All the neurological superficial and deep tendon reflexes/jerk reflexes are discussed here. Also for paediatrics age group of children.
There may be presence of two types of reflex – Superficial reflex and Deep tendon reflex
A. Superficial reflexes :
Reflexes on the surface the responses that are induced from the body’s surface are known as superficial reflexes. These reflexes are motor reactions to skin scraping.
Now mainly there are five superficial reflexes : Abdominal reflex, Anal reflex, Spinal reflex, Plantar reflex and Cremasteric reflex.
1. Abdominal reflex :
A superficial neurological reflex elicited by stroking the belly near the umbilicus is known as an abdominal reflex. It can be used to assess the severity of a central nervous system (CNS) injury. It is polysynaptic because it is a superficial reflex (involving multiple connections between nerves).
- Procedure – The examiner proceeds a gentle scratch over the skin of anterior abdominal wall without causing any injury.
- Result – Rectus abdominis muscle gets contracted.
2. Anal reflex :
The reflexive contraction of the external anal sphincter upon stroking the skin around the anus is known as the anal wink, anal reflex, perineal reflex, or anocutaneous reflex.
- Procedure – This is done by scratching the skin around the anus.
- Result – As a result contraction of the anal sphincter is seen.
3. Spinal reflex :
Spinal reflexes are investigator-evoked artefacts that result from the activation of spinal motor neurons by stretch receptors in the muscle or nociceptors in the skin, which cause contractions/twitches in certain somatic muscles.
- Procedure – This is done by scratching of skin over the sacro-spinalis muscle.
- Result – Here contraction of the sacro-spinalis muscle occurs ipsilaterally.
4. Plantar response :
The plantar reaction, also known as the Babinski response, is a vital neurologic test that involves stroking the sole (plantar surface) of the foot and seeing what the toes do. If the big toe rises, it could spell disaster.
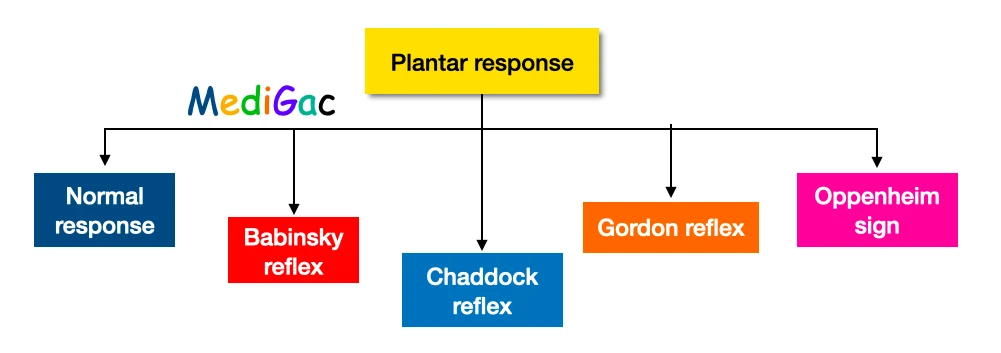
I. Normal Response :
- Procedure – In a hockey-stick motion, the examiner scratches the lateral border of the sole, reaching to the balls of the toes.
- Result – As a result greater toes plantar flexion occurs, along with flexion and adduction of other toes occurs.
II. Babinksy Reflex :
- Procedure – In a hockey-stick motion, the examiner scratches the lateral border of the sole, reaching to the balls of the toes.
- Result – Here, dorsiflexion of great toe occurs along with fanning out of other toes occurs.
III. Chaddock Reflex :
- Procedure – This is checked by providing gentle scratching the skin below the lateral malleolus.
- Result – Same response of plantar extensor occurs like Babinsky reflex.
IV. Gordon Reflex :
- Procedure – This is checked by providing pinch to the Tendo-Achilles or squeezing the caff-muscle.
- Result – Same response occurs like Babinsky reflex.
V. Oppenheim sign :
- Procedure – This is done by pressing the skin over the anterior border of the tibia.
- Result – Same response like Babinsky occurs.
5. Cremasteric reflex :
The cremasteric response is a superficial reflex produced when the inner region of the thigh is stroked in human males. The cremaster muscle contracts as the skin is stroked, pulling the ipsilateral testicle up toward the inguinal canal.
- Procedure – This is checked, by providing gentle scratch over the skin of inner aspect of the thigh in upper part.
- Result – As a result Testis gets drawn upwards along with contraction of dartos muscle.
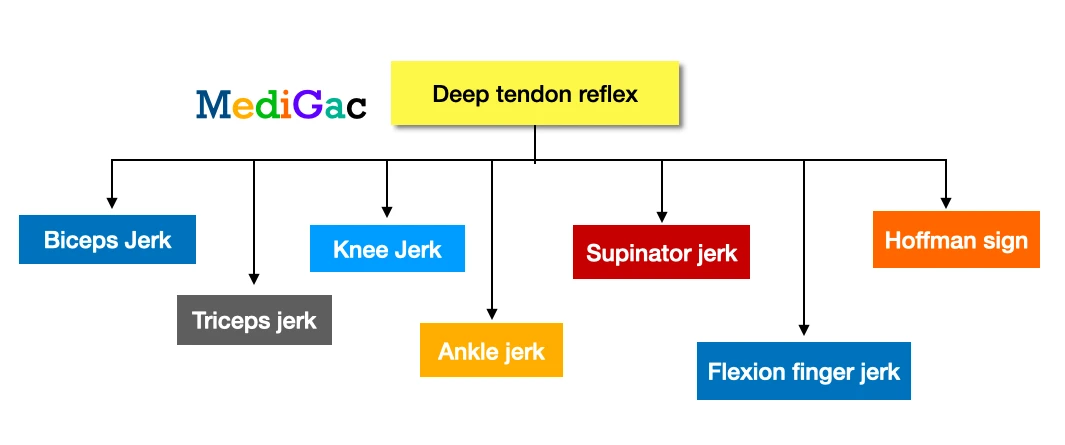
B. Deep tendon reflexes (DTR) :

Reflex action shown by providing stimulus into the deep tendons of some muscles. There are mainly seven deep tendon reflex, and they are – Biceps jerk, Triceps jerk, Knee jerk, Ankle jerk, Supinator jerk, Flexion finger jerk, Hoffman sign.
1. Biceps jerk :
The biceps reflex is a reflex test that looks at how the C5 and C6 reflex arcs work together. The test is performed by rapidly depressing the biceps brachii tendon as it passes through the cubital fossa with a tendon hammer. To produce a reflex contraction of the biceps muscle and a jerk of the forearm, the test activates stretch receptors inside the biceps brachii muscle, which interact primarily with the C5 spinal nerve and somewhat with the C6 spinal nerve.
- Procedure – The examiner used to tap the biceps tendon sharply and gently.
- Result – The biceps muscle will be contracted, and the elbow will be flexed.
2. Triceps jerk :
The triceps reflex, also known as the deep tendon reflex, is a reaction that causes the triceps brachii muscle to contract involuntarily. It is started by the 7th nerve root of the cervical (neck) spinal nerve (the small segment of the nerve that emerges from the spinal cord). The reflex is examined as part of a neurological assessment to evaluate the sensory and motor pathways in the C7 and C8 spinal nerves.
- Procedure – Over the triceps tendon, the tester will tap.
- Result – The triceps will be contracted while the elbow is extended.
3. Knee jerk :
The patellar reflex, often known as the knee-jerk, is a stretch reflex that tests the L2, L3, and L4 spinal segments.
- Procedure – The examiner will touch the quadriceps tendon with a sharp tap.
- Result – There will be a contraction of the quadriceps muscle as well as an extension movement of the knee joint.
4. Ankle jerk :
When the Achilles tendon is tapped while the foot is dorsiflexed, the ankle jerk response, also known as the Achilles reflex, occurs. It’s a stretch reflex that evaluates the function of the gastrocnemius muscle and the nerve that feeds it.
- Procedure – Tendo-Achiles of heel gets a harsh tap from the examiner.
- Result – With plantar flexion of the ankle, the calf muscle will contract.
5. Supinator jerk :
The supinator reflex is a reflex motor arc connected with the brachioradialis muscle that is tested.
- Procedure – On the brachioradialis tendon near insertion, the examiner will provide a sharp tap above the radial styloid process.
- Result – With flexion of the semipronated elbow, the brachioradialis will contract.
6. Flexion finger jerk :
Finger jerk occurs when the biceps tendon is tapped or when the brachioradial reflex is elicited. When the middle finger flipped from the palmar surface, Hoffmann’s sign was characterised as reflex bending of the thumb.
- Procedure – The examiner will tap the palmar aspect of the child’s proximal phalanges with his or her index finger.
- Result – A minor flexion movement of the fingers will occur.
7. Hoffman sign :
When the examiner flicks the middle finger’s fingernail down, the Hoffman sign causes an involuntary flexion movement of the thumb and perhaps index finger. The thumb flexes and adducts swiftly due to the reflexive route.
- Procedure – The examiner used to briskly flick down the patient’s middle finger’s terminal phalanx while grasping its middle phalanx.
- Result – Flexion of the thumb with adduction and flexion of the terminal phalanges of the other fingers.