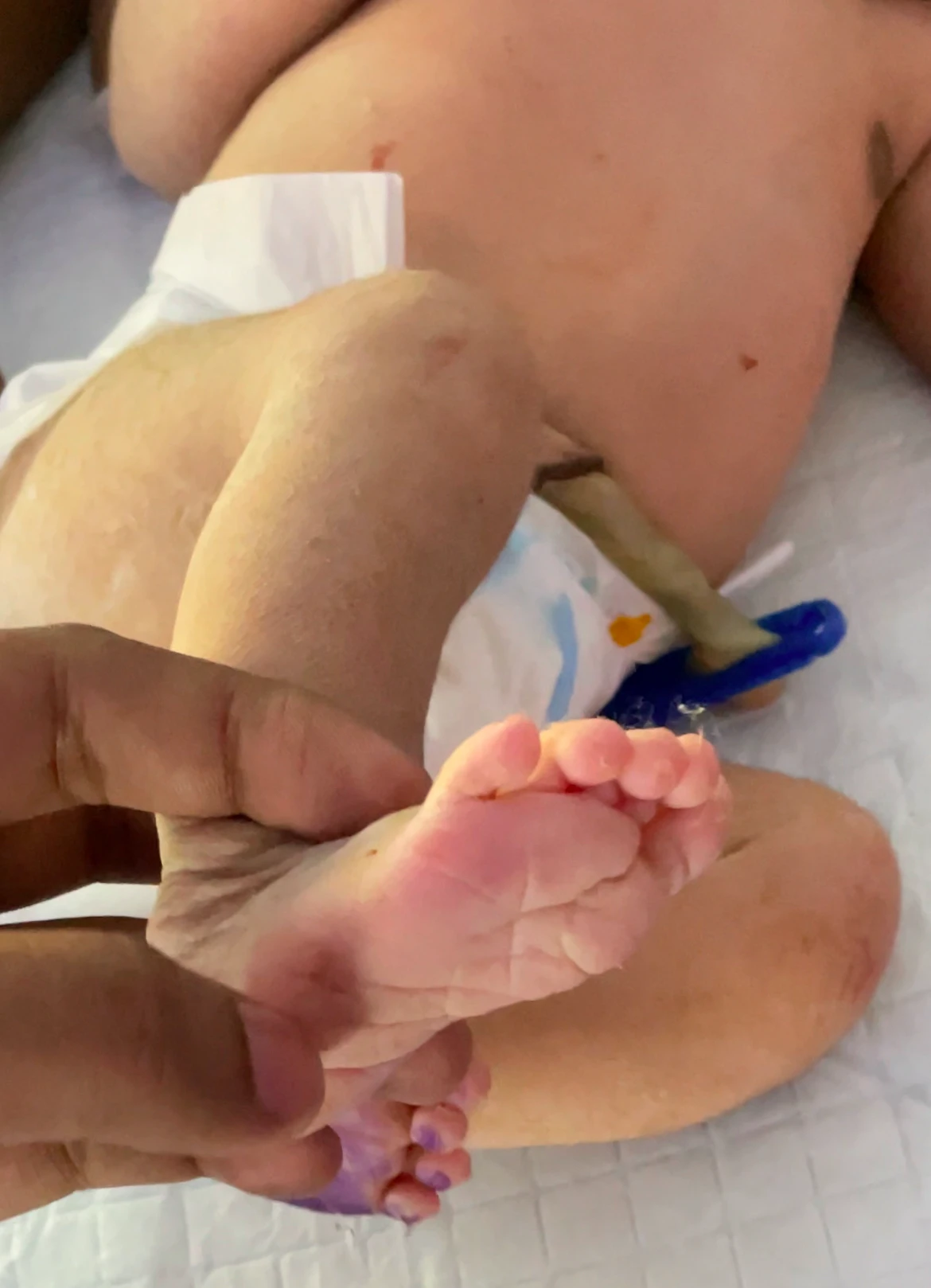
- The big toe dorsiflexes (bends back) and the other toes fan or spread out when the bottom of the foot is stroked from the hell upward along the external part of the foot.
- Around the age of one year, it vanishes.
