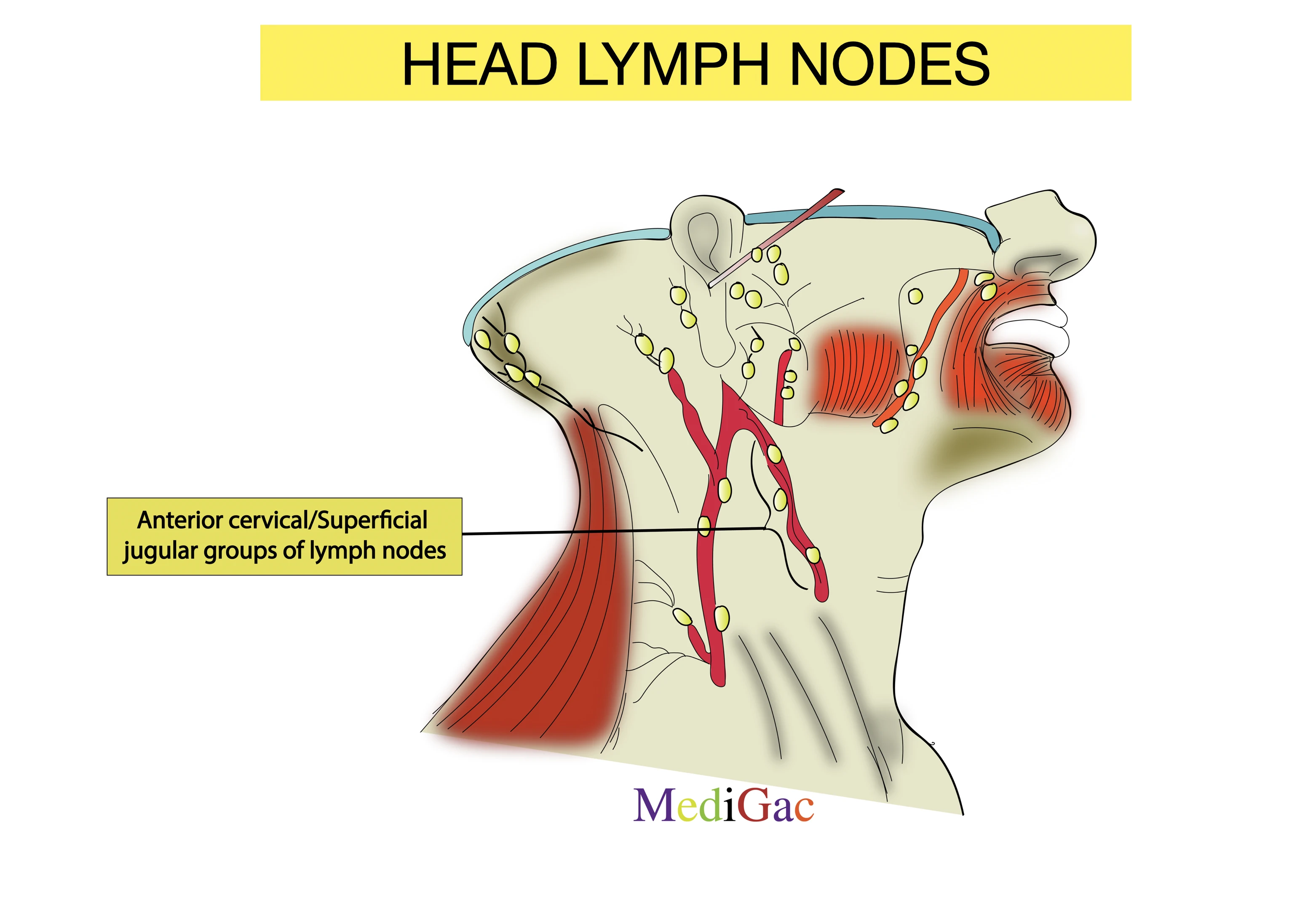
Lymph nodes of the head with Location/Position, Drainage and pathology. Lymph nodes of the head are Buccinator, Nasolabial, Mandibular, Anterior cervical/Superficial jugular, Superficial cervical/External jugular groups of lymph nodes.
A. What are the surface groups of lymph nodes :
1. Occipital groups of lymph nodes :
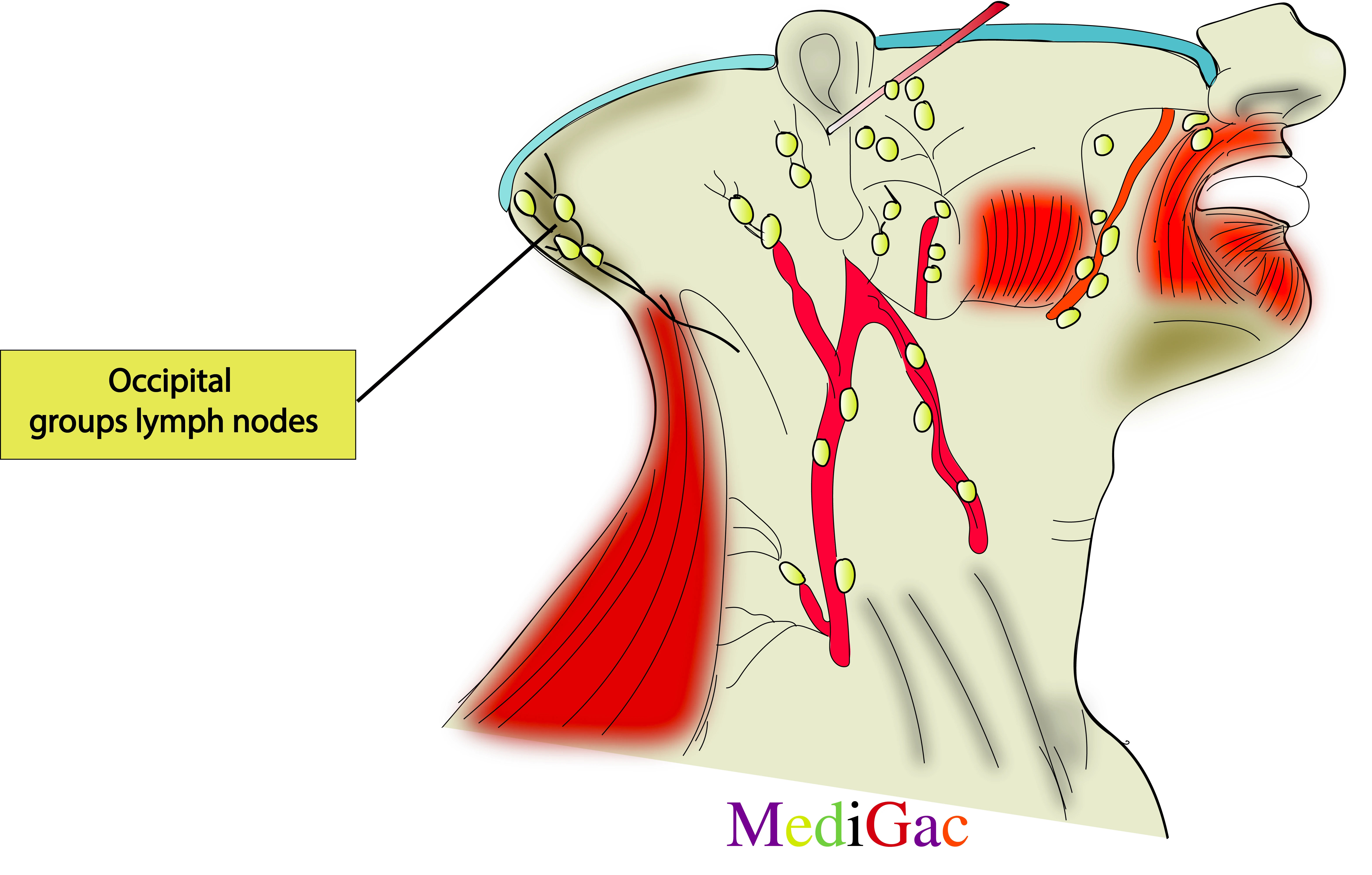
I. Location/Position/Relations of Occipital lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Situated bilaterally to the external occipital protuberance.
- Muscle relations – Above the lower border of Occipitofrontalis, and upper border of the Semispinalis capitis.
- Vascular relations – Medial or above the occipital artery and vein.
II. Drainage of Occipital lymph nodes :
- Lymphatic fluid drains from the particular side of the face and scalp into the occipital nodes in the neck.
- The lymph is then drained into the left deep cervical lymph nodes, which run parallel to the left internal jugular vein.
- Lymph vessels in the neck’s superficial tissues flow into the left superficial cervical lymph nodes and the left external jugular vein.
- The lymphatic trunks of the left jugular convey lymph from the head and neck into the thoracic duct, also known as the left lymphatic duct.
III. Pathologies of Occipital lymph nodes :
Due to various causes occipital lymph node can swell. We have discussed all the causes briefly.
- Bacterial infections – Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
- Ringworm/Tinea capitis fungal infection to the scalp.
- Rubella virus infection or German measles.
- Autoimmune disease – Psoriasis.
- Melanoma or skin cancer.
2. Mastoid groups of lymph nodes :
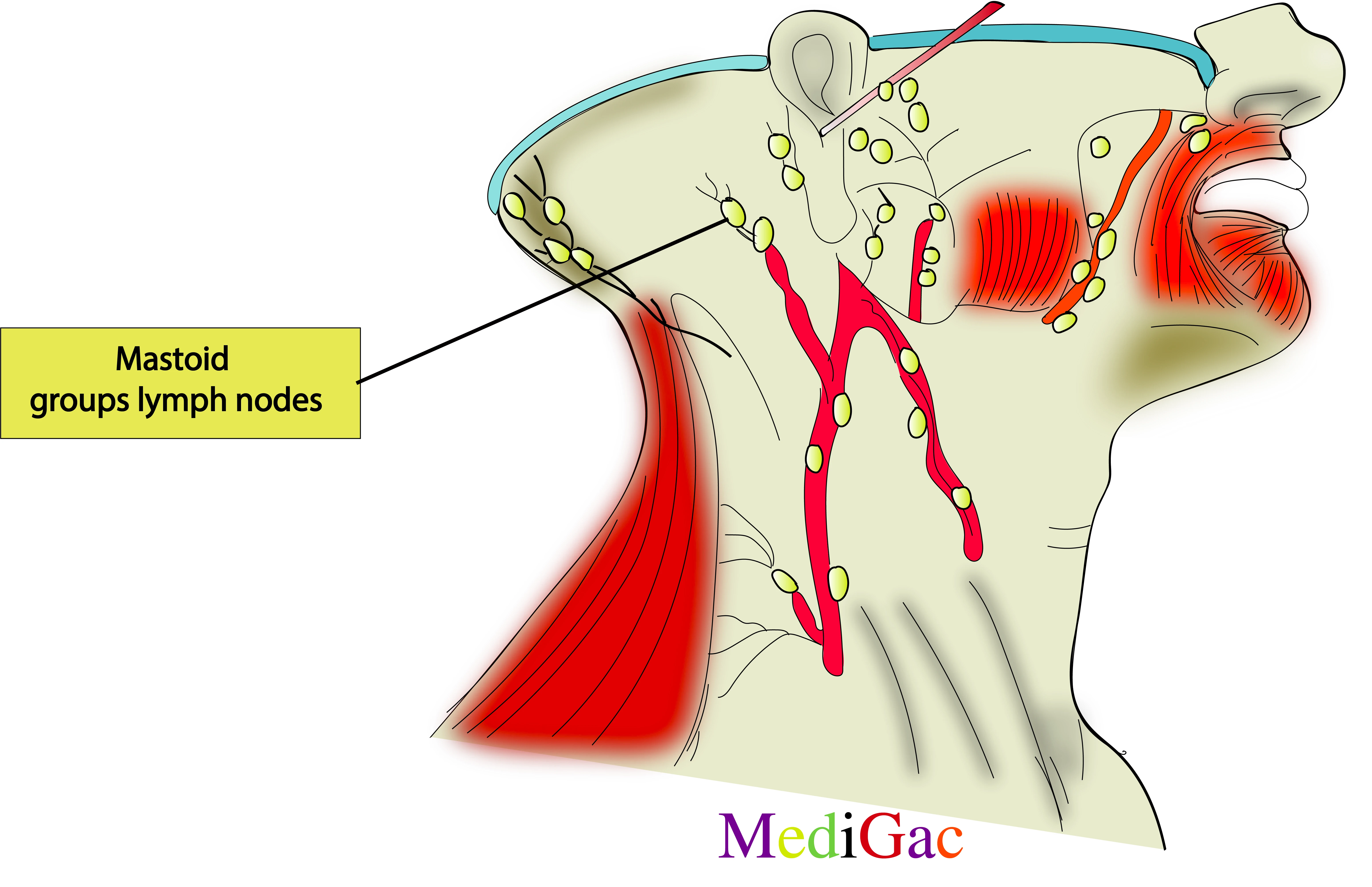
I. Location/Position/Relations of Mastoid lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Just below the mastoid process of temporal bone.
- Muscle relations – Anterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle insertion, Lateral to the digastric muscle origin.
- Vascular relation – Lateral to the occipital vein and artery, lateral and below to the posterior auricular artery.
II. Drainage of Mastoid lymph nodes :
Lymphatic fluid drains from the particular side of the face and scalp into the Mastoid nodes in the neck. Then the drainage of lymphatic is same as occipital groups.
III. Pathologies of Mastoid lymph nodes :
- Mastoiditis
- Ear infections
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Skin cyst
3. Superficial parotid groups of lymph nodes :
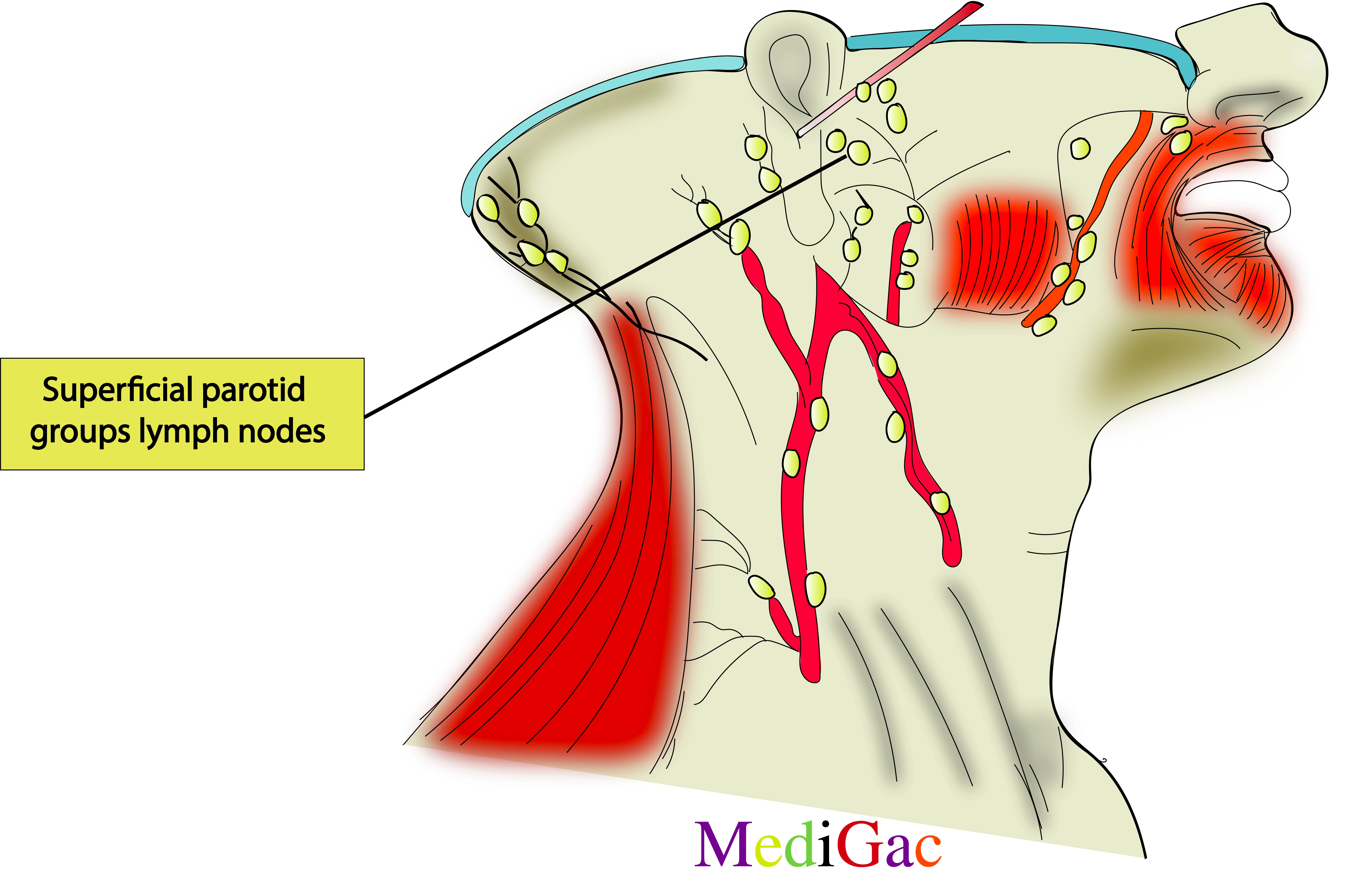
I. Location/Position/Relations of Superficial Parotid lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Above the central part and zygomatic process of temporal bone.
- Cartilaginous relations – Anterior to the auricular cartilage.
- Muscle relations – Above the insertion of the Auricular anterior muscle.
- Vascular relations – Posterior to the superior temporal artery and vein.
- Nerve relations – Surrounding the auriculotemporal branch of trigeminal nerve.
- Visceral relations – Postero superiror part of the parotid gland.
II. Drainage of Superficial Parotid lymph nodes :
- A set of lymph nodes anterior to the ear is known as the superficial parotid lymph nodes.
- The root of the nose, the eyelids, the frontotemporal area, the external acoustic meatus, and the tympanic cavity, as well as the posterior regions of the palate and the floor of the nasal cavity, are all drained by their afferent veins.
III. Pathologies of Superficial Parotid lymph nodes :
- Bacterial infections
- Viral Infections – Mumps, Flu
- Sore throat
- Ear infections
- Carcinoma
4. Deep parotid groups of lymph nodes :
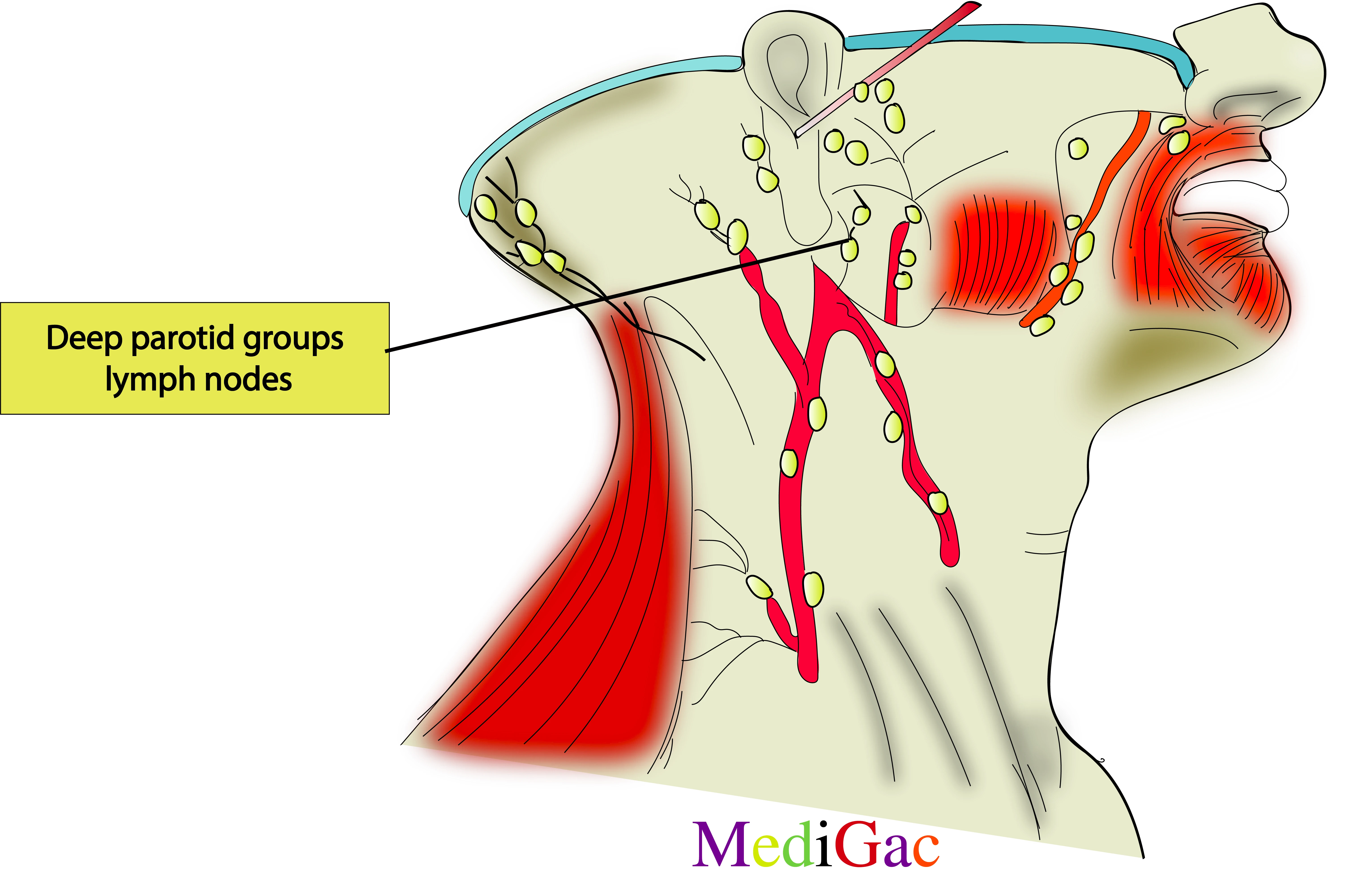
I. Location/Position/Relations of Deep Parotid lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Posterior to the condyle of Mandible.
- Vascular relations – Along the external carotid artery.
- Nerve relations – Medial to the origin of the zygomatic and temporal branch of facial nerve.
- Visceral relations – Deep to the parotid gland in the postero medial part.
II. Drainage of Deep Parotid lymph nodes :
- Lymphatic fluid drains from the particular side of the face and scalp into the deep parotid nodes in the neck.
- The lymph is then drained into the left deep cervical lymph nodes, which run parallel to the left internal jugular vein.
III. Pathologies of Deep Parotid lymph nodes :
- Bacterial infections
- Viral Infections – Mumps, Flu
- Sore throat
- Ear infections
- Carcinoma
5. Pre-auricular groups of lymph nodes :
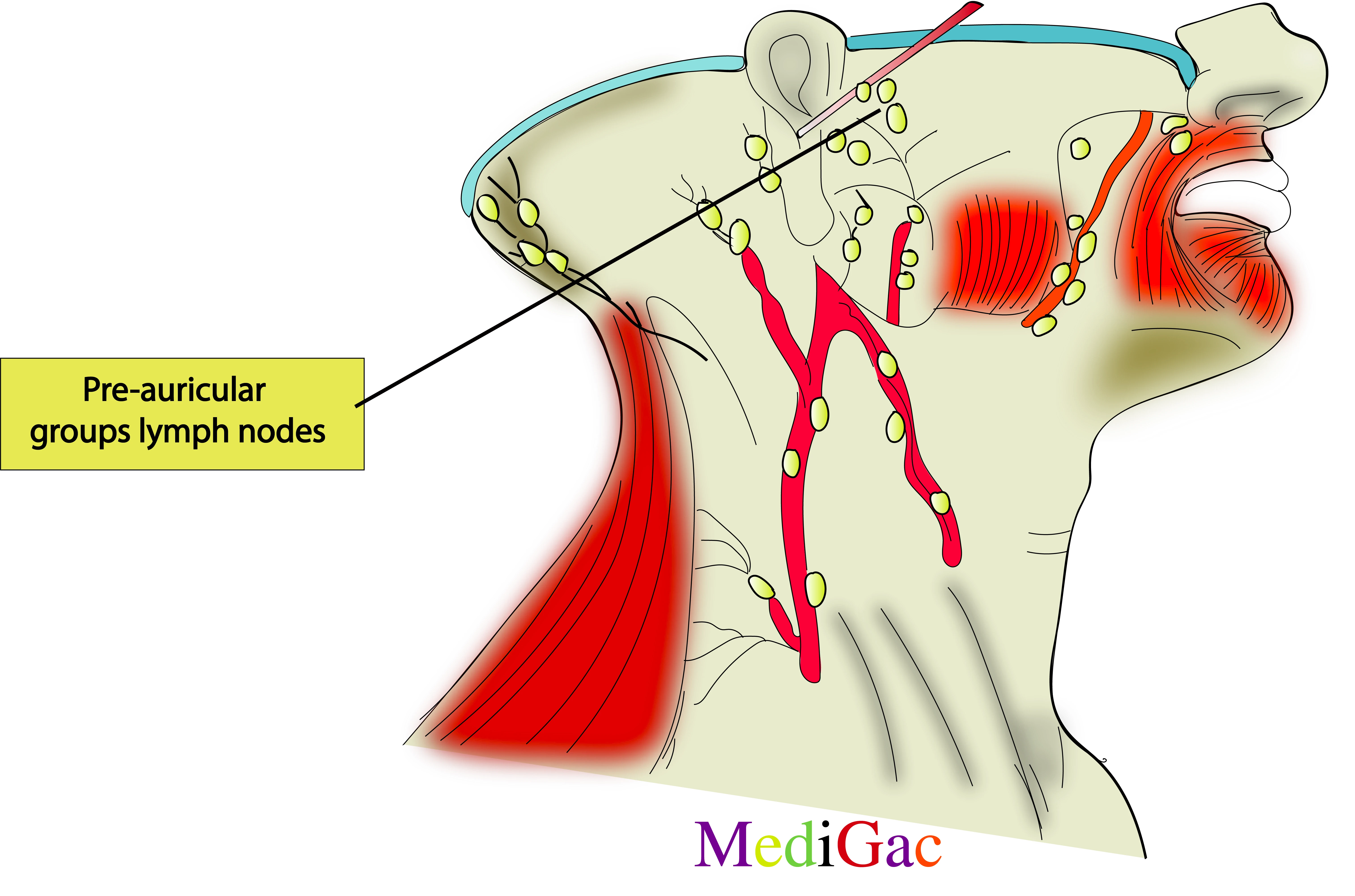
I. Location/Position/Relations of Pre-Auricular lymph nodes :
- Present anterior to the Tragus of ear lobule.
- Above the zygomatic process of the temporal bone.
II. Drainage of Pre-Auricular lymph nodes :
- Lymphatic fluid drains from the particular side of the face and scalp into the pre auricular nodes in the neck.
- The lymph is then drained into the left deep cervical lymph nodes, which run parallel to the left internal jugular vein.
III. Pathologies of Pre-Auricular lymph nodes :
- Otitis externa
- Infections of salivary glands
- Viral conjunctivitis
6. Infra-post-auricular groups of lymph nodes :
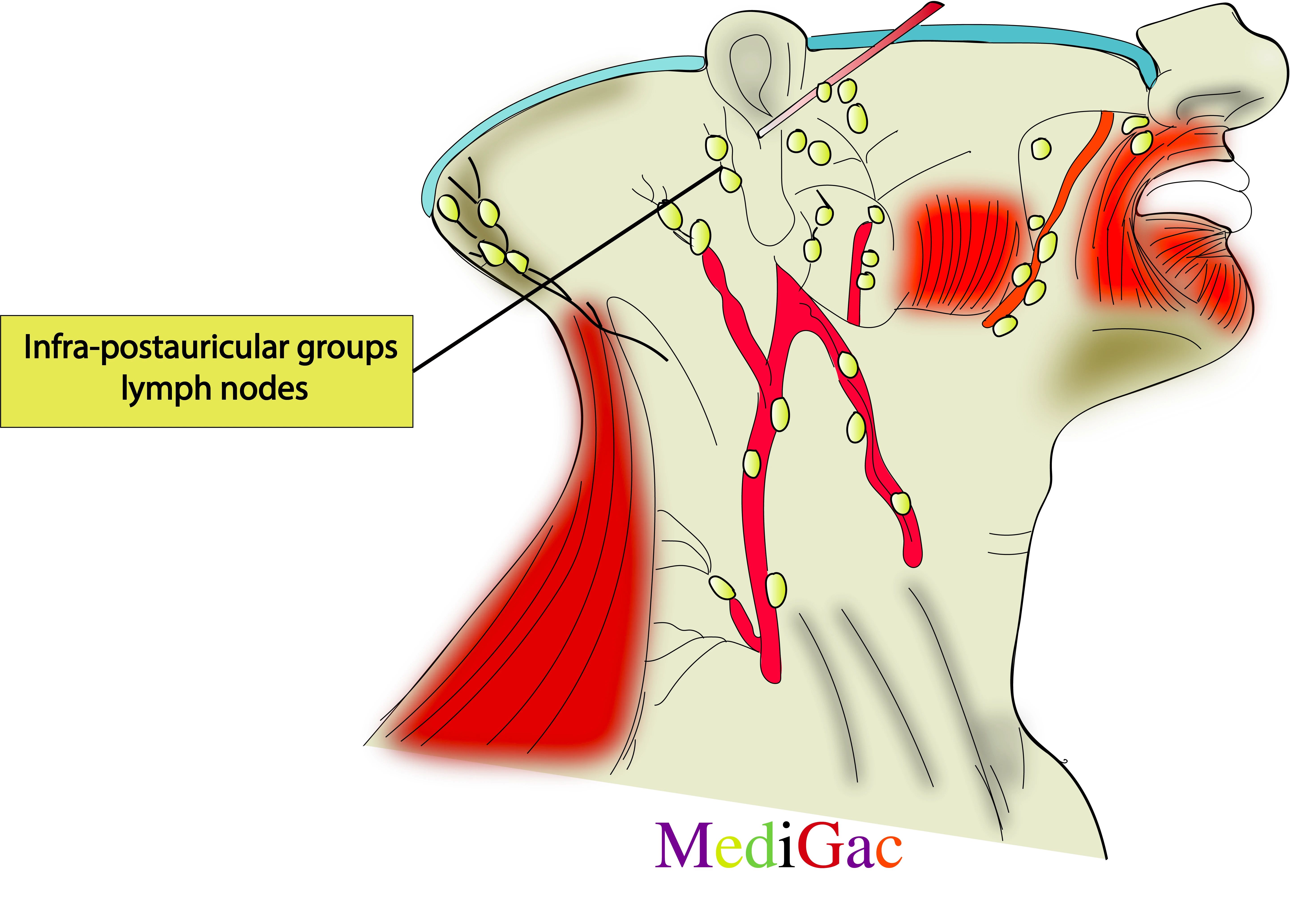
I. Location/Position/Relations of Infra-Post auricular lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Above the lower border of Mastoid process of temporal bone.
- Muscle relations – Below the Auricular posterior muscle.
- Vascular relations – Along the posterior auricular artery and vein.
II. Drainage of Infra-Post auricular lymph nodes :
- Lymphatic fluid drains from the particular side of the face and scalp into the post auricular nodes in the neck.
- The lymph is then drained into the left deep cervical lymph nodes, which run parallel to the left internal jugular vein.
III. Pathologies of Infra-Post auricular lymph nodes :
- Ear infections(most common)
- Allergies
- Common cold
- Sinus infection
7. Intra-glandular parotid groups of lymph nodes :
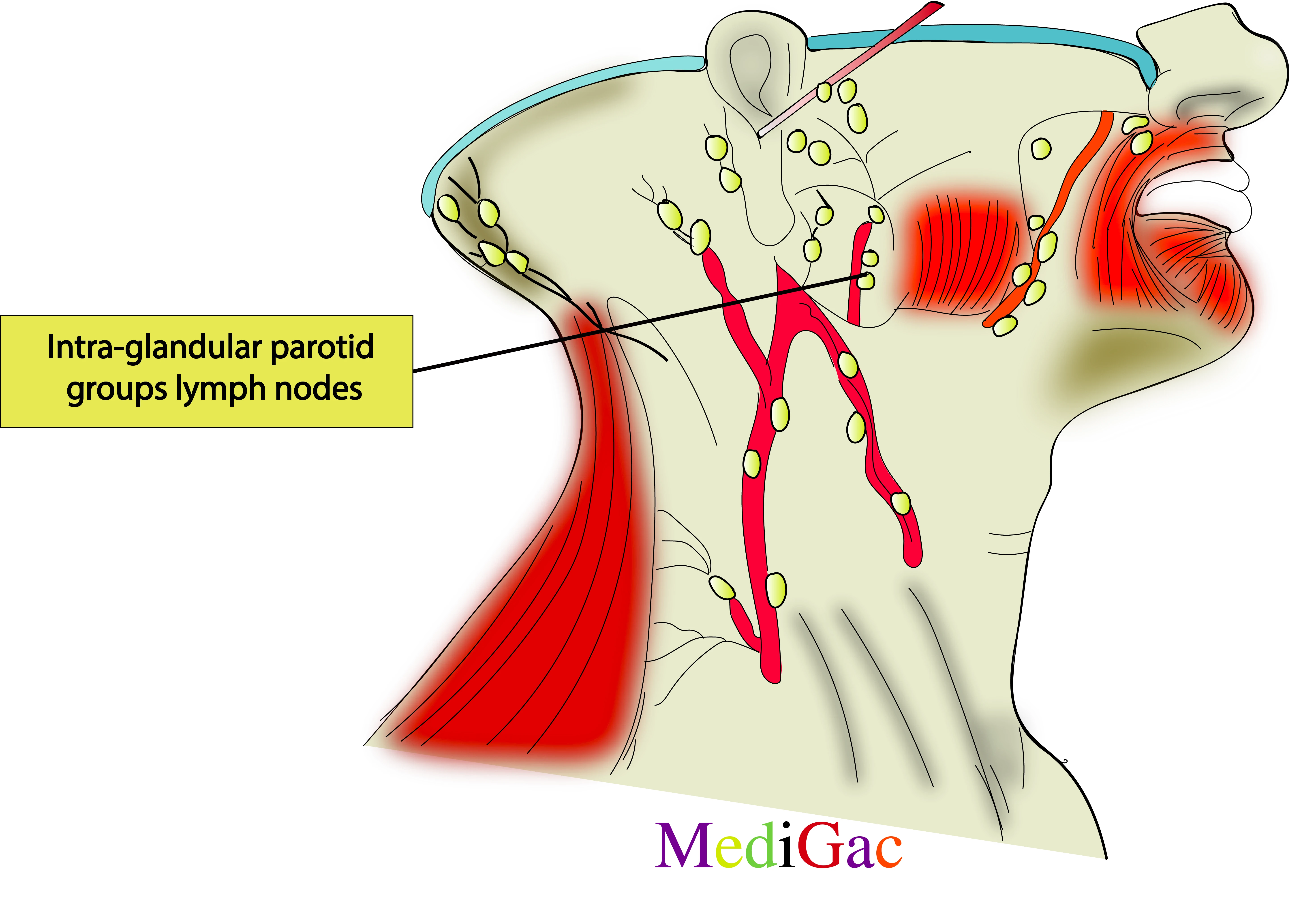
I. Location/Position/Relations of Intra-Glandular parotid lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Along the Angle of mandible.
- Vessels relations – Facial artery and vein.
II. Drainage of Intra-Glandular parotid lymph nodes :
- Lymphatic fluid drains from the particular side of the face and scalp into the post auricular nodes in the neck.
- The lymph is then drained into the left deep cervical lymph nodes, which run parallel to the left internal jugular vein.
III. Pathologies of Intra-Glandular parotid lymph nodes :
- Parotid gland infection
- Common cold
- Sore throat
B. What are the facial groups of lymph nodes :
1. Buccinator groups of lymph nodes :
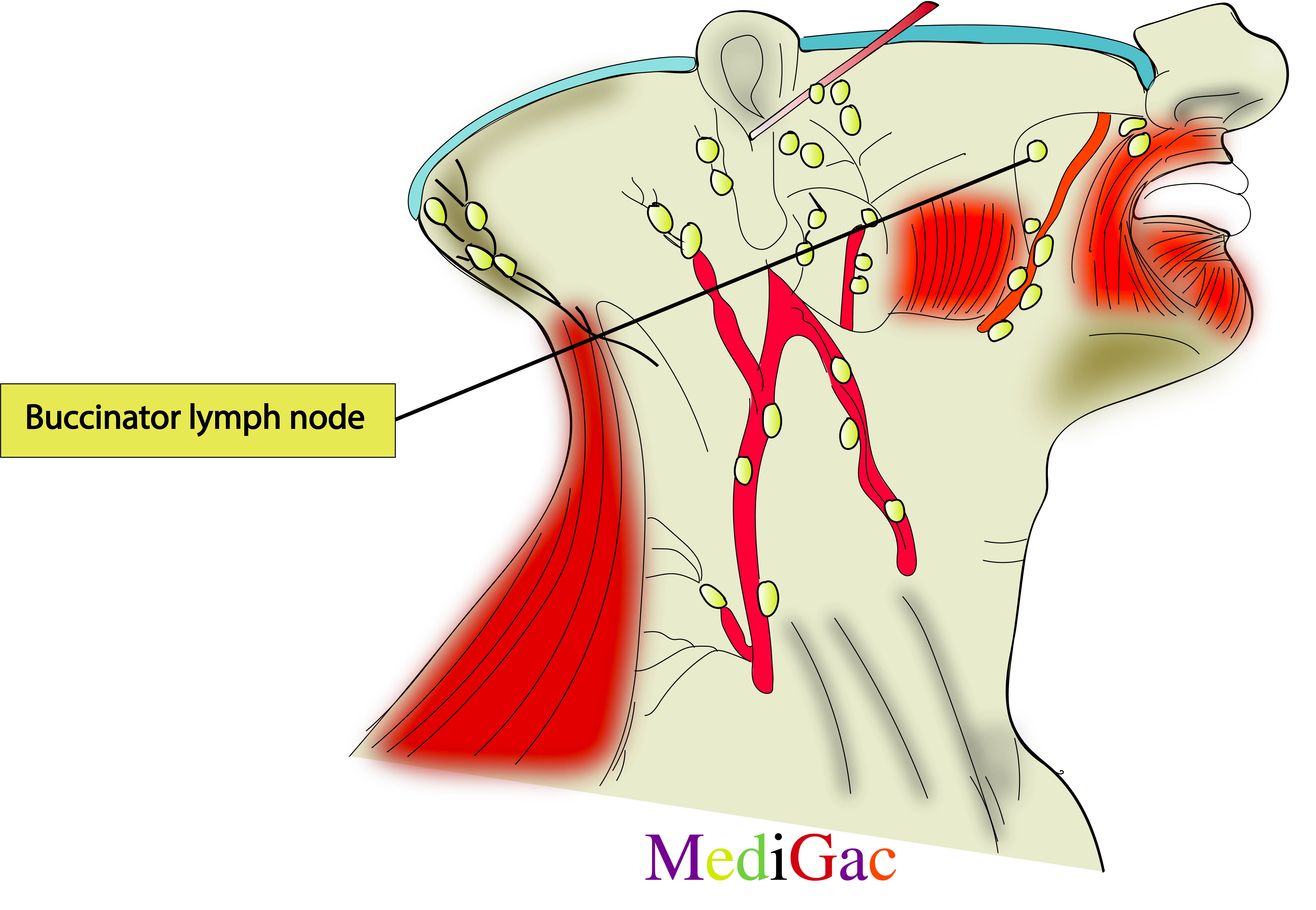
I. Location/Position/Relations of Buccinator lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Above the maxilla, specifically above the 3rd molar prominence.
- Vessels relations – Above the facial vein and artery.
- Nerve relations – Zygomatic and Buccal branches of Facial nerve.
II. Drainage of Buccinator lymph nodes :
Lymphatic fluid of the face enters into the buccinator group lymph nodes during circulation and then it drains into the deep cervical groups of lymph nodes.
III. Pathologies of Buccinator lymph nodes :
- Mouth infection
- Oral cancer
2. Nasolabial groups of lymph nodes :
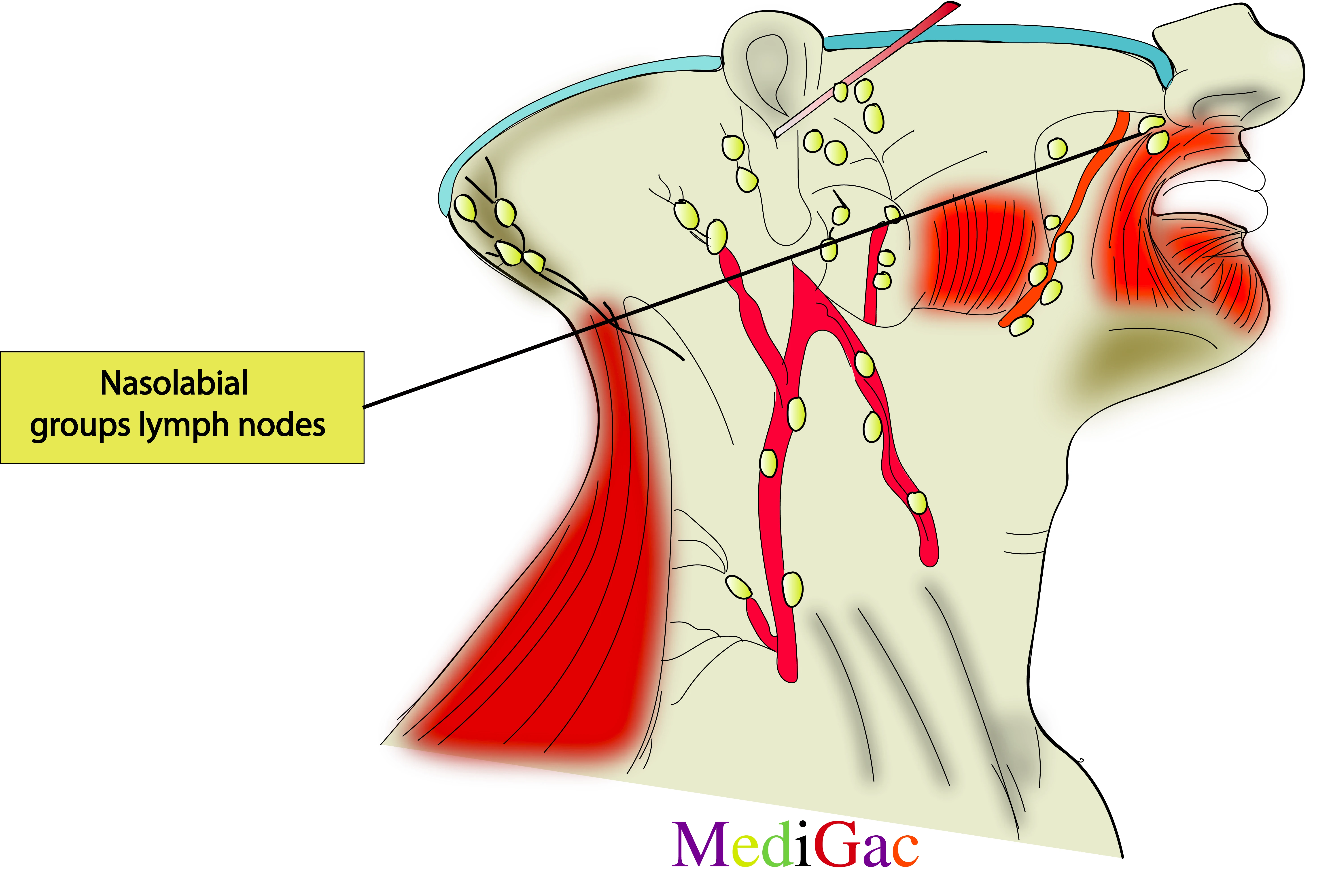
I. Location/Position/Relations of Nasolabial lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Medial to the infraorbital foramen of Maxilla.
- Muscle relations – In between the triangle formed by Nasalis(transverse part), Orbicularis oculi and Levator labii superioris.
- Vessels relations – Above the angular vein.
- Nerve relations – Above the buccal branch of facial nerve and infraorbital nerve.
II. Drainage of Nasolabial lymph nodes :
- A face lymph node located near the nose and upper lip is known as the nasolabial lymph node.
- Lymph from the circulation enters into the deep cervical groups of lymph nodes.
III. Pathologies of Nasolabial lymph nodes :
- Bacterial infections
- Viral infections
3. Sub-Mandibular groups of lymph nodes :
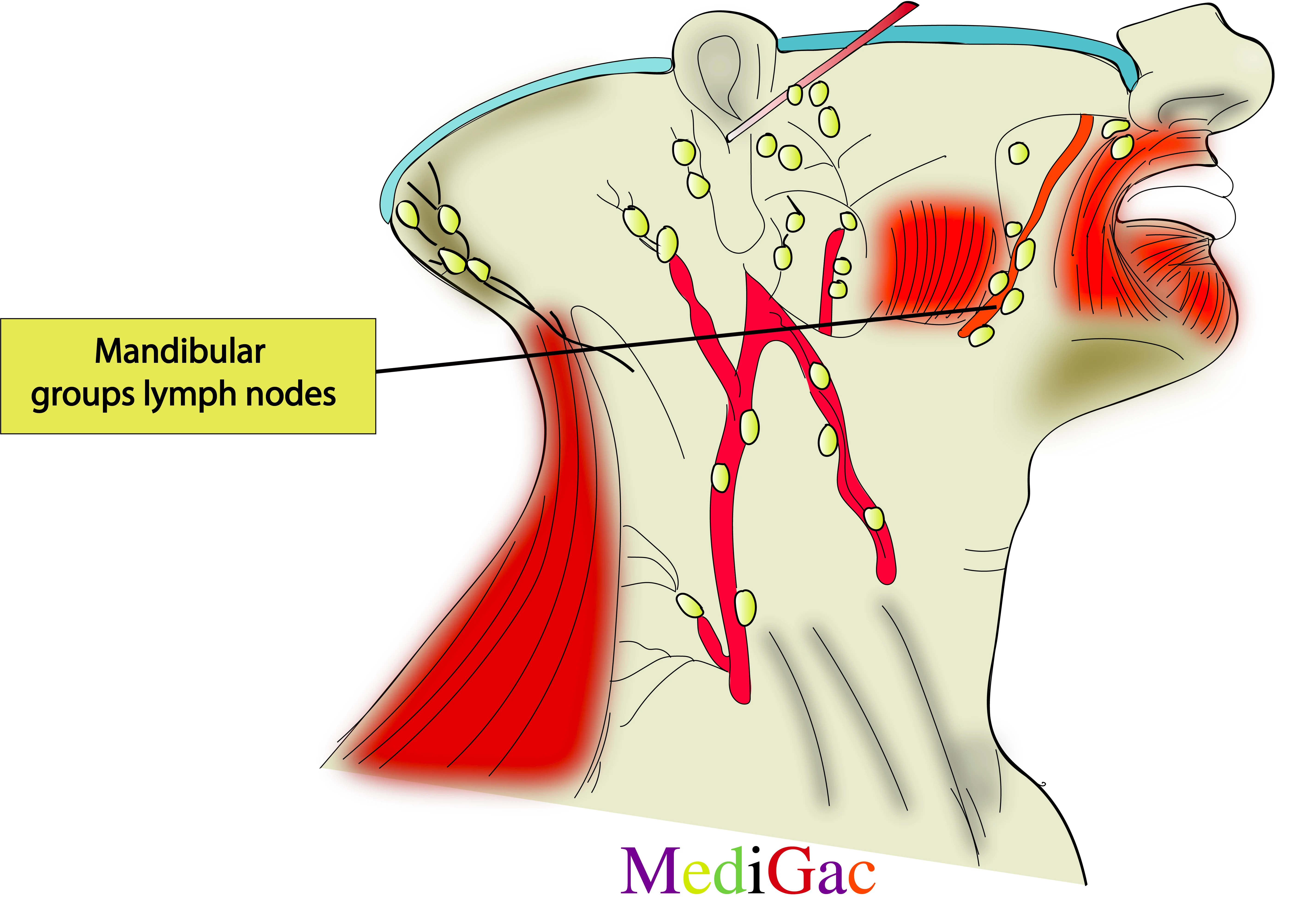
I. Location/Position/Relations of Sub-Mandibular lymph nodes :
- Bony relations – Below the border of Submandibular base.
- Muscle relations – Above the insertion of the Platysma muscle.
- Vascular relations – Facial vein and artery.
- Nerve relations – Marginal mandibular branch of facial nerve.
II. Drainage of Sub-Mandibular lymph nodes :
- The lymph from the face drains into the submandibular and submental nodes in the neck.
- The lymph then drains into the deep cervical lymph nodes, which are found along the internal jugular vein’s path.
- The lymph is then carried into the thoracic duct by the jugular lymph artery.
III. Pathologies of Sub-Mandibular lymph nodes :
- Non-malignant : Mumps, Sialandenitis, Sjogren syndrome, cysts and infections.
- Infections of teeth, upper respiratory tract, sinuses and tonsils.
4. Anterior cervical/Superficial jugular groups of lymph nodes :
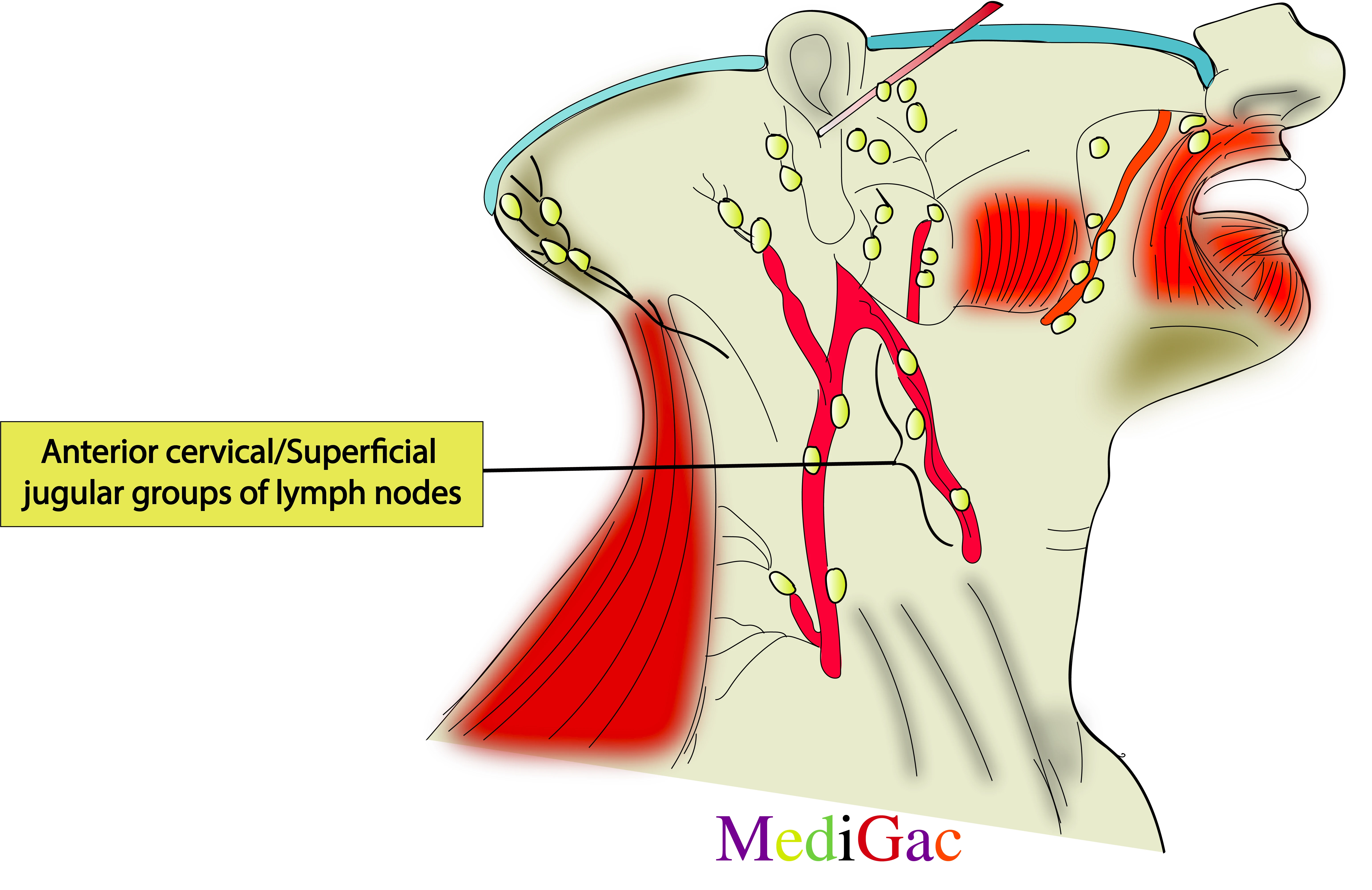
I. Location/Position/Relations of Anterior cervical lymph nodes :
- Bone/Cartilage relations – Above the lower part of thyroid cartilage.
- Muscle relations – Below the Sternohyoid muscle.
- Vessels relations – Along the Superior thyroid vein.
- Viscera relations – Above the thyroid gland.
II. Drainage of Anterior cervical lymph nodes :
- The anterior cervical lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes located in front of the sternocleidomastoid muscle on the anterior region of the neck.
- These can be divided into two categories : deep and superficial.
- The superficial group is responsible for draining the anterior neck’s superficial surfaces.
III. Pathologies of Anterior cervical lymph nodes :
- Viral infections – Adenovirus, Rhinovirus, enterovirus, HSV, influenza
- Bacterial infections – Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes and Mycobacterium pneumoniae.
- Thyroid disorders – Goitre, Carcinoma etc.
5. Superficial posterior cervical/External jugular groups of lymph nodes :
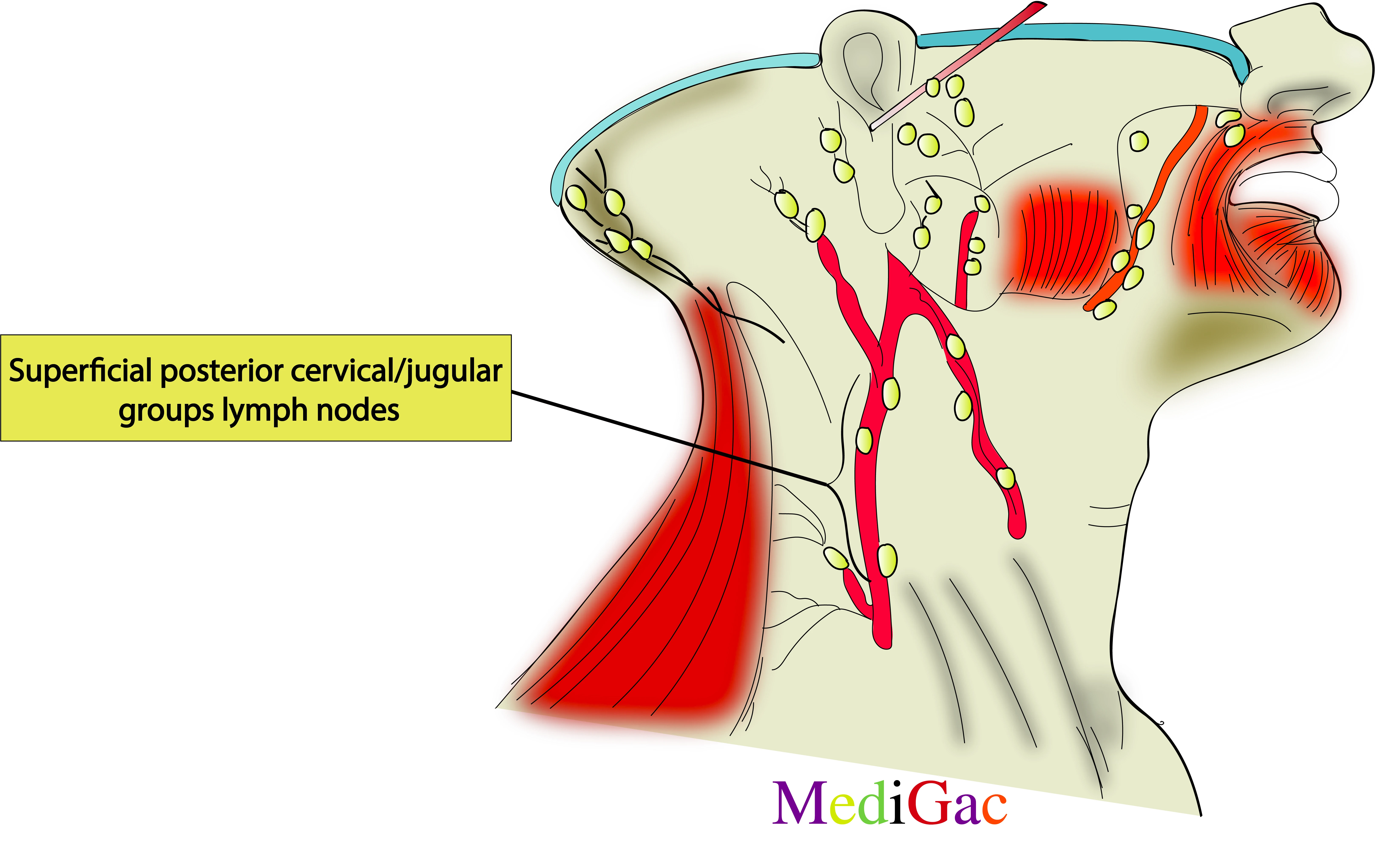
I. Location/Position/Relations of Superficial Cervical lymph nodes :
- Vascular relations – Along the internal jugular vein.
- Muscle relations – Below the anterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle.
- Nerve relations – Lateral to the vagus nerve.
II. Drainage of Superficial Cervical lymph nodes :
- The superficial lateral cervical lymph nodes are located between the inferior side of the parotid gland and the supraclavicular nodes, along the path of the external jugular vein.
- The nodes are intercalated along the path of the vessels that drain the parotid and infraauricular nodes.
III. Pathologies of Superficial Cervical lymph nodes :
- Viral infections – Adenovirus, Rhinovirus, enterovirus, HSV, influenza
- Bacterial infections – Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes and Mycobacterium pneumoniae.
- Thyroid disorders – Goitre, Carcinoma etc.