3. Glabellar tap Reflex :
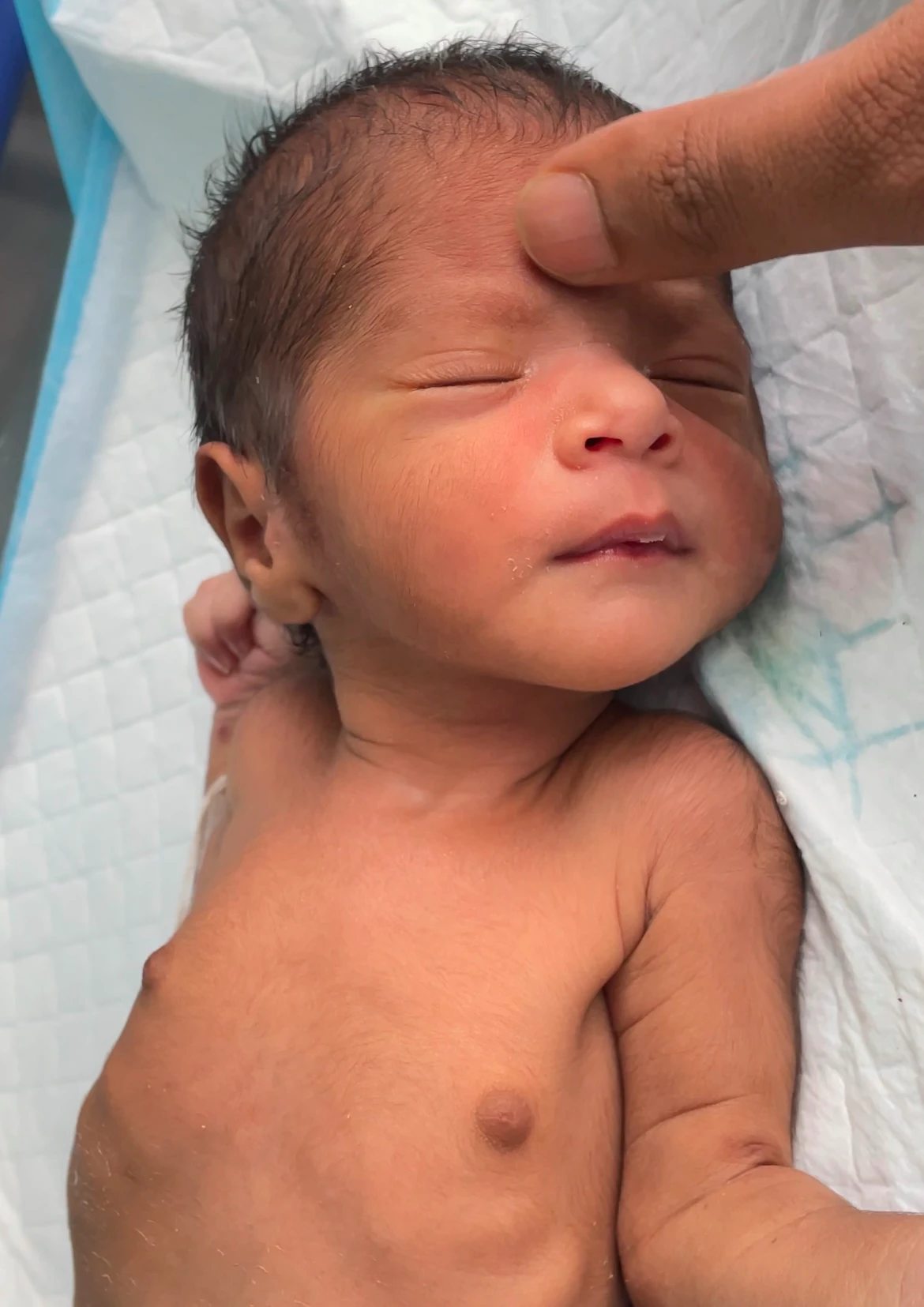
- Tapping on the supraorbital ridge’s outer edge, the glabella, or the orbital boundary.
- tapping across the brow to the hairline
- Bilateral eye blinking may occur as a result of this.
4. Sucking Reflex :

- When anything comes into contact with the top of the infant’s mouth, the infant will start sucking.
- This used to go away around the age of four months.
5. Grasp Reflex :

- When you place a finger on the inside of the infant’s palm or stroke it, the hand closes around it.
- At around 4-6 months of age, this goes away.
6. Rooting Reflex :
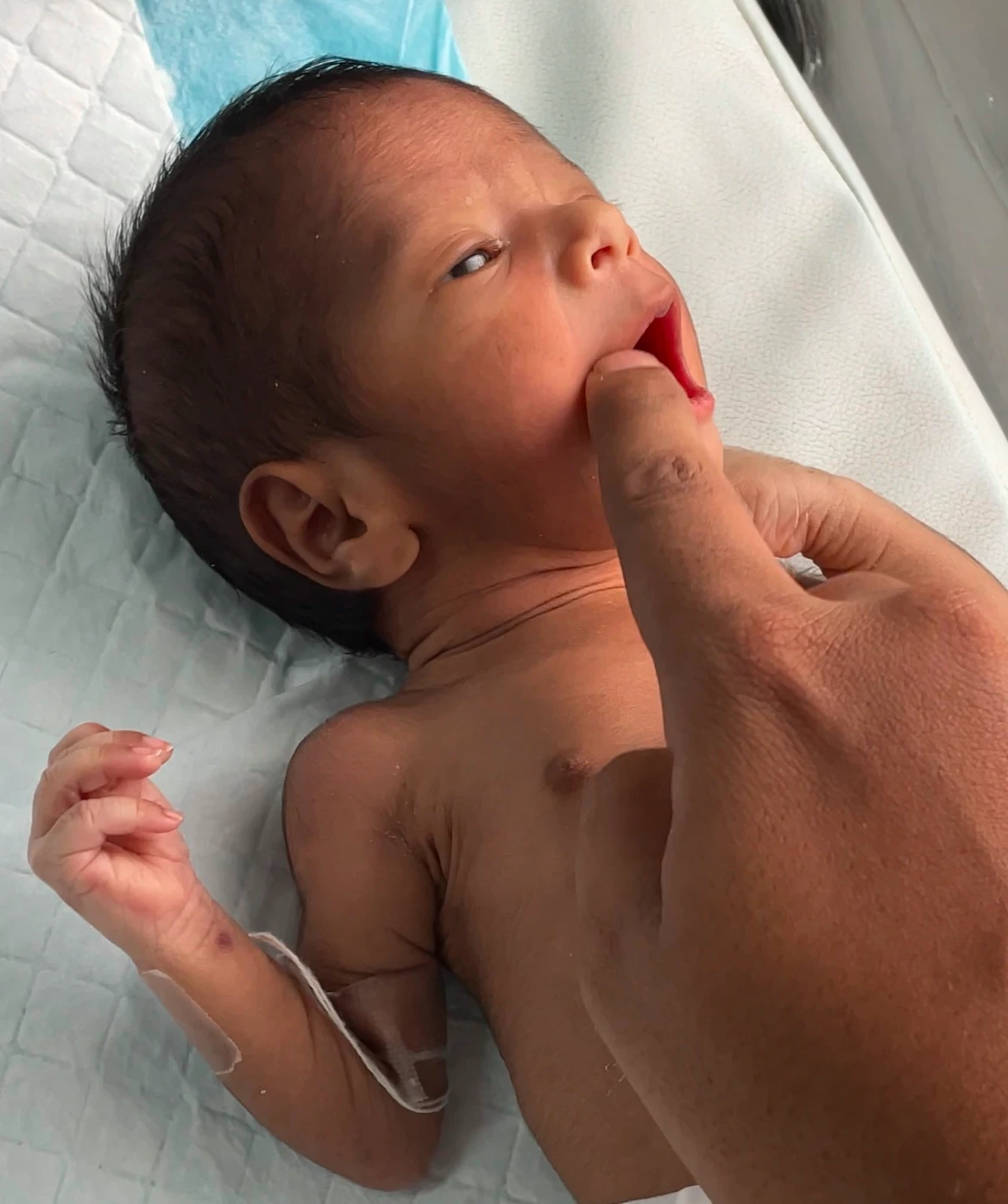
- The head will turn towards the stroked cheek or side of the mouth, and the infant’s mouth will open in an attempt to suck. When feeding, this aids the baby in locating the food source.
- At around 4 months of age, this vanishes.
7. Stepping Reflex :
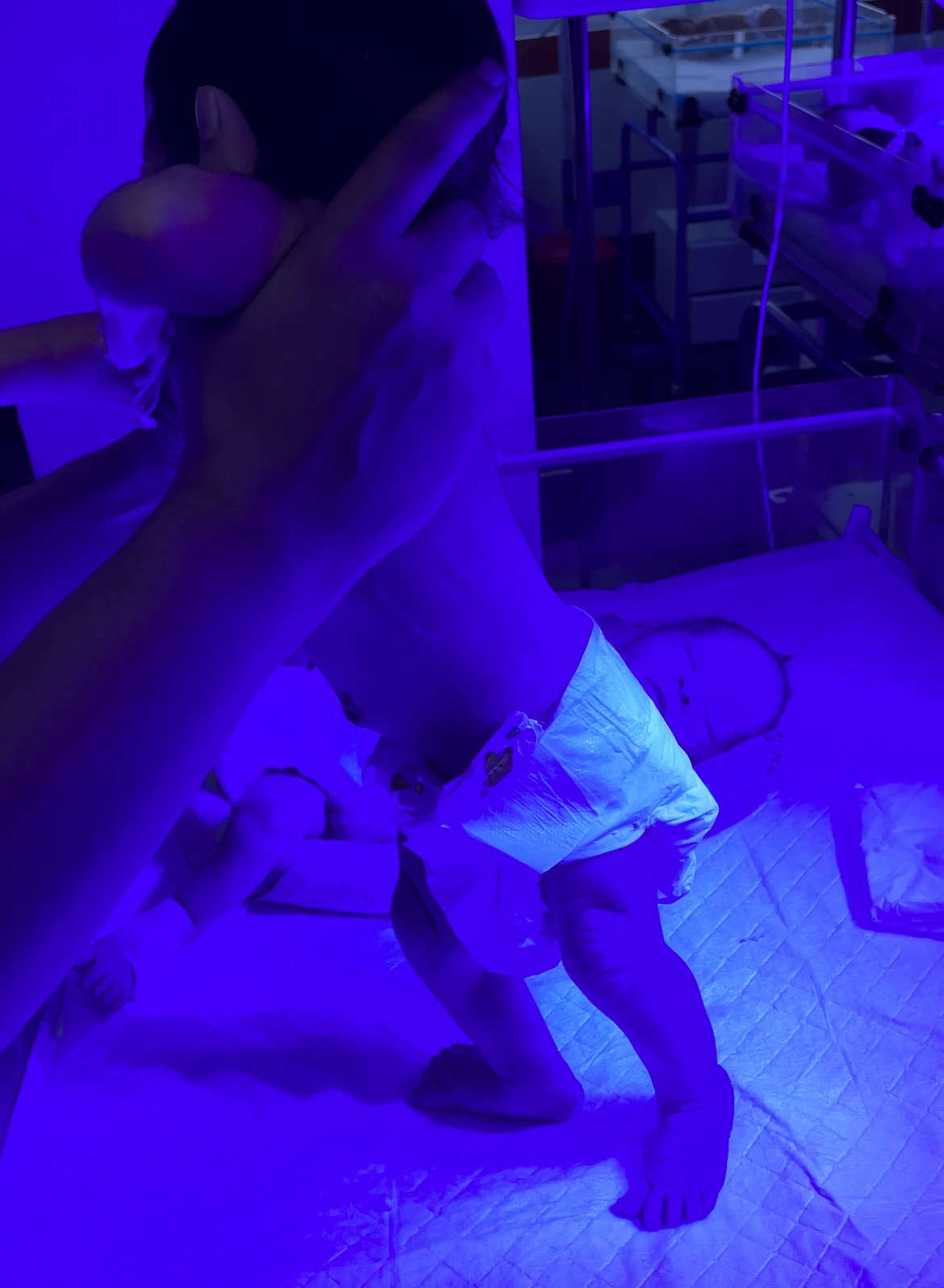
- When the child is held upright with his or her legs and feet touching a surface, the infant will move his or her leg as if walking or taking steps.
- At around 3-4 months of age, this vanishes.
8. Cross extension Reflex :
- The baby is placed in a supine position with one leg outstretched. It is pressed or tickled on the sole of the foot.
- The contralateral leg is flexed, adducted, and then stretched in response.
9. Placing Reflex :
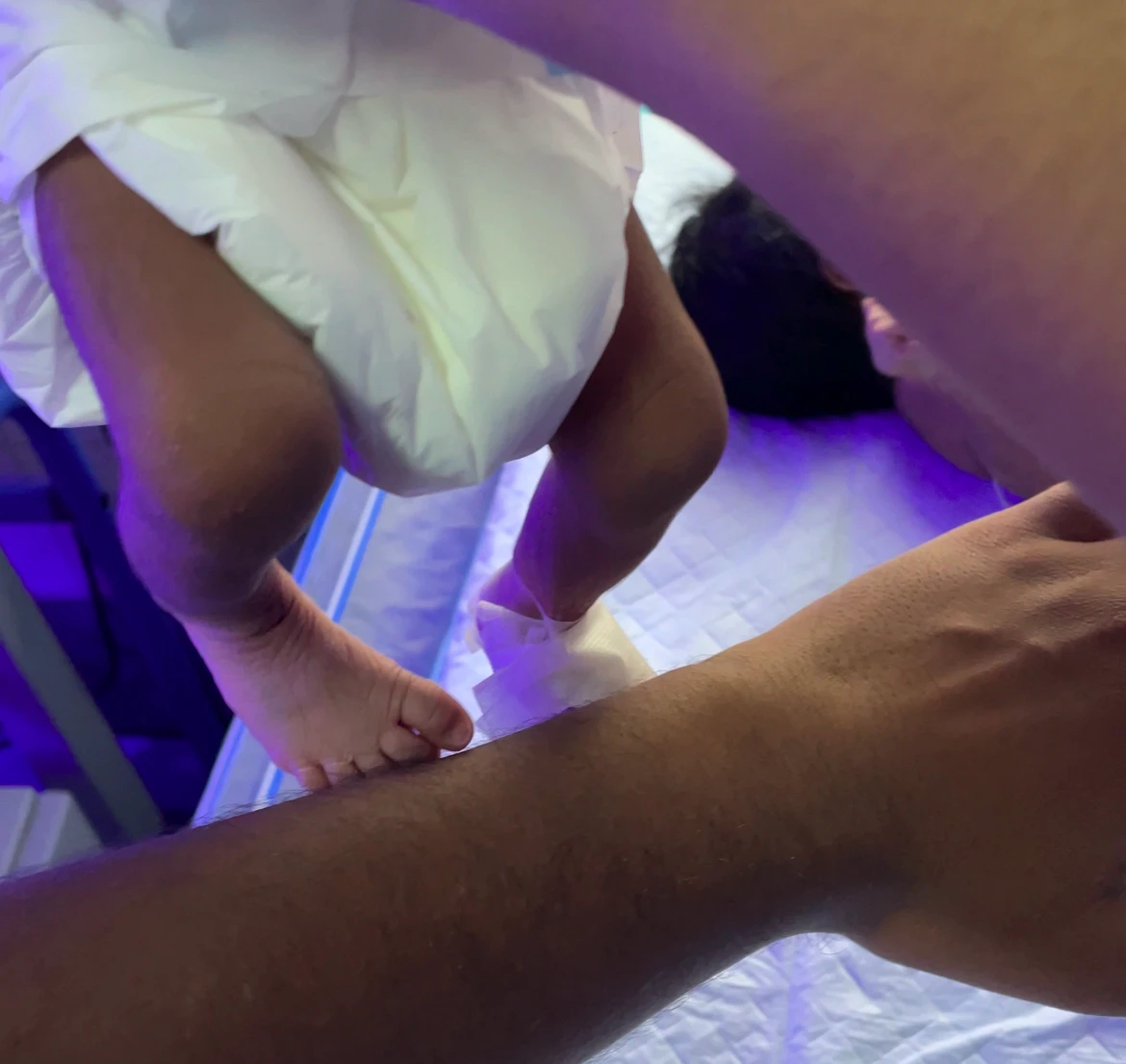
- At the underside of an table, rubbing the dorsum of the foot or the anterior portion of the leg.
- As a result, the leg is lifted and the foot is placed on the tabletop.
- This first emerges at 34 weeks of pregnancy and vanishes at 6 weeks.
10. Neck righting Reflex :
- This begins at the 34-week mark of pregnancy.
- The head is righted as a result of the labyrinthine righting reflex and the body on head righting reflex, but the body remains in a lateral position. This causes the neck to twist, which triggers the neck righting reflex.
- Brings the thoracic and lumbar area into an upright position in that order.
11. Tonic neck Reflex :
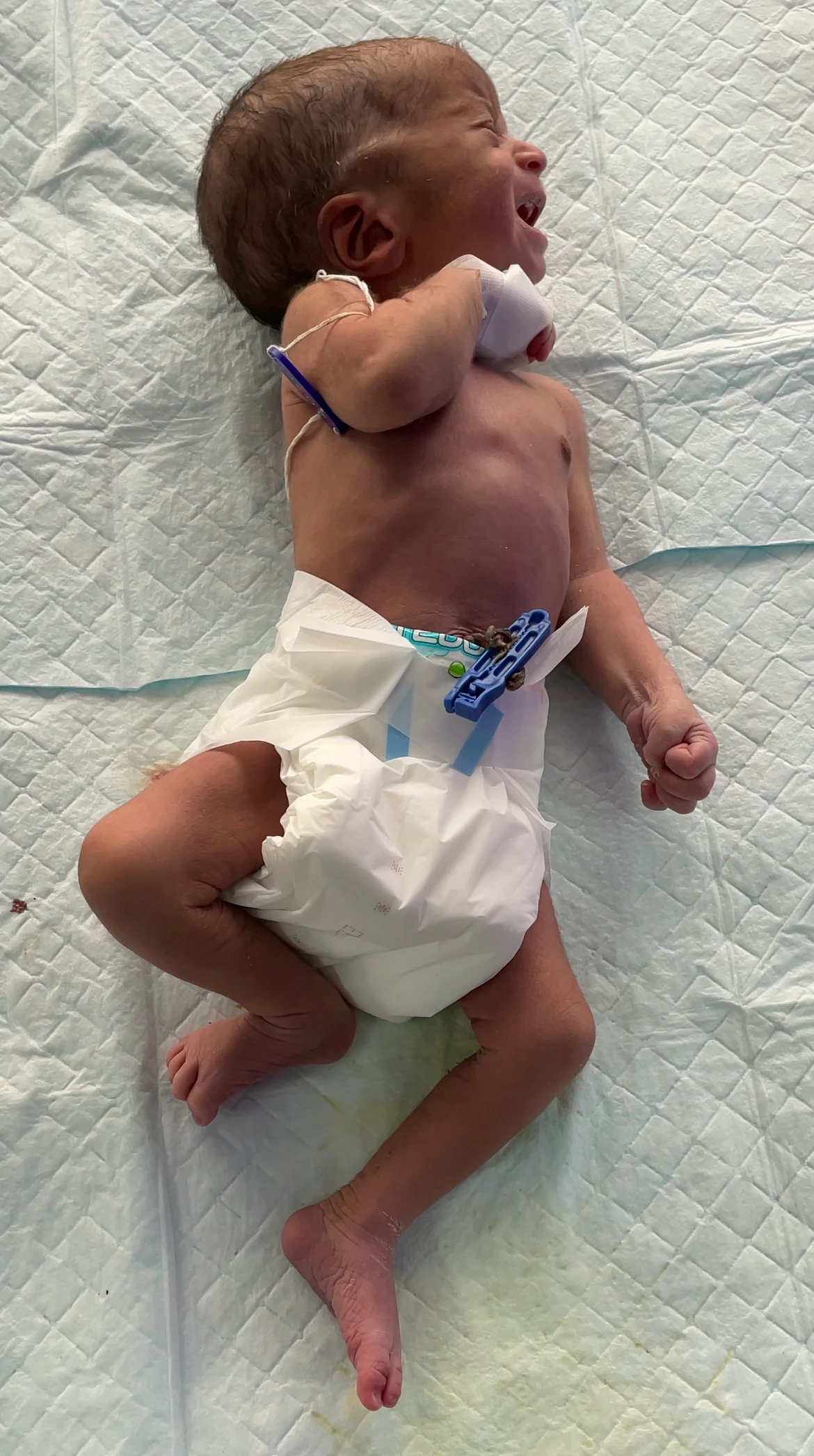
When the infant’s head is turned to one side, that side’s leg and arm will stretch, while the opposing side’s leg and arm will flex.
This normally goes away at the age of four months.
12. Gallant Reflex :
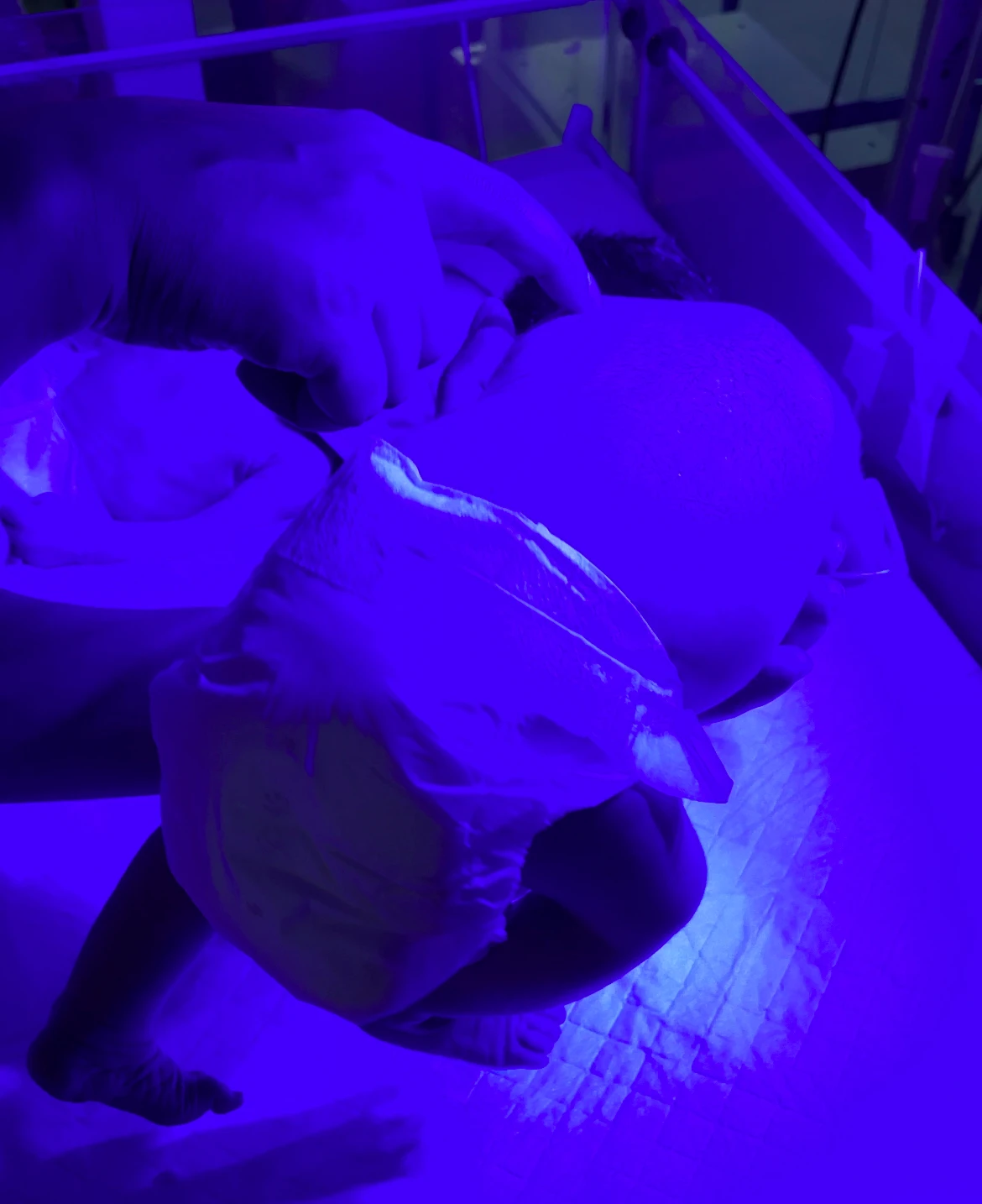

- Running a finger down the paravertebral area on one side while holding the youngster in ventral suspension or in a prone posture.
- The pelvis swings towards the stimulated side in response.
13. Magnet Reflex :
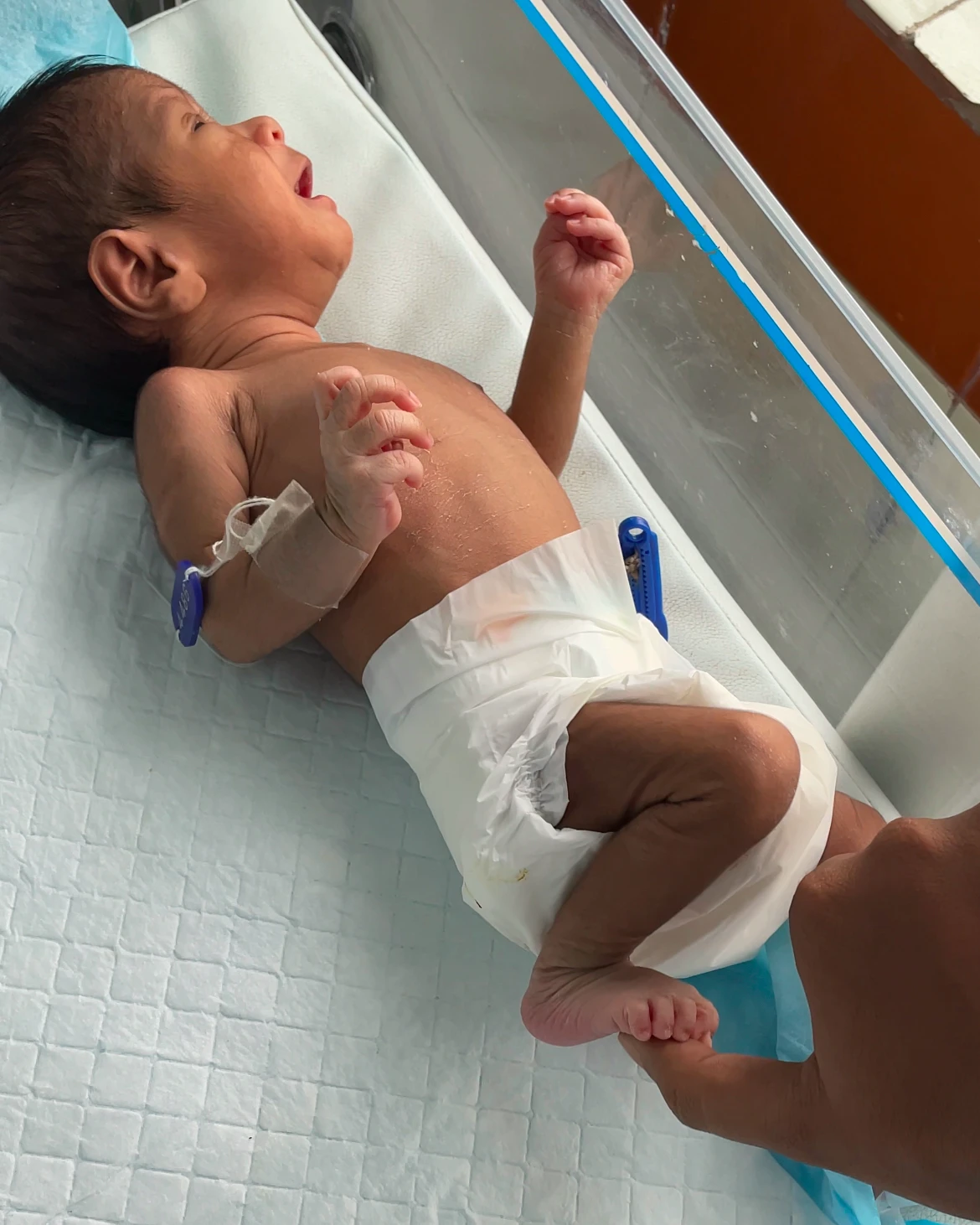
- When pressure is given to the soles of a newborn’s feet while he or she is laying in a supine posture, he or she pushes back, and if the object is progressively released from the sole, it follows the path like a magnet